|
thiophanate-methyl
Fungicide, wound protectant
FRAC 1, B1; benzimidazole precursor
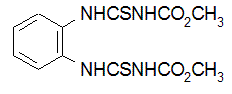
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thiophanate-methyl (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, JMAF)
IUPAC name dimethyl 4,4'-(o-phenylene)bis(3-thioallophanate)
Chemical Abstracts name dimethyl [1,2-phenylenebis(iminocarbonothioyl)]bis[carbamate]
CAS RN [23564-05-8] EEC no. 245-740-7 Development codes NF 44 (Nippon Soda)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 342.4 M.f. C12H14N4O4S2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 172 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 0.0095 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.50 Solubility Practically insoluble in water (23 ºC). In acetone 58.1, cyclohexanone 43, methanol 29.2, chloroform 26.2, acetonitrile 24.4, ethyl acetate 11.9 (all in g/kg, 23 ºC). Slightly soluble in hexane. Stability Stable in neutral, aqueous solution at room temperature. Stable to air and sunlight. Quite stable in acidic solution at room temperature; unstable in alkaline solution; DT50 24.5 h (pH 9, 22 ºC). Formulated product is stable ³2 y below 50 ºC. pKa 7.28
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by K. Ishii (Abstr. Int. Congr. Plant Prot., 7th, Paris, 1970, p. 200). Introduced by the Nippon Soda Co., Ltd. Registered in Japan in 1971. Patents DE 1930540 Manufacturers Aimco; Cerexagri; Jiangsu Eternal; Nippon Soda; Rallis; Sharda; Tide
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Carbendazim precursor. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective and curative action. Absorbed by the leaves and roots. Uses A fungicide used at 30-50 g/ha and effective against a wide range of fungal pathogens including: eyespot and other diseases of cereals; scab on apples and pears; Monilia disease and bitter rot on apples; Monilia spp. on stone fruit; canker on fruit trees; powdery mildews on pome fruit, stone fruit, vegetables, cucurbits, strawberries, vines, roses, etc.; Botrytis and Sclerotinia spp. on various crops; leaf spot diseases on beet, oilseed rape, celery, celeriac, etc.; club root on brassicas; dollar spot, Corticium, and Fusarium spp. on turf; grey mould in vines; blast in rice; sigatoka disease in bananas; and many diseases in floriculture. Also used on almonds, pecans, tea, coffee, peanuts, soya beans, tobacco, chestnuts, sugar cane, citrus fruit, figs, hops, mulberries, and many other crops. Used additionally as a wound protectant for pruning cuts on trees. Formulation types DP; PA; SC; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline and copper-containing compounds. Selected products: 'Topsin M' (Nippon Soda, Cerexagri); 'Aimthyl' (Aimco); 'Alert' (Nagarjuna Agrichem); 'Capital' (Rocca); 'Cekufanato' (Cequisa); 'Cycosin' (BASF); 'Do' (Sanonda); 'Hilnate' (Hindustan); 'Maxim' (Crop Health); 'Mildothane' (Bayer CropScience); 'Roko' (Biostadt); 'Tiposi' (Tide); 'Vapcotop' (Vapco); 'Vithi-M' (Vipesco); mixtures: 'Toram' (+ thiram) (Efthymiadis)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Cercobin' (BASF); 'Enovit M' (Sipcam); 'TOPS' (UAP) mixtures: 'Homai' (+ thiram) (Nippon Soda); 'Super Homai' (+ thiram+ diazinon) (Nippon Soda); 'Compass' (+ iprodione) (BASF); 'Getter' (+ diethofencarb) (Sumitomo); 'Konker R' (+ vinclozolin) (BASF); 'Rex' (+ epoxiconazole) (BASF); 'Snooker' (+ iprodione) (BASF); 'Spectro' (+ chlorothalonil) (Cleary); 'Spot Light' (+ cyproconazole) (Bayer CropScience); 'Tops MZ' (+ mancozeb) (Gustafson) Discontinued products: 'Easout' * (Ciba) mixtures: 'Castaway Plus' * (+ gamma-HCH) (Rhône-Poulenc)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 162). Residues determined by colorimetry (Pestic. Anal. Man., 1979, II; V. L. Miller et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1977, 60, 1154), by glc (A. Ambrus et al., ibid., 1981, 64, 733), or by hplc (S. Ono, Nihon Noyaku Gakkaishi, 1982, 7, 363; N. Shiga et al., ibid., 1977, 2, 27; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M3).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 83, 85 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 7500, female rats 6640, male mice 3510, male rabbits 2270 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male and female rats >10 000 mg/kg. Mild skin and eye irritant. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 1.7 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 160 mg/kg diet, for dogs 50 mg/kg diet. ADI (JMPR) 0.08 mg/kg b.w. [1998]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV EC classification R68| Xn; R20| R43| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral and percutaneous LD50 for Japanese quail >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for rainbow trout 7.8, carp 11 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 20.2 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Chlorella 0.8 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees; LD50 (topical) >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 61% is excreted in the urine and 35% in the faeces within 90 minutes after the last dose. Metabolism involves cyclisation to carbendazim (q.v.). The principal metabolite in rats is methyl 5-hydroxybenzimidazol-2-carbamate. Plants In plants, cyclisation occurs, leading to the formation of carbendazim (q.v.). Soil/Environment Soil persistence is c. 3-4 weeks. In soil, in aqueous solution, and under the influence of u.v. light, cyclisation occurs, leading to the formation of carbendazim (q.v.). This then undergoes degradation to 2-aminobenzimidazole and 5-hydroxy-2-aminobenzimidazole. Soil adsorption Kd 1.2.
|