|
cyanamide
Herbicide, plant growth regulator
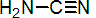
NOMENCLATURE
Chemical Abstracts name cyanamide
Other names carbamic acid nitrile; amidocyanogen; hydrogen cyanamide; cyanoamine; cyanogenamide CAS RN [420-04-2] EEC no. 206-992-3
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 42.0 M.f. CH2N2 Form Colourless, hygroscopic crystals. M.p. 45-46 ºC B.p. 83 ºC/0.5 mmHg V.p. 500 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = -0.82 (20 ºC) Henry 4.58 ´ 10-6 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.282 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 4.59 kg/l (20 ºC). Soluble in alcohols, phenols and ethers. Sparingly soluble in benzene and halogenated hydrocarbons. Practically insoluble in cyclohexane. In methyl ethyl ketone 505, ethyl acetate 424, n-butanol 288, chloroform 2.4 (all in g/kg, 20 ºC). Stability Stable to light. Decomposed by alkalis (with the formation of dicyandiamide and polymerisation) and acids (with the formation of urea). On heating to 180 ºC, dicyandiamide is formed, and polymerisation commences. F.p. 207 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
Manufacturers Degussa AG
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Catalase inhibition, requiring the plant to detoxify hydrogen peroxide by other routes, which affects the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway. This in turn leads to an increase in reduced nucleotide production, ultimately affecting budbreak. Mode of action Contact herbicide. Uses Early post-emergence control of broad-leaved weeds in alliums (onions, leeks, chives, shallots, and garlic) and bulb flowers. Also used to remove side shoots and inhibit sprouting in hops and vines. The calcium salt (q.v. in Superseded) is used as a fertiliser, and formerly was also used as a herbicide. Formulation types EC.
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Alzodef' (SKW Piesteritz); 'Dormex' (Dormex, Degussa AG)
ANALYSIS
Product by the Kjeldahl method or by argentometric determination. Details from SKW Trostberg. Residues (1) By colorimetric determination of a derivative. Details from Degussa. (2) By hplc (J. Prunonosa et al., J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Appl., 1986, 50, 253-269).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 223 mg/kg (c. 300 mg/kg for 'Alzodef', 49% aqueous solution). Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 848 mg/kg (c. 1700 mg/kg for 'Alzodef'). Severe skin and eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1 mg/l air (>13 mg/l air for 'Alzodef'). NOEL (91 w) 1 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.01 mg/kg. Other A vasomotor reaction may occur when handling or using cyanamide combined with alcohol consumption. EC classification T; R25| Xn; R21| Xi; R36/38| R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 350 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 ppm. Fish Toxic to fish; LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 44, carp 87, rainbow trout 90 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 3.2 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 13.5 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Other beneficial spp. EC10 (16 h) for Pseudomonas putida 24 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The main urinary metabolite in the rat, rabbit and dog is acetylcyanamide. Plants In plants, converted to nitrogenous compounds which are rapidly taken up. Soil/Environment In soil, converted to nitrogenous compounds which are rapidly taken up. No residue problems.
|