|
triasulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
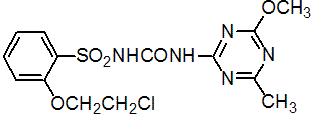
NOMENCLATURE
Common name triasulfuron (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
IUPAC name 1-[2-(2-chloroethoxy)phenylsulfonyl]-3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(2-chloroethoxy)-N-[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]benzenesulfonamide
CAS RN [82097-50-5] Development codes CGA 131 036 (Ciba-Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 401.8 M.f. C14H16ClN5O5S Form Fine white powder. M.p. 178.1 °C (decomp.) V.p. <2 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 1.1 (pH 5.0), -0.59 (pH 6.9), -1.8 (pH 9.0) (25 ºC) Henry <8 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.5 g/cm3 Solubility In water 32 (pH 5), 815 (pH 7), 13 500 (pH 8.4) (all in mg/l, 25 ºC). In acetone 14, dichloromethane 36, ethyl acetate 4.3 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). In ethanol 420, n-octanol 130, n-hexane 0.04, toluene 300 (all in mg/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable for more than 2 years under normal storage conditions. Partial decomposition below the melting point. On hydrolysis, DT50 8.2 h (pH 1), 3.1 y (pH 7), 4.7 h (pH 10). pKa 4.64 (20 ºC)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by J. Amrein & H. R. Gerber (Proc. 1985 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 55). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents US 4514212; EP 44808 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Selectivity derives from rapid metabolism in the crop. Metabolic basis of selectivity in sulfonylureas reviewed (M. K. Koeppe & H. M. Brown, Agro-Food-Industry, 6, 9-14 (1995)). Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots, and rapidly translocated to meristems. Uses Control of broad-leaved weeds pre- and post-emergence in wheat, barley and triticale, at 5-10 g/ha. Formulation types WG. Selected products: mixtures: 'Lintur' (+ dicamba-sodium) (Syngenta); 'Satis' (+ fluoroglycofen-ethyl) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Amber' (Syngenta); 'Lo-Gran' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Dicuran Forte' (+ chlorotoluron) (Syngenta); 'Fuego' (+ dicamba) (dicamba as diglycolamine salt) (Syngenta); 'Keos' (+ isoproturon) (Syngenta); 'Logran B-Power' (+ butafenacil) (Syngenta); 'Logran extra' (+ terbutryn) (Syngenta); 'Rave' (+ dicamba-sodium) (Syngenta); 'Teal' (+ bromoxynil+ ioxynil) (Syngenta); 'Tricuran' (+ chlorotoluron+ terbutryn) (Syngenta); 'Zoom' (+ dicamba-sodium) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Analysis by glc or by hplc with u.v. detection. Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707). Details from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.18 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 32.1 mg/kg b.w. daily, for mice 1.2 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 33 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.012 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail and ducks >2150 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout, carp, catfish, sheepshead minnow and bluegill sunfish >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (96 h) >100 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5-14 d) for Selenastrum 0.035, Scenedesmus 0.77, Anabaena 1.7, Navicula >100 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (48 h) for Quahog clam 56 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees. LD50 (acute and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1000 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Mainly excreted in the urine in unchanged form. Plants In wheat, metabolism is by hydroxylation (para to the sulfonyl urea bridge), followed by conjugation of various hydroxy metabolites with glucose. DT50 in forage c. 3 days. In straw and grain, no residues were detectable at harvest time. Soil/Environment The degradation behaviour in soil is determined by the soil type, pH, and especially temperature and moisture content. Field studies with silty loam, clay loam and sandy loam showed a median DT50 19 d, depending on soil type.
|