|
thiodicarb
Insecticide, molluscicide
IRAC 1A; oxime carbamate
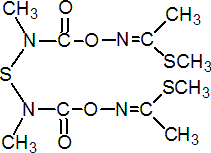
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thiodicarb (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 3,7,9,13-tetramethyl-5,11-dioxa-2,8,14-trithia-4,7,9,12-tetra-azapentadeca-3,12-diene-6,10-dione
Chemical Abstracts name dimethyl N,N'-[thiobis[(methylimino)carbonyloxy]]bis(ethanimidothioate)
CAS RN [59669-26-0] EEC no. 261-848-7 Development codes CGA 45156 (Ciba-Geigy); UC 80 502; UC 51762 (both Union Carbide); RPA 80600 M (Rhône-Poulenc) Official codes AI3-29311; OMS 3026
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is 96% pure. Mol. wt. 354.5 M.f. C10H18N4O4S3 Form Colourless crystals; (tech., pale tan crystals). M.p. 173-174 ºC V.p. 5.7 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 1.62 Henry 4.31 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.44 g/ml (20 ºC) Solubility In water 35 mg/l (25 ºC). In dichloromethane 150, acetone 8, methanol 5, xylene 3 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Stable at pH 6, rapidly hydrolysed at pH 9 and slowly at pH 3 (DT50 c. 9 d). Aqueous suspensions are decomposed by sunlight. Stable up to 60 ºC.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by A. A. Sousa et al. (J. Econ. Entomol., 1977, 70, 803) and reviewed by H. S. Yang & D. E. Thurman (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1981, 3, 687). Discovered almost simultaneously by Union Carbide Agricultural Products Co., Inc. (now Bayer CropScience) and by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Introduced by Union Carbide. European distribution rights acquired by Sipcam-Phyteurop in 2002. Patents US 4382957 Manufacturers Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide with predominantly stomach action, but also limited contact action. As a seed treatment, rapidly translocated systemically through the plant. Molluscicide which provokes paralysis and death. Uses Control of all stages of major Lepidoptera and Coleoptera pests and some Hemiptera and Diptera on cotton, soya beans, maize, vines, fruit, vegetables, and many other crops, at 200-1000 g/ha; seed treatment rates are 2500-10 000 g/tonne. Also used as a molluscicide for control of slugs in cereals and oilseed rape. Formulation types DP; GB; RB; SC; SG; WG; WP; Aqueous flowable; Dust. Compatibility Incompatible with acidic and alkaline substances, certain heavy-metal oxides, and salts of certain fungicides such as maneb, mancozeb (except WP formulations), cuprammonium carbonate, or Bordeaux mixtures. Not miscible with vegetable oil diluents. Selected products: 'Larvin' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Skipper' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Exodus' (Me2); 'Genesis' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Judge' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Larbate' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Minavin' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Securex' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Semevin' (Bayer CropScience, Sipcam Phyteurop)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 279; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 997.14). Residues determined by glc of a derivative (Pestic. Anal. Man., II, 201J; Pestic. Reg. Sec.,180.407) or by hplc. Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 89, 91 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 66 (in water), 120 (in corn oil), dogs >800, monkeys >467 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg; slightly irritating to their eyes and skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.32 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 3.75 mg/kg daily, for mice 5.0 mg/kg daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.03 mg/kg b.w. [2000]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification T+; R25, R26| N; R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail 2023 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for mallard ducks 5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.4, rainbow trout >3.3 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.027 mg/l. Bees Moderately toxic to bees exposed to direct spray. No hazard to honeybees after spray residues have dried.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In rats, rapidly degraded to methomyl, which was rapidly converted to methomyl methylol, oxime, sulfoxide and sulfoxide oxime. These unstable intermediates were converted to acetonitrile and CO2, which were eliminated primarily by respiration and in the urine; a small fraction of acetonitrile was further degraded to acetamide, acetic acid and CO2 (K. Huhtanen & H. W. Dorough, Pestic. Biochem. Physiol., 1976, 6, 571-583). Plants Major metabolites include thiodicarb methomyl, acetonitrile and CO2. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soils of various types, under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, by hydrolysis and photolysis. The primary degradation products are methomyl and methomyl oxime. DT50 of thiodicarb in soil is 3-8 d, depending upon the soil type.
|