|
beta-cyfluthrin
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name beta-cyfluthrin (BSI, draft E-ISO); beta-cyfluthrine ((f) draft F-ISO); cyfluthrin-beta (Canada)
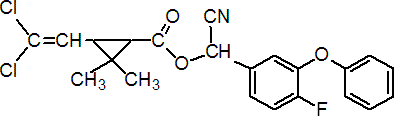
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzyl (1RS,3RS;1RS,3SR)-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(4-fluoro-3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl 3-(2,2-dichloroethenyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [68359-37-5] unstated stereochemistry EEC no. 269-855-7 Development codes FCR 4545 (Bayer) Official codes OMS 3051
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Comprises a mixture of four diastereoisomeric pairs of enantiomers:
I (R)-a-cyano-4-fluoro-3-phenoxybenzyl (1R)-cis-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropanecarboxylate + (S)-a, (1S)-cis-;
II (S)-a, (1R)-cis- + (R)-a, (1S)-cis-;
III (R)-a, (1R)-trans- + (S)-a, (1S)-trans-;
IV (S)-a, (1R)-trans- + (R)-a, (1S)-trans- .
Tech. grade contains: <2% diastereoisomer I, 30-40% diastereoisomer II, <3% diastereoisomer III, and 53-67% diastereoisomer IV. Mol. wt. 434.3 M.f. C22H18Cl2FNO3 Form Colourless crystals; (tech. is a white powder with slight characteristic smell). M.p. (II) 81 ºC; (IV) 106 ºC B.p. decomp. >210 °C V.p. (II) 1.4 ´ 10-5 mPa; (IV) 8.5 ´ 10-5 mPa (both 20 ºC) KOW (II) logP = 5.94; (IV) logP = 5.91 Henry (II) 2.9 ´ 10-3; (IV) 3.1 ´ 10-2 (both in Pa m3 mol-1, 20 °C) S.g./density 1.34 g/cm3 (22 ºC) Solubility In water: (II) 2.1, (IV) 1.2 (both in mg/l, 20 ºC). In dichloromethane and toluene, both pairs >200 g/l (20 ºC). (II) In hexane 2-5, isopropanol 5-10 (both in g/l, 20 ºC). (IV) in hexane 1-2, isopropanol 2-5 (both in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Thermally stable at room temperature. Hydrolysis DT50 (22 ºC) for (II): 117 d (pH 4), 20 d (pH 7), 6 d (pH 9); for (IV): 25 d (pH 4), 11 d (pH 7), 5 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by M. C. Botte et al. (3rd ANPP Conf., 1993, 1, 185). Introduced by Bayer AG. Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Jiangsu Yangnong; Mitchell Cotts
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Acts on the nervous system, with rapid knockdown and long residual activity. Uses Insecticide effective against Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Hemiptera and Homoptera on cotton, fruit, vegetables, cereals and other crops, at 7.5-20 g/ha. Also against migratory locusts and grasshoppers; and in animal health. Formulation types EC; EW; GR; UL; SC. Selected products: 'Bulldock' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Responsar' (animal health use) (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Chinook' (+ imidacloprid) (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bullock' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Ducat' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience); 'Full' (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Confidor Ultra' (+ imidacloprid) (Makhteshim-Agan, Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Poncho' * (+ imidacloprid) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Details of methods for product and residue analysis available from Bayer CropScience. Analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. Diastereoisomer ratio by hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 43).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 380 (in polyethyleneglycol), 211 (in xylene), 11 (cremophor/water) (all in mg/kg); for mice 165 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for rats >5000 mg/kg. No irritation to skin and slight primary irritation to the eye (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats c. 0.1 mg/l (aerosol), 0.53 mg/l (dust). NOEL (90 d) for rats 125, dogs 60 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.02 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification T+; R26/28| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >2000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 89, bluegill sunfish 280 ng/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.0018 mg/l. Algae >0.01 mg/l. Bees LD50 <0.1 mg/bee. Worms >1000 mg/kg
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Beta-cyfluthrin was largely and very quickly eliminated; 98% was eliminated after 48 h via the urine and the faeces. Plants Since beta-cyfluthrin is not systemic, it penetrates only slightly into the plant tissues and is hardly translocated into other plant parts. The concentration is very low and can be neglected. Soil/Environment Degradation in different soils is rapid. Leaching behaviour can be classified as immobile. The metabolites of beta-cyfluthrin are readily accessible to further microbial degradation to the point of mineralisation to CO2 in the soil.
|