|
triazophos
Insecticide, acaricide, nematicide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name triazophos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
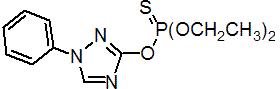
IUPAC name O,O-diethyl O-1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-diethyl O-(1-phenyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl) phosphorothioate
CAS RN [24017-47-8] EEC no. 245-986-5 Development codes Hoe 002960 (Hoechst); AE F002960 (AgrEvo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is ³92% pure. Mol. wt. 313.3 M.f. C12H16N3O3PS Form Light yellow to dark brown liquid, with a typical phosphate ester odour. M.p. 0-5 ºC B.p. Exothermic decomposition above 140 °C V.p. 0.39 mPa (30 ºC); 13 mPa (55 ºC) KOW logP = 3.34 S.g./density 1.24 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 39 mg/l (pH 7, 20 °C). In acetone, dichloromethane, methanol, isopropanol, ethyl acetate and polyethyleneglycols >500, n-hexane 11.1 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to light. Hydrolysed by aqueous acids and alkalis. F.p. Cannot be determined; exothermic decomposition above 140 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by M. Vulic et al. (Abstr. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 7th, Paris, 1970, p. 123). Introduced by Hoechst AG (now Bayer CropScience). First marketed in 1973. Patents DE 1670876; DE 1299924; US 3686200 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience; Sannong; Sharda
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Broad-spectrum insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Non-systemic, but penetrates deeply into plant tissues. Uses Control of aphids, thrips, midges, beetles, lepidopterous larvae, cutworms and other soil insects, spider mites and other species of mite, etc. in ornamentals, fruit trees (including citrus - 0.03%-0.1%), vegetables (200-600 g/ha), cotton (250-600 g/ha), rice (200-400 g/ha), vines, bananas, strawberries, oilseed rape, cereals, sugar beet, sugar cane, maize, soya beans, peanuts, guavas, mangoes, oil palms, olives, coffee, grassland, and in forestry. Also controls some free-living nematodes, particularly in ornamentals and strawberries, and as a bulb dip for tulips and garlic. Formulation types EC; UL. Selected products: 'Current' (Devidayal); 'Hilazofos' (Hindustan); 'Hostathion' (Bayer CropScience); 'March' (Crop Health); 'Triumph' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Try' (Sanonda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Spark' (Bayer CropScience); 'Trelka' (Bayer CropScience) mixtures: 'Deltaphos' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Sherdiphos' (+ cypermethrin+ dimethoate) (Bayer CropScience)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 288). Residues determined by glc with FPD (W. G. Thier et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 127).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 68, 70 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 57-59, dogs >320->500 mg/kg b.w. daily. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. No skin or eye irritation. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.531 mg/l air. NOEL In 2 y feeding trials, rats receiving 1 mg/kg diet and dogs receiving 0.3 mg/kg diet were unaffected, except for inhibition of blood serum cholinesterase. ADI (JMPR) 0.001 mg/kg b.w. [1993]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) Ib EC classification T; R23/25| Xn; R21| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 4.2-27.1 mg/kg, depending on carrier and sex. LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 325 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 5.6, golden orfe 7.5-18 mg/l. LC50 (21 d) for trout 0.01 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.003 mg/l. Algae LC50 (96 h) 1.15 mg/l. Bees Toxic to honeybees. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 187 mg/kg dry artificial soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals Mainly eliminated via urine (75-94% of applied radioactivity). Excretion DT50 <1 d. Plants In cotton plants, 1-phenyl-3-hydroxy-1,2,4-triazole is found as a metabolite, and the occurrence of a desethyl derivative of triazophos is presumed (W. G. Thier et al., Fresenius' Z. Anal. Chem., 1973, 267, 181-186). Soil/Environment Soil: DT50 (aerobic, field) 6-12 d, DT90 39-114 d. DT50 (lab.) 7-46 d, DT90 109-181 d. Water: rapidly degraded in aquatic systems: DT50 (elimination from water) <3 d, (elimination from water/sediment system) <11 d; DT90 (elimination from the system) <47 d.
|