|
trifloxysulfuron-sodium
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
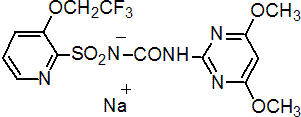
NOMENCLATURE
trifloxysulfuron-sodium
CAS RN [199119-58-9] Development codes CGA 362622 (Ciba-Geigy)
trifloxysulfuron
Common name trifloxysulfuron (BSI, pa ISO)
IUPAC name 1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-[3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridylsulfonyl]urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinesulfonamide
CAS RN [145099-21-4] Development codes CGA 292230 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
trifloxysulfuron-sodium
Mol. wt. 459.3 M.f. C14H13F3N5NaO6S Form Odourless, white to off-white powder. M.p. 170.2-177.7 °C V.p. <1 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 1.4 (pH 5), -0.43 (pH 7) (25 °C) Henry 2.6 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.63 g/cm3 (21 °C) Solubility In water 25 700 mg/l (pH 7.4, 25 °C). Stability Hydrolysis DT50 6 (pH 5), 20 (pH 7), 21 (pH 9) (all in d, 25 °C); photolysis DT50 7 h (25 °C). pKa 4.76 (20 °C)
trifloxysulfuron
Mol. wt. 437.4 M.f. C14H14F3N5O6S
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by Hudetz et al., Proc. South. Weed Sci. Soc. 53, 163-166 (2000) and by S Howard et al., (Proc. BCPC Conf. - Weeds, 2001, 1, 29). Discovered in 1995 and under development by Syngenta AG; Patents EP-B-540697; US-A-5403814 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibitor of acetolactate synthase. Cotton tolerance is based on enhanced metabolism and low translocation out of the treated leaves. Mode of action Readily absorbed by shoots and roots and is translocated via xylem and phloem to shoots, roots and apical meristems. Susceptible weeds show chlorotic symptoms within days and die within 1-3 weeks. Uses The sodium salt is under development for post-emergence grass, sedge, and broad-leaved weed control, at 5-7.5 g/ha, in cotton, and, at 1500 g/ha, in admixture with ametryn, in sugar cane. Weed control in plantations and in turf are also being examined. Weeds controlled include Cyperus spp., Euphorbia spp., Ipomoea spp., Cassia spp., Xanthium spp., Brachiaria spp., and Rottboellia exaltata. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Envoke' (Syngenta); mixtures: 'Krismat' (+ ametryn) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
trifloxysulfuron-sodium
'Enfield' (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
By HPLC; for details, contact Syngenta AG.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats (4 h) >5.03 mg/l. NOEL NOAEL (2 y) for rats 500 ppm. ADI 0.15 mg/kg b.w. Other Not mutagenic, not genotoxic, not teratogenic, not a reproductive hazard; not a neurotoxin. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (company classification)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
trifloxysulfuron-sodium
Not harmful to most organisms but highly toxic to green algae and certain aquatic plant species. Birds LD50 for mallard ducks >2000, bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary NOEC for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail 5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish >103 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >108 mg/l. Algae IC50 (120 h) for Navicula >150, Skeletonema 80, Anabaena 0.28, Selenastrum 0.0065 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster >103 mg/l, mysid shrimp 60 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral and contact) >25 mg/bee. Worms Acute LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Not harmful to Typhlodromus, Aphidius, Poecilus; no effect on soil microbes (respiration, nitrification) or on activated sewage sludge.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Rapidly absorbed and degraded, and shows no tendency to accumulate in organisms or the environment. Animals Rapidly absorbed and excreted (c. 70% via urine, 6% via faeces); after 7 d, remaining residues were <0.3% of dose; metabolism is via O-demethylation, bridge cleavage, glucuronide conjugation. Plants Metabolism proceeds via Smile's rearrangement, bridge cleavage, various hydrolytic, oxidative, and conjugation reactions; very low residues in edible parts of target crops (cane stalk, cotton seed). Soil/Environment Soil adsorption Koc 29-584 ml/cm3 depending on soil type and pH; increasing adsorption over time; Degrades in soil mainly by hydrolysis. DT50 (20 °C, 40% MWC; various soils) 49-78 d. Aqueous DT50 (aerobic) 7-25 d.
|