|
triclopyr
Herbicide
HRAC O WSSA 4; pyridinecarboxylic acid
NOMENCLATURE
triclopyr
Common name triclopyr (BSI, E-ISO, F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); no name (Eire)
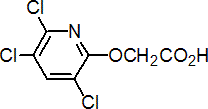
IUPAC name 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyloxyacetic acid
Chemical Abstracts name [(3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridyl)oxy]acetic acid
CAS RN [55335-06-3] Development codes Dowco 233 (Dow)
triclopyr-butotyl
CAS RN [64700-56-7] Development codes M 4021 (Agrimont)
triclopyr-triethylammonium
CAS RN [57213-69-1], formerly [69653-73-2]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
triclopyr
Mol. wt. 256.5 M.f. C7H4Cl3NO3 Form Fluffy, colourless solid. M.p. 150.5 ºC B.p. Decomposes at 208 ºC V.p. 0.2 mPa (25 ºC, vapour pressure balance) KOW logP = 0.42 (pH 5), -0.45 (pH 7), -0.96 (pH 9) Henry 9.77 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.85 (21 ºC). Solubility In water 0.408 (purified), 7.69 (pH 5), 8.10 (pH 7), 8.22 (pH 9) (all in g/l, 20 ºC). In acetone 581, acetonitrile 92.1, hexane 0.09, toluene 19.2, dichloromethane 24.9, methanol 665, ethyl acetate 271 (all in g/l). Stability Stable under normal storage conditions and to hydrolysis, but subject to photodecomposition, DT50 <12 h. pKa 3.97
triclopyr-butotyl
Mol. wt. 356.6 M.f. C13H16Cl3NO4 Henry 2.50 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.)
triclopyr-triethylammonium
Mol. wt. 357.7 M.f. C13H19Cl3N2O3 Henry 1.16 ´ 10-9 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by B. C. Byrd et al. (Proc. West. Soc. Weed Sci., 1975, 28, 44). Introduced by Dow Chemical Co. (now Dow AgroSciences). Triclopyr-triethylammonium was first registered in 1979, as a herbicide for use on non-crop areas and in forestry. Triclopyr-butotyl was subsequently registered in 1980. Manufacturers Agriphar; Aimco; Dow AgroSciences; Gharda; Punjab; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid). Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, rapidly absorbed by the foliage and roots, with translocation throughout the plant, accumulating in meristematic tissue. Induces auxin-type responses in susceptible species (mainly broad-leaved weeds, grass weeds being unaffected at normal application rates).
triclopyr
Uses Control of woody plants and many broad-leaved weeds (e.g. nettles, docks, brambles, gorse, broom) in grassland, uncultivated land, industrial areas, coniferous forests, plantation crops, and rice fields. In plantation crops (oil palm, rubber) at 125-250 g a.e./ha for covercrop maintenance, and at 0.72-1.0 kg a.e./ha to control Eupatorium odoratum and other problem plants; in pastures at 1-2 kg/ha to control annual and perennial herbaceous weeds, and at 2-4 kg/ha against Rubus spp. and other woody plants; in forestry at 4-8 kg/ha for site preparation, and at 1.5-2.0 kg/ha for conifer release; for industrial sites at 2-8 kg/ha; in rangeland at 0.24-1.0 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Clovers are sensitive, as also are larch, lodgepole pine, ornamentals, and edible crops. Selected products: 'Trident' (Agriphar)
triclopyr-butotyl
Formulation types EC. Selected products: 'Garlon 4' (Dow AgroSciences)
triclopyr-triethylammonium
Selected products: 'Garlon 3A' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
triclopyr
Mixtures: 'Stampir' (+ propanil) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Nu-Shot' (+ 2,4-D+ dicamba) (Nufarm UK); 'Starmix' (+ glyphosate) (Nichimen) Discontinued products: 'Convoy' * (Nufarm Whyte); 'Rely' * (Hoechst) mixtures: 'Broadshot' * (+ 2,4-D+ dicamba) (Cyanamid); 'Fettel' * (+ dicamba+ mecoprop) (Zeneca)
triclopyr-butotyl
'Pathfinder II' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Remedy' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Timbrel' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Turflon' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Triptic 48' (United Phosphorus Ltd) mixtures: 'Crossbow' (+ 2,4-D-butotyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Doxstar' (+ fluroxypyr-meptyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Grazon 90' (+ clopyralid) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Pastor' (+ clopyralid+ fluroxypyr-meptyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Togar BT' (+ picloram-isoctyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Broadsword' (+ 2,4-D-2-ethylhexyl+ dicamba) (dicamba as butotyl ester) (United Phosphorus Ltd) Discontinued products: 'Exetor' * (Dow AgroSciences); 'Rely' * (Dow AgroSciences) mixtures: 'Access' * (+ picloram-isoctyl) (Dow AgroSciences)
triclopyr-triethylammonium
'Grandstand' (Dow AgroSciences) mixtures: 'Confront' (+ clopyralid) (clopyralid also as triethylammonium salt) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Redeem' (+ clopyralid) (clopyralid as triethylammonium salt) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Xrm-5202 Premium' (+ 2,4-D+ clopyralid) (2,4-D and clopyralid as triisopropanolammonium salts) (Riverdale)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by glc. Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
triclopyr
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 692, female rats 577 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >256 ppm. NOEL (2 y) for rats 3.0 mg/kg b.w. daily, for mice 35.7 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.005 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
triclopyr
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 1698 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks >5000, Japanese quail 3278, bobwhite quail 2935 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 117, bluegill sunfish 148 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 133 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 45 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees; contact LD50 >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, excretion is primarily via the urine as the unchanged compound. For details of minor urinary metabolites, see C. Timchalk et al., Toxicology, 1990, 62, 71. Plants In plants, DT50 c. 3-10 d. The main metabolite is 3,5,6-trichloro-2-methoxypyridine. Soil/Environment In soil, fairly rapid degradation by microbial activity, with an average half-life of 46 d, depending on soil and climatic conditions. The major degradation product is 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (which has a soil half-life of 30-90 d), with a smaller amount of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-methoxypyridine. Koc c. 59 ml/g; Kd c. 87 (unaged samples), c. 225 (aged) ml/g.
|