|
thiram
Fungicide
FRAC M3; multi-site: dimethyldithiocarbamate
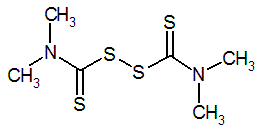
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thiram (BSI, E-ISO); thirame ((m) F-ISO); TMTD (USSR); thiuram (JMAF)
IUPAC name tetramethylthiuram disulfide; bis(dimethylthiocarbamoyl) disulfide
Chemical Abstracts name tetramethylthioperoxydicarbonic diamide
CAS RN [137-26-8] EEC no. 205-286-2 Official codes ENT 987
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 240.4 M.f. C6H12N2S4 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 155-156 ºC V.p. 2.3 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.73 Henry 3.3 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.29 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 18 mg/l (room temperature). In ethanol <10, acetone 80, chloroform 230 (all in g/l, room temperature). In hexane 0.04, dichloromethane 170, toluene 18, isopropanol 0.7 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Decomposed in acidic media. Some deterioration on prolonged exposure to heat, air or moisture. DT50 (est.) (22 ºC) 128 d (pH 4), 18 d (pH 7), 9 h (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicidal properties described by W. H. Tisdale & A. L. Flenner (Ind. Eng. Chem., 1942, 34, 501). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. (who no longer manufacture or market it), by Bayer AG (who no longer manufacture it), UCB Chemicals, and later by other companies. Patents US 1972961 to Du Pont; DE 642532 to I. G. Farbenindustrie Manufacturers Crompton; General Quimica; India Pesticides; Sharda; UCB
APPLICATIONS
Mode of action Basic contact fungicide with protective action. Uses Protective fungicide applied to foliage to control: Botrytis spp. on grapes, soft fruit, lettuce, vegetables and ornamentals; rust on ornamentals; scab and storage diseases on apples and pears; leaf curl and Monilia on stone fruit. Used in seed treatments alone or in combination with added insecticides or fungicides to control damping-off diseases (e.g. Pythium spp.), and other diseases like Fusarium spp. of maize, cotton, cereals, legumes, vegetables and ornamentals. Also used as a bird repellent. Formulation types DP; FS; SC; WG; WP; WS; Liquid seed treatment. Selected products: 'Ceku TMTD' (Cequisa); 'Pomarsol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Thiram Granuflo' (UCB); 'Thiram' (Crompton); 'Thiratox' (Efthymiadis); 'Thyram Plus' (Agrichem Int.); 'Tiurante' (General Quimica); mixtures: 'Anchor' (+ carboxin) (Crompton); 'Gaucho M' (+ imidacloprid+ pencycuron) (Bayer CropScience); 'Gaucho T' (+ imidacloprid) (West Africa) (Bayer CropScience); 'Toram' (+ thiophanate-methyl) (Efthymiadis); 'Vitavax 200FF' (+ carboxin) (Crompton); 'Zaprawa Funaben T' (+ carbendazim) (Azot)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'AApirol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Aatiram' (Bayer CropScience); 'Basultra' (BASF); 'Buck Back' (UCB); 'Defiant' (UCB); 'Evershield T' (Gustafson); 'Kodiak T' (Gustafson); 'Moly-T' (Gustafson); 'Protector D' (Trace); 'Rhodiason' (Bayer CropScience); 'Rhodiauram' (Bayer CropScience); 'Sadoplon' (Azot); 'Thianosan' (UCB); 'Thiraflo' (Crompton); 'Thiraphox' (Papaeconomou); 'Triple-Noctin' (Gustafson); 'Zaprawa Nasienna T' (Azot) mixtures: 'Apron Elite' (+ carbendazim+ cymoxanil+ oxadixyl) (Syngenta); 'Benlate T' (+ benomyl) (Hokko); 'Favour' (+ metalaxyl) (Syngenta); 'Fortiva' (+ metalaxyl+ thiabendazole) (seed) (Limagrain); 'Healthied T' (+ pefurazoate) (SDS Biotech KK); 'Homai' (+ thiophanate-methyl) (Nippon Soda); 'Hy-TL' (+ thiabendazole) (Agrichem Int.); 'Monceren T' (+ pencycuron) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil Extra' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Poland) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil Flow' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Chile) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil Gel 206' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Poland) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil Plus' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Uruguay) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil T' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, E Europe) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil TM Liquido' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, Italy) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil Vital' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, E Europe) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, E Europe) (Bayer CropScience); 'Raxil-Thiram' (+ tebuconazole) (seed treatment, USA) (Gustafson); 'sHYlin' (+ thiabendazole) (Agrichem Int.); 'Stiletto' (+ carboxin+ metalaxyl) (Trace); 'Super Homai' (+ diazinon+ thiophanate-methyl) (Nippon Soda); 'Teevic' (+ pencycuron) (Bayer CropScience); 'Viram Plus' (+ carbendazim) (Vipesco); 'Vitavax CT' (+ carboxin) (Helena); 'Vitavax M' (+ carboxin) (Helena); 'Wakil' (+ carbendazim+ cymoxanil+ oxadixyl) (Syngenta); 'Zaprawa Oxafun T' (+ carboxin) (Azot) Discontinued products: 'Arasan' * (DuPont); 'Tersan' * (DuPont); 'Liro Granuflo' * (Ciba-Geigy); 'Polyram Ultra' * (BASF); 'Tripomol' * (Elf Atochem) mixtures: 'Ceredon T' * (+ benquinox) (Bayer); 'Tuzet' * (+ urbacid+ ziram) (Bayer); 'Apron Combi' * (+ metalaxyl+ thiabendazole) (seed) (Novartis); 'Ascot' * (+ thiabendazole) (Ciba); 'Combinex' * (+ permethrin) (Fargro); 'Hy-Vic' * (+ thiabendazole) (Agrichem Int.); 'Lindex Plus' * (+ fenpropimorph+ gamma-HCH) (DowElanco, Solvay Duphar); 'Oftanol T' * (+ isofenphos) (Bayer CropScience); 'Vitavax RS' * (+ carboxin+ gamma-HCH) (Uniroyal); 'Vitavax-R' * (+ carboxin) (Uniroyal)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 169) or by hydrolysis to dimethylamine, estimated by titration (ibid., 1970, 1, 672; 1980, 1A, 1360; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 966.08). Residues determined by conversion to carbon disulfide, estimated by glc or colorimetry of a derivative (ibid., 972.29; Analyst (London), 1981, 106, 782); see also L. Roland et. al., in Med. Fac. Landbouw. Univ. Gent, 1992, 57, 1255-1260. Details available from UCB Chemicals.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 65, 67 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). IARC ref. 53 class 3 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2600, mice 1500-2000, rabbits 210 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Moderate eye irritant; slight skin irritant. In percutaneous toxicity test in humans, application of the dry powder to the skin produced very slight erythema in 9% of cases. Skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 4.42 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 1.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 0.75 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1992]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III EC classification R68| Xn; R20/22| Xi; R36/37| R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for male ring-necked pheasants 673, mallard ducks >2800, starlings >100, redwing blackbirds >100 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for ring-necked pheasants >5000, mallard ducks >5000, bobwhite quail >3950, Japanese quail >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.0445, rainbow trout 0.128 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.21 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) 0.065 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >2000 mg/bee (80% formulation); (contact) 73.7 mg/bee (75% formulation). Worms LC50 (14 d) 540 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 78 (WHO, 1988). Animals Rapid and extensive metabolism. Degradation products are excreted or integrated into natural constituents. Plants Foliar application results mainly in unchanged thiram. Some conjugation to the glucoside is observed, followed by further degradation and incorporation. Application as a seed treatment results in extensive metabolism with residues incorporated into natural plant constituents. Soil/Environment DT50 0.5 d (sandy soil, pH 6.7).
|