|
validamycin
See also The BioPesticide Manual, 2nd Ed., entry 2:146
Fungicide
FRAC 26, H3; antibiotic
NOMENCLATURE
Common name validamycin (JMAF); validamycin A (Japanese Antibiotics Research Association)
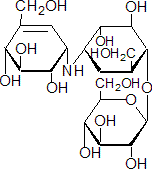
IUPAC name 1L-(1,3,4/2,6)-2,3-dihydroxy-6-hydroxymethyl-4-[(1S,4R,5S,6S)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-hydroxymethylcyclohex-2-enylamino]cyclohexyl b-D-glucopyranoside
Chemical Abstracts name [1S-(1a,4a,5b,6a)]-1,5,6-trideoxy-4-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1-[[4,5,6-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-cyclohexen-1-yl]amino]-D-chiro-inositol
CAS RN [37248-47-8]; [38665-10-0] validoxylamine A (metabolite)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 497.5 M.f. C20H35NO13 Form Colourless, odourless, hygroscopic powder. M.p. 125.9 °C V.p. <2.6 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = -4.21 (calc.) S.g./density 1.402 (20 °C) Solubility In water >610 ´ 103 mg/l (20 °C). In hexane, toluene, dichloromethane and ethyl acetate < 0.01, acetone 0.0266, methanol 62.3 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5, 7, and 9 (25 °C). Specific rotation [a]D24 +110?(water); hydrochloride [a]D22 = +49?(c = 1 in water) pKa 6.14 (20 °C)
COMMERCIALISATION
Production By the fermentation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. limoneus nov. var. History Antibiotic described by T. Iwasa et al. (J. Antibiot., 1970, 23, 595). Correct structure reported by T. Suami et al. (ibid., 1980, 33, 98). Introduced by Takeda Chemical Industries Ltd (now Sumitomo Chemical Takeda Agro Company Ltd) and first marketed in Japan in 1972. Manufacturers Sharda; Sumitomo Chemical Takeda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of trehalase, an enzyme which mediates the digestion of the carbohydrate trehalose and transport of glucose to the hyphals tips. Mode of action Non-systemic antibiotic with fungistatic action. Causes abnormal branching of the tips of the pathogen, followed by cessation of further development. Uses Control of Rhizoctonia solani in rice, potatoes, vegetables, strawberries, tobacco, ginger and other crops; damping-off diseases of cotton, rice and sugar beet, etc. Applied as a foliar spray, soil drench, seed dressing, or by soil incorporation, at 1.25-1.56 g/ha (liquid), 9-12 g/ha (DL formulation), and 0.090 mg/kg (DL or seed dressing). Formulation types [DL]; DP; DS; SL; Liquid. Selected products: 'Validacin' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Mycin' (Sanonda); 'Rhizocin' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Vivadamy' (Vipesco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Sheathmar' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda, Dhanuka); 'Valimun' (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Solacol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Valida' (Nichimen) mixtures: 'Dantotsupadanvalida' (+ cartap hydrochloride+ clothianidin) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Hustler' (+ cartap hydrochloride+ clothianidin+ ferimzone+ phthalide) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Kasu-rab-valida-sumi' (+ fenitrothion+ kasugamycin+ phthalide) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rab-validatrebon' (+ etofenprox+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate+ phthalide) (Hokko); 'Vimix' (+ 1-naphthylacetic acid+ 2-naphthyloxyacetic acid) (Vipesco)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc of a derivative with FID (K. Nishi & K. Konishi, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1976, 8, 309).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >20 000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 mg/l air. NOEL In 90 d feeding trials, rats receiving 1000 mg/kg diet and mice receiving 2000 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. In 2 y feeding trials, NOEL for rats was 40.4 mg/kg b.w. daily. Other Non-mutagenic in bacterial reversion assay systems. Non-teratogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds No effect on chickens or quail at 12.5 g/kg administered orally. Fish LC50 (72 h) for carp >40 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (24 h) for D. pulex >40 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, cleavage to glucose and validoxylamine A occurs. Plants As for animals. Soil/Environment Stable in sunlight. Rapid microbial degradation in soil, forming validoxylamine A; DT50 £5 h.
|