|
cyhalofop-butyl
Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; aryloxyphenoxypropionate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name cyhalofop-butyl (pa ISO, ANSI)
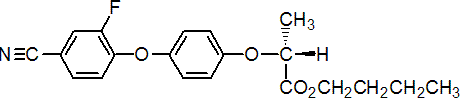
IUPAC name butyl (R)-2-[4-(4-cyano-2-fluorophenoxy)phenoxy]propionate
Chemical Abstracts name butyl (R)-2-[4-(4-cyano-2-fluorophenoxy)phenoxy]propanoate
CAS RN [122008-85-9]; [122008-78-0] (for acid) Development codes DE-537; XDE-537; XRD-537; DEH112; EF 1218; NAF-541
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Purity 96.5% nominal. Material is the resolved (R)- isomer. Mol. wt. 357.4 M.f. C20H20FNO4 Form White crystalline solid. M.p. 49.5 °C B.p. decomp. >270 °C V.p. 5.3 ´ 10-2 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.31 (25 °C) Henry 9.51 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.172 (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.44 (unbuffered), 0.46 (pH 5), 0.44 (pH 7.0) (all mg/l, 20 °C). In acetonitrile >250, n-heptane 6.06, n-octanol 16.0, dichloroethane >250, methanol >250, acetone >250, ethyl acetate >250 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable at pH 4, hydrolysed slowly at pH 7. At pH 1.2 or pH 9, decomposition is rapid.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Discovered in the mid-1980s by The Dow Chemical Company (now Dow AgroSciences) and reported by P. G. Ray et al. (Proc. 10th Australian & 14th Asian-Pacific Weed Conference, Brisbane, Australia, September 1993, p. 41). Introduced in Asia in 1995; now marketed in rice-growing territories worldwide. Patents US 4894085 (1990); US 4897481 (1990); EP 302203 (1989) Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Selectivity between susceptible grasses and dicotyledonous plants is attributed to the forms of ACCase present and their compartmentalisation within plant cells. Susceptible grasses contain the susceptible eukaryotic form of ACCase; dicotyledonous plants contain both susceptible eukaryotic and herbicide-resistant prokaryotic forms of ACCase, rendering them resistant to cyhalofop-butyl. Rice tolerance to cyhalofop-butyl is due to rapid metabolism to the herbicidally inactive diacid (t1/2 <10 hr), whereas susceptible grasses metabolise cyhalofop-butyl to the herbicidally active monoacid. Mode of action Post-emergence herbicide with foliar uptake only and no soil activity. A systemic herbicide that is readily absorbed by plant tissue, is moderately phloem-mobile and accumulates in meristematic regions. Grass weeds cease growth immediately after treatment, with yellow patches appearing within 2-3 days to one week, leading to necrosis and death of the whole plant within 2 to 3 weeks. Uses For post-emergence control of grass weeds in rice. Applied at 75-100 g/ha in tropical rice and 180-310 g/ha in temperate rice. For selectivity in Poaceae species, see M. Ito et al., J. Weed Sci. & Tech. 43(2) 122-128 (1998). Phytotoxicity Rice is completely tolerant to due to rapid metabolism to the inactive diacid. Formulation types EC; EW; GR. Compatibility Not compatible with most broadleaf and sedge herbicide products. Selected products: 'Cleaner' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Clincher' (Dow AgroSciences); mixtures: 'Clincher Bas' (+ bentazone-sodium) (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Agrostar' (+ pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+ butamifos) (Sumitomo); 'Bazooka 36' (+ thenylchlor+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Nohyaku); 'Bazooka A' (+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, Tokuyama, DuPont); 'Bazooka' (+ thenylchlor+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, Tokuyama, DuPont); 'Inegreen D' (+ daimuron+ mefenacet+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Bayer, Hokko); 'Inegreen' (+ mefenacet+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Bayer); 'Joystar' (+ daimuron+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cafenstrole) (Kumiai); 'Joyster' (+ daimuron+ bensulfuron-methyl+ cafenstrole) (Kumiai); 'Papika A I Kilo' (+ thenylchlor+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, Tokuyama, Dow AgroSciences, DuPont); 'Papika A' (+ thenylchlor+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Tokuyama, Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, DuPont, Dow AgroSciences); 'Papika' (+ thenylchlor+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Tokuyama, Nihon Nohyaku, Hokko, DuPont, Dow AgroSciences); 'Redstar' (+ daimuron+ halosulfuron-methyl+ cafenstrole) (Nissan); 'Revolver' (+ mefenacet+ pyrazosulfuron-ethyl) (Nissan); 'Sheriff' (+ dimethametryn+ imazosulfuron+ pretilachlor) (Otsuka, Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Striker' (+ pyrazosulfuron-ethyl+ cafenstrole) (Nissan, Yashima) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Tabijin A' * (+ pretilachlor+ pyriminobac-methyl+ azimsulfuron+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Kumiai)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats, and for male and female mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >2000 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 for rats >5.63 mg/l. NOEL For male rats 0.8 mg/kg b.w. daily, female rats 2.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. Other Non-mutagenic in Ames, DNA repair and micronucleus tests. Not teratogenic. In in vivo cytogenetic studies, no induction of structural chromosomal aberration observed. Rat and rabbit studies indicate cyhalofop-butyl is not teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) II (EC)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
The high toxicity of cyhalofop-butyl to fish and other aquatics is mitigated by the rapid degradation to less-toxic metabolites. Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 ppm. Fish LC50 for rainbow trout >0.49, bluegill sunfish 0.76 mg/l. These values are at or above the aqueous solubility of cyhalofop-butyl. Daphnia LC50 >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum >1, Navicula sp. 0.64-1.33 mg/l. Soil and plant transformation products are less toxic to Selenastrum capricornutum. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 0.52, scud (Gammarus sp.) 0.81 mg/l. These values are at or above the aqueous solubility of cyhalofop-butyl. Bees NOEC for honeybees >100 mg/bee. Worms LD50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rats, dogs, ruminants and poultry readily metabolise cyhalofop-butyl by hydrolysis to the acid. Depending on the animal, the acid may also break down to other metabolites. The acid and any additional degradates are then rapidly excreted. Residue levels of cyhalofop-butyl and its metabolites are low in milk, eggs and tissues. Plants Rice tolerance is due to rapid metabolism to the inactive diacid (DT50 <10 h) and to subsequent formation of polar and non-polar metabolites. Susceptible grass sensitivity is due to rapid metabolism of cyhalofop-butyl to the herbicidally active monoacid. Soil/Environment Laboratory metabolism and field dissipation studies show that cyhalofop-butyl is rapidly metabolised in soil and sediment/water systems to cyhalofop acid; in the field, cyhalofop-butyl DT50 2-10 h in soil, <2 h in sediment/water. In turn, cyhalofop acid has DT50 <1 d in soil, c. 7 d in sediment/water. Cyhalofop-butyl is relatively immobile in soil adsorption studies.
|