|
triazamate
Insecticide
IRAC 1A; carbamoyltriazole
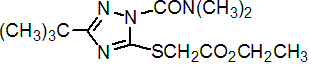
NOMENCLATURE
Common name triazamate (BSI, pa E-ISO)
IUPAC name ethyl (3-tert-butyl-1-dimethylcarbamoyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-ylthio)acetate
Chemical Abstracts name ethyl [[1-[(dimethylamino)carbonyl]-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl]thio]acetate
CAS RN [112143-82-5] Development codes RH-7988; RH-57988 (both Rohm & Haas); WL 145158; CL 900050; AC 900,050 (all Cyanamid); BAS 323I (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 314.4 M.f. C13H22N4O3S Form White to light tan, crystalline solid, with a slight sulfur odour (tech.). M.p. 52.1-53.3 °C V.p. 0.13 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 2.15 (pH 7, 25 °C); a separate study gives logP = 2.69 Henry 1.26 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.222 (20.5 °C) Solubility In water 399 ppm (pH 7, 25 ºC). Soluble in dichloromethane and ethyl acetate (tech.). Stability Stable under normal storage conditions and at pH £7.0; DT50 220 d (pH 5), 49 h (pH 7), 1 h (pH 9). pKa Non-ionising pH 2.7-10.2 F.p. 189 °C (EEC A9) Other properties Surface tension (90% aqueous saturation) 46.5 mN/m (20 °C) (EEC A5).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Aphicide reported by A. Murray et al. (Proc. 1988 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1, 73). Introduced by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences), who entered into an agreement with Shell (now BASF AG) in 1991 for development outside US; launched in France in 1993.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Acts by contact and ingestion, exhibiting systemic and translaminar movement. Uses Control of aphids (including those resistant to carbamate and organophosphorus insecticides) by foliar application on a wide variety of crops, at 35-280 g/ha. Suitable for inclusion in IPM programmes, because it is minimally toxic to beneficial insects. Formulation types EW; WP. Selected products: 'Aztec' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Aphistar' (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Aztec' * (Cyanamid)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 100-200, female rats 50-100 mg tech./kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Practically non-irritating to the skin; moderate eye irritant (rabbits). A skin sensitiser (guinea pigs, maximisation test). Inhalation LC50 for rats 0.47 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for male dogs 0.023, female dogs 0.025 mg/kg daily; (2 y) for male rats 0.45, female rats 0.58 mg/kg daily; (18 mo) for male mice 0.13, female mice 0.17 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.0015 mg/kg b.w. (proposed). Other Not mutagenic, not genotoxic, not teratogenic, not oncogenic, not a reproductive toxicant. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II EC classification (Xn; R23/25| R43)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 (single dose) for bobwhite quail 8 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks 292, quail 411 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.74, rainbow trout 0.53, sheepshead minnow 5.9 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.014 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 240 mg/l; NOEC (72 h) 38 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (120 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 190 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic; LD50 (96 h, oral) 41 mg/bee; (96 h, contact, for tech.) 27 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 350 mg/kg; NOEC <95 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Poecilus cupreus and Aleochara bilineata: no toxic effects at 140 g/ha (lab.). Coccinella septempunctata: 87% effects at 140 g/ha (lab.); no toxic effects in semi-field tests. Aphidius rhopalosiphi "mummies": 20% mortality at 140 g/ha (lab.). Chrysoperla carnea: no effect on third instar, 60% effect on second instar at 140 g/ha (lab.); no effects on first instar in extended lab. tests.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Very rapidly metabolised by enzyme-catalysed hydrolysis and oxidation in all biological systems studied. Transient metabolites are either degraded further (soils and plants), or are eliminated (vertebrates). Animals Hydrolysis, followed by decarbamoylation. Plants Hydrolysis, followed by decarbamoylation. Soil/Environment DT50 2-6 h. Koc 140-360 (5 soils, 25? °C). Aqueous photolysis DT50 150 d (pH c. 4). Metabolites found in leachates are not acutely toxic to Daphnia magna. Neither parent triazamate nor a dimethylcarbamoyl-containing metabolite has any potential for bioaccumulation or for persistence in the environment. Short aerobic half-life coupled with moderate soil adsorption make it unlikely that triazamate will leach.
|