|
ziram
Fungicide, bird repellent, rodent repellent
FRAC M3; multi-site: dimethyldithiocarbamate
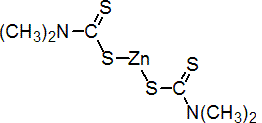
NOMENCLATURE
Common name ziram (BSI, E-ISO, JMAF); zirame ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate)
Chemical Abstracts name (T-4)-bis(dimethyldithiocarbamato-S,S')zinc
CAS RN [137-30-4] EEC no. 205-288-3
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 305.8 M.f. C6H12N2S4Zn Form Colourless powder. M.p. 246 ºC; (tech., 240-244 ºC) V.p. <1 ´ 10-3 mPa (extrapolated) KOW logP = 1.23 (20 °C) Henry <1.9 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.66 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 1.58-18.3 mg/l (20 °C). In acetone 2.88, methanol 0.22, toluene 2.33, n-hexane 0.07 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 18 h (pH 7).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it). Manufacturers Cerexagri; FMC; India Pesticides; Sharda; UCB
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of enzymes containing copper ions or sulfhydryl groups. Mode of action Basic contact, foliar fungicide with protective action. Repellent to birds and rodents. Uses Fungicidal control in pome fruit, stone fruit, nuts, vines, vegetables, and ornamentals. In particular, control of scab in apples and pears, Monilia, Alternaria, Septoria, peach leaf curl, shot-hole, rusts, black rot and anthracnose. Also used as a wildlife repellent, when smeared as a paste on to tree trunks or sprayed on to ornamentals, dormant fruit trees, and other crops. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic, except to zinc-sensitive crops such as tobacco and cucurbits. Formulation types PA; WG; WP; Liquid. Compatibility Incompatible with compounds containing iron, copper, mercury, TEPP, lime, or calcium arsenate. Selected products: 'AAvolex' (Stähler); 'Cekuziram' (Cequisa); 'Crittam' (Siapa); 'Cuman' (Syngenta); 'Mezene' (Isagro); 'Miram' (Crop Health); 'Triscabol' (Cerexagri); 'Ziram Granuflo' (UCB)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'AAprotect' (Bayer CropScience); 'Fruttene' (Sipcam); 'Fuclasin' (Bayer CropScience); 'Pomarsol Z' (Bayer CropScience); 'Thionic' (UCB) Discontinued products: 'Sepilate' * (DuPont); 'Zerlate' * (DuPont); 'Ziramon' * (DuPont); 'Ventine' * (Ciba); 'Ziramugec' * (Sipcam Phyteurop) mixtures: 'Tuzet' * (+ thiram+ urbacid) (Bayer)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by acid hydrolysis, the carbon disulfide liberated being converted to dithiocarbonate which is estimated by titration with iodine (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 236-238, 116-119; ibid., 1998, H, 101; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 965.15). Determination of zinc CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 235. Residues determined by acid hydrolysis followed by colorimetry of the liberated carbon disulfide (W. K. Lowen & H. L. Pease, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 3, 69; G. E. Keppel, J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1971, 54, 528; Analyst (London), 1981, 106, 782).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77, 79 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 53 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2068, guinea pigs 100-150, rabbits 100-300 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Irritating to mucous membranes; highly irritating to eyes; not irritating to skin. Skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.07 mg/l. NOEL In 1 y feeding trials, rats receiving 5 mg a.i./kg daily showed no effect, neither did weanling rats receiving 100 mg/kg diet for 30 d, nor beagle dogs receiving 100 ppm in the diet for 13 w. ADI (JMPR) 0.003 mg/kg b.w. (group ADI for ferbam and ziram) [1996]. Other I.p. LD50 for rats, guinea pigs, and rabbits 5-73, mice 17 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R68| Xn; R22| Xi; R36/37/38
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail 97 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.9 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.048 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (7 d) 190 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 78 (WHO, 1988). Animals Ziram, orally administered to rats, was mostly eliminated within 1-2 d, leaving 1-2% of the dose in the tissues and carcass after 7 d. Plants The major metabolite in plants is dimethylamine salt of dimethyldithiocarbamic acid; tetramethylthiourea, carbon disulfide and sulfur can also be formed. Dimethyldithiocarbamic acid can be present as the free acid or as the metabolic conversion products, DDC-b-glucoside, DDC-a-aminobutyric acid and DDC-a-alanine. Soil/Environment In soil, aerobic DT50 42 h. Unlikely to leach.
|