|
triflumuron
Insecticide
IRAC 15; benzoylurea
NOMENCLATURE
Common name triflumuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
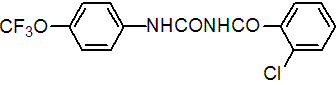
IUPAC name 1-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-3-(4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name 2-chloro-N-[[[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]benzamide
CAS RN [64628-44-0] Development codes SIR 8514 (Bayer) Official codes OMS 2015
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 358.7 M.f. C15H10ClF3N2O3 Form Colourless, odourless powder. M.p. 195 ºC V.p. 4 ´ 10-5 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.91 (20 °C) S.g./density 1.445 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.025 mg/l (20 ºC). In dichloromethane 20-50, isopropanol 1-2, toluene 2-5, hexane <0.1 g/l (20 ºC). Stability Stable to hydrolysis in neutral media and in acids; hydrolysed by alkali: DT50 (22 ºC) 960 d (pH 4), 580 d (pH 7), 11 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by G. Zoebelein et al. (Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 9th, Annu. Mtg. Am. Phytopathol. Soc., 71st, 1979, Abstract 309) and by I. Hammann & W. Sirrenberg (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1980, 33, 1). Introduced by Bayer AG. Patents DE 2601780 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Chitin synthesis inhibitor. Mode of action Ingested insecticide, acting by inhibition of moulting. Uses Control of Lepidoptera, Psyllidae, Diptera, and Coleoptera on fruit, soya beans, vegetables, forest trees, and cotton. Also used against larvae of flies, fleas and cockroaches in public and animal health. Formulation types EC; OF; SC; UL; WP. Selected products: 'Alsystin' (crop protection use) (Bayer CropScience); 'Baycidal' (public health) (Bayer CropScience); 'Starycide' (animal health use) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Soystin' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Raxil T' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Australia) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Methods for determination of residuesavailable from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats and mice >5000, dogs >1000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg; not irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats >0.12 mg/l air (aerosol), >1.6 mg/l air (dust). NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 20 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 20 mg/kg diet. ADI 0.0072 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 561 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >320, golden orfe >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.225 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (96 h) for Scenedesmus >25 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Adult stages are not affected, slight effects on juvenile stages possible; safe to predatory mites.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Triflumuron labelled in the 2-chlorobenzoyl moiety was metabolised in rats by hydrolytic cleavage, forming metabolites which contained only the 2-chlorophenyl ring and were partly hydroxylated and conjugated. Correspondingly, in experiments with labelling in the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl group, metabolites were found which contained only the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl ring, partly in hydroxylated form. Plants Following spray application to apples, soya beans and potatoes, triflumuron is only slightly metabolised; metabolites were the same as those formed in animals. For residue analyses, it is sufficient to determine the parent compound in the harvested crops. Soil/Environment Degradation: In laboratory tests, triflumuron was moderately quickly degraded in the soil; degradation in the field was more rapid by a factor of 3-5. Repeated applications over 3 years to soil without vegetation did not result in any accumulation in the soil. In practice-relevant applications in forests, the concentrations of residues found in the soil were very low at all times, and declined below the limit of detection after a few months. Metabolism: In soil, 50% of applied triflumuron labelled in the 2-chlorobenzoyl moiety was degraded to CO2 within 112 days and c. 20% of the radioactivity was bound to the soil. When using triflumuron labelled in the 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl moiety, the compound was mineralised more slowly, while the percentage of bound residues was markedly increased. Metabolism was mainly induced by microbes, and resulted in metabolites which contained just one of the two rings in each case.
|