|
tricyclazole
Fungicide
FRAC 16.1, I1; MBI: reductase
NOMENCLATURE
Common name tricyclazole (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
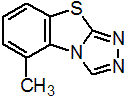
IUPAC name 5-methyl-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b][1,3]benzothiazole
Chemical Abstracts name 5-methyl-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-b]benzothiazole
CAS RN [41814-78-2] EEC no. 255-559-5 Development codes EL-291 (Lilly)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 189.2 M.f. C9H7N3S Form Crystalline solid. M.p. 184.6-187.2 ºC B.p. 275 °C V.p. 5.86 ´ 10-4 mPa (20 ºC, Knudsen-Effusion Weight Loss Method) KOW logP = 1.42 Henry 1.86 ´ 10-7 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 ºC, calc.) S.g./density 1.4 (20 °C) Solubility In purified water 0.596 g/l (20 ºC). In acetone 13.8, methanol 26.5, xylene 4.9 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable at 52 ºC (highest storage temperature tested). Relatively stable to u.v. light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by J. D. Froyd et al. (Phytopathology, 1976, 66, 1135). Introduced in Philippines (1976) by Eli Lilly & Co. (agrochemical interests now Dow AgroSciences). Patents GB 1419121 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences; Nagarjuna Agrichem; Sharda; Tide
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Melanin biosynthesis inhibitor (reduction of 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene and vermelone). Mode of action Systemic fungicide, absorbed rapidly by the roots, with translocation through the plant. Uses Control of rice blast (Pyricularia oryzae) in transplanted and direct-seeded rice at 100 g/ha. Can be applied as a flat drench, transplant root soak, or foliar application. One or two applications by one or more of these methods give a season-long control of the disease. Formulation types DP; GR; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Beam' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Bim' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Tizole' (Tide)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Blas-T' (Crystal); 'Sazole' (Sanonda) mixtures: 'Beam Admire' (+ imidacloprid) (Japan) (Nihon Bayer) Discontinued products: 'Bema' * (Dow)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID or by hplc (E. W. Day et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 11, 263). Residues in plant tissue determined by glc with FPD, the main metabolite (hydroxymethyl analogue) first being converted to a derivative (idem, ibid.). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07). Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 314, mice 245, dogs >50 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats 0.146 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 9.6 mg/kg b.w., for mice 6.7 mg/kg b.w.; (1 y) for dogs 5 mg/kg b.w.; 3-generation reproduction for rats 3 mg/kg b.w. ADI 0.03 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >100 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 16.0, rainbow trout 7.3, goldfish fingerlings 13.5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >20 mg/l; NOEC (21 d) 0.96 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapid and extensive metabolism. Plants The principal metabolite in plants is the hydroxymethyl analogue. Soil/Environment Kd 4 (loamy sand, pH 6.5, 1.5% o.m.), 45 (loam, pH 5.7, 3.1% o.m.), 21 (clay loam, pH 7.4, 1.9% o.m.), 22 (silty clay loam, pH 5.7, 4.1% o.m.).
|