|
trinexapac-ethyl
Plant growth regulator
NOMENCLATURE
trinexapac-ethyl
Common name trinexapac-ethyl (BSI, pa E-ISO)
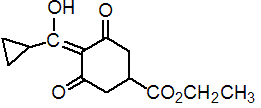
IUPAC name ethyl 4-cyclopropyl(hydroxy)methylene-3,5-dioxocyclohexanecarboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl 4-(cyclopropylhydroxymethylene)-3,5-dioxocyclohexanecarboxylate
Other names cimectacarb-ethyl* (rejected name) CAS RN [95266-40-3] Development codes CGA 163 935 (Ciba-Geigy)
trinexapac
Common name trinexapac (BSI, pa E-ISO)
CAS RN [104273-73-6] Development codes CGA 179500 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
trinexapac-ethyl
Composition Tech. is ³92% pure. Mol. wt. 252.3 M.f. C13H16O5 Form White, odourless solid; (tech. is a yellow to red-brown liquid (30 °C) and a solid-liquid melt (20 °C), with a slight sweet odour). M.p. 36 ºC B.p. >270 ºC V.p. 1.6 mPa (20 ºC); 2.16 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 1.60 (pH 5.3, 25 ºC) Henry 5.4 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.215 g/cm3 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 2.8 (pH 4.9), 10.2 (pH 5.5), 21.1 (pH 8.2) (all in g/l, 25 ºC). In ethanol, acetone, toluene, n-octanol 100%, n-hexane 5% (25 ºC). Stability Heat-stable up to boiling point. Photolytically and hydrolytically stable under normal environmental conditions (pH 6-7, 25 ºC). Less stable in alkali. pKa 4.57 F.p. 133 ºC (1013 mbar) (EEC A9)
trinexapac
Mol. wt. 224.2 M.f. C11H12O5 M.p. 144.4 °C B.p. c. 220 °C V.p. 2.3 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) (OECD 104, EEC A4) KOW logP = 1.8 (pH 2) S.g./density 1.41 (20 °C) Solubility In water 13 (pH 5.0), 200 (pH 6.8), 260 (pH 8.4) (all in g/l). In acetone 95, ethyl acetate 37, methanol 84, octanol 17 (all in g/l). pKa pKa1 5.32, pKa2 3.93
COMMERCIALISATION
History First reported by E. Kerber et al., Proc. Br. Crop Protection Conf., 1989, I, 83. Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in Switzerland in 1992. Patents EP 126713; US 4693745 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
trinexapac-ethyl
Biochemistry Inhibits 3b-hydroxylation of GA20 to GA3 in gibberellin biosynthesis. The reduced level of gibberellins leads to growth retardation of plants. Mode of action Plant growth regulator and retardant, which reduces stem growth by inhibition of internode elongation. Absorbed by the foliage, with translocation to the growing shoot. Uses Used for the prevention of lodging in cereals and in winter oilseed rape, at 0.1-0.3 kg/ha. Also used in turf, at 0.15-0.5 kg/ha, to reduce mowing; and as a maturation promoter in sugar cane at 0.1-0.25 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Could cause inhibition or growth stoppage of some plants, e.g. grasses, aquatic plants and algae. Formulation types EC; ME; WP. Compatibility Compatibility of little importance because of late timing of application; compatible with certain late-season fungicides. Selected products: 'Bonus' (Syngenta); 'Moddus' (Syngenta); 'Primo' (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
trinexapac-ethyl
'Sonis' (Syngenta); 'Shortcut' (Scotts UK) Discontinued products: 'Metro' * (Novartis); 'Vision' * (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
All methods use hplc, for both ester and acid metabolite.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
trinexapac-ethyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 4460 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >4000 mg/kg. Not irritant to skin or eyes of rabbits. Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (48 h) for rats >5.3 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 115 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice 451 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 31.6 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.316 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U (company classification)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
trinexapac-ethyl
Birds LD50 for ducks and quail >2000 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for ducks and quail >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for trout, carp, bluegill sunfish, catfish, fathead minnow 35-180 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) 142 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic; LD50 (oral) >293 mg/bee; (contact) >115 mg/bee. Worms Low toxicity to earthworms; LC50 >93 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, goats and hens, 90% excretion occurs within 24 h, all as the acid metabolite. Plants Rapid metabolism to the acid, which remains by far the predominant metabolite. Soil/Environment In soil, the ester undergoes rapid degradation, DT50 <1 d. The acid has Kd values 1.5-16, Koc 140-600. Further metabolism is rapid, DT50 typically 2-5 w. Within 4-8 w, 50% is mineralised to CO2.
|