|
trifluralin
Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; dinitroaniline
NOMENCLATURE
Common name trifluralin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF); trifluraline ((f) F-ISO)
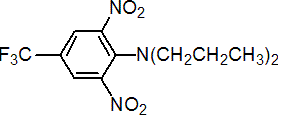
IUPAC name a,a,a-trifluoro-2,6-dinitro-N,N-dipropyl-p-toluidine
Chemical Abstracts name 2,6-dinitro-N,N-dipropyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzenamine
CAS RN [1582-09-8] EEC no. 216-428-8 Development codes L-36 352 (DowElanco); EL-152 (Lilly)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 335.3 M.f. C13H16F3N3O4 Form Yellow-orange crystals. M.p. 48.5-49 ºC; (tech., 43-47.5 ºC) B.p. 96-97 °C/24 Pa V.p. 6.1 mPa (25 ºC) (EEC A4) KOW logP = 4.83 (20 ºC) (EEC A8) Henry 15 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.36 (22 ºC) (EEC A3) Solubility In water 0.184 (pH 5), 0.221 (pH 7), 0.189 (pH 9) (all in mg/l) (EEC A6); tech. 0.343 (pH 5), 0.395 (pH 7), 0.383 (pH 9) (all in mg/l) (EEC A6). In acetone, chloroform, acetonitrile, toluene, ethyl acetate >1000, methanol 33-40, hexane 50-67 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable at 52 ºC (highest storage temperature tested). Stable to hydrolysis at pH values of 3, 6 and 9 (52 ºC). Decomposed by u.v. irradiation (E. Leitis & D. G. Crosby, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1974, 22, 842). F.p. 151 ºC (closed cup); tech. 153 ºC (open cup) (both Pensky-Martens)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by E. F. Alder et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1960, p. 23). Introduced in USA (1961) by Eli Lilly & Co. (agrochemical interests now Dow AgroSciences). Patents US 3257190 Manufacturers Agrochem; Atanor; Budapest Chemical; Dintec; Drexel; Makhteshim-Agan; Milenia; Nortox; Nufarm Ltd; Oxon; Q.E.A.C.A.; Westrade
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Microtubule assembly inhibition. Mode of action Selective soil-herbicide, which acts by entering the seedling in the hypocotyl region. Also inhibits root development. Uses Pre-emergence control of many annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in brassicas, beans, peas, carrots, parsnips, lettuce, capsicums, tomatoes, artichokes, onions, garlic, vines, strawberries, raspberries, citrus fruit, oilseed rape, peanuts, soya beans, sunflowers, safflowers, ornamentals, cotton, sugar beet, sugar cane, and in forestry. Used with linuron or isoproturon for control of annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in winter cereals. Normally applied pre-planting with soil incorporation, at 0.5-1.0 kg/ha, but post-planting application is also possible for some crops. Formulation types EC; GR. Selected products: 'Treflan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trifsan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Eflurin' (Efthymiadis); 'Herbiflurin' (Vapco); 'Ipersan' (Q.E.A.C.A.); 'Olitref' (Budapest Chemical); 'Premerlin' (Milenia); 'Sinfluran' (Westrade); 'Tri-4' (BASF); 'Trifluran' (Cequisa); 'Triflurex' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Trigard' (FCC); 'Trilin' (Griffin); 'Triplen' (Sipcam); 'Zeltoxone' (Syngenta Spain); mixtures: 'Team' (+ benfluralin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Commence' (+ clomazone) (FMC); 'Cotolina' (+ fluometuron) (Aragro)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Fluran' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Heritage' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Legacy' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Orifan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Treflox' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trifluralina' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Triflusan' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Agrisolutions' (Agriliance); 'Ashlade Trimaran' (Nufarm UK); 'Brassix' (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Fluralin' (Papaeconomou); 'Flutrix' (Industria Prodotti); 'Lance' (Milenia); 'Tandril 48' (DAPT); 'Tarene' (BASF); 'Trefanocide' (Shionogi, Bayer CropScience); 'Trefron' (Agrochem); 'Tremolin GR' (Shionogi, Bayer CropScience); 'Triap' (Independent Agribusiness); 'Trif' (Chemia); 'Trific' (Agriliance); 'Triflur' (Nufarm UK); 'Trigermin' (Chemiplant); 'Trinetra' (Parry); 'Trinoxol' (Nufarm SA); 'Tritac' (Milenia); 'Triverdex' (Atanor); 'Trust' (Agriliance) mixtures: 'Axit GR' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Centaure' (+ clomazone+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Chandor' (+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Comboral' (+ pendimethalin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Crescendo' (+ isoxaben+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Elset Mix' (+ isoxaben+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Elset' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Gadisan' (+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Galace' (+ diflufenican) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Premiere' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Rokenyl' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sciandor' (+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Snapshot 2.5TG' (+ isoxaben) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Trinulan' (+ linuron) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Yield' (+ oryzalin) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Ardent' (+ diflufenican) (Bayer CropScience); 'Autumn Kite' (+ isoproturon) (Griffin); 'Blois' (+ linuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Buckle' (+ tri-allate) (Monsanto); 'Cottonex Com' (+ fluometuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Cowark' (+ prometryn) (Shionogi, Bayer CropScience); 'Freedom' (+ alachlor) (Monsanto); 'Hawk' (+ clodinafop-propargyl) (Syngenta); 'Linnet' (+ linuron) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Saherb' (+ desmedipham+ ethofumesate+ phenmedipham) (Azot); 'Salute' (+ metribuzin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Terbalin' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Tri-Scept' (+ imazaquin-ammonium) (BASF) Discontinued products: 'Elancolan' * (Dow); 'Digermin' * (Isagro); 'Tristar' * (PBI) mixtures: 'Mudekan' * (+ linuron) (Dow); 'Alpha Terbalin' * (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ashlade Summit' * (+ terbutryn) (Ashlade); 'Autumn Kite' * (+ isoproturon) (AgrEvo); 'Neminfest' * (+ linuron) (Isagro); 'Passport' * (+ imazethapyr) (BASF); 'Trifluron' * (+ linuron) (United Phosphorus)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 292; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 973.14) or by u.v. spectrometry (ibid., 973.13; CIPAC Handbook, loc. cit.). Residues determined by glc with ECD (J. B. Tepe & R. E. Scroggs, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1967, 5, 527; Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1972, 6, 703). In drinking water by glc with ECD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 990.06). Details from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
IARC ref. 53 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 >5000 mg/kg (rabbits). Non-irritating to skin; slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.8 mg/l. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials in rats, the only effect at the low dose of 813 mg/kg in diet was the formation of renal calculi. This has been shown to be reversible in a 90 d study in dogs, and a NOEL established at 2.4 mg/kg daily. NOEL in mice was 73 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.024 mg/kg. Water GV 20 mg/l (TDI 7.5 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III, IV EC classification Material containing <0.5 ppm N-nitrosodipropylamine is Xi; R36| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for young rainbow trout 0.088, young bluegill sunfish 0.089 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.245 mg/l; NOEC (21 d) 0.051 mg/l. Algae EC50 (7 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 12.2 mg/l; NOEC 5.37 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LD50 (96 h) for grass shrimp (Palaemonetes sp.) 0.64 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg dry soil; NOEC (reduced bodyweight) <171 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Degradation in animals is as for soil (J. L. Emmerson & R. C. Anderson, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 1966, 9, 84-97). Following oral administration, c. 70% is eliminated in the urine and 15% in the faeces within 72 h. Plants Degradation in plants is as for soil. Soil/Environment Adsorbed by the soil, and is extremely resistant to leaching. Little lateral movement in the soil. Metabolism involves dealkylation of the amino group, reduction of the nitro group to an amino group, partial oxidation of the trifluoromethyl group to a carboxy group, and subsequent degradation to smaller fragments (T. Golab et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1979, 27, 163); DT50 57-126 d. Duration of residual activity in soil is 6-8 mo. In laboratory studies, degradation was more rapid under anaerobic conditions, e.g. for loam soil, DT50 (anaerobic) 25-59 d, DT50 (aerobic) 116-201 d. Soil photolysis DT50 41 d; aqueous photolysis DT50 0.8 h. Koc 4400-40 000; Kd ranges from 3.75 (0.01% o.m., pH 6.6) to 639 (16.9% o.m., pH 6.8) (H. J. Pedersen et al., Pestic. Sci., 44, 131 (1995)).
|