|
thiobencarb
Herbicide
HRAC N WSSA 8; thiocarbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thiobencarb (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); thiobencarbe ((m) F-ISO); benthiocarb (JMAF)
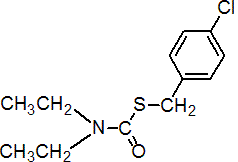
IUPAC name S-4-chlorobenzyl diethylthiocarbamate; S-4-chlorobenzyl diethyl(thiocarbamate)
Chemical Abstracts name S-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl] diethylcarbamothioate
CAS RN [28249-77-6] EEC no. 248-924-5 Development codes B-3015 (Kumiai); IMC3950
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is c. 93% pure. Mol. wt. 257.8 M.f. C12H16ClNOS Form Pale yellow to brownish-yellow liquid. M.p. 3.3 ºC B.p. 126-129 ºC/0.008 mmHg V.p. 2.93 mPa (23 ºC) KOW logP = 3.42 S.g./density 1.145-1.180 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 30 mg/l (20 ºC). Readily soluble in acetone, ethanol, xylene, methanol, benzene, n-hexane, and acetonitrile. Stability Stable in water at pH 5-9 for 30 days (21 ºC). Stable to light and heat.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1970, No. 2, p. 29). Introduced in Japan (1969) by Kumiai Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. and in USA by Chevron Chemical Co. Patents BP 1259471; JP 65740; US 3582314 Manufacturers Ihara/Kumiai
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits lipid synthesis (not ACCase inhibition). Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by coleoptile, mesocotyl, roots and leaves. Inhibits shoot growth of emerging seedlings. Uses Pre-emergence to early post-emergence control of Echinochloa, Leptochloa, and Cyperus spp., and other monocotyledonous and annual broad-leaved weeds in direct-seeded and transplanted rice, at 3-6 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to rice. Formulation types EC; GR. Selected products: 'Saturn' (Kumiai); 'Bigturn' (Sanonda); 'Bolero' (Valent); 'Siacarb' (Siapa); mixtures: 'Wolf-Ace' (+ bensulfuron-methyl+ mefenacet) (Kumiai)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Tobosa' (Crystal) mixtures: 'Satunil' (+ propanil) (Brazil, Thailand) (Iharabras, TJC); 'Thionil' (+ propanil) (Crystal) Discontinued products: 'Bentionil' * (Caffaro, Dow AgroSciences)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1988, D, 159; K. Kojima et al., USA-Japan Seminar Envir. Toxicol. Pestic., 1971; K. Ishikawa et al., Agric. Biol. Chem., 1971, 35, 1161; S. K. De Datta et al., Weed Res., 1971, 11, 41; Y. Ishii, Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1974, No. 19, p. 21).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 1033, female rats 1130, male mice 1102, female mice 1402 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits and rats >2000 mg/kg. Irritating to skin and eyes. Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats 43 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 0.9 mg/kg b.w. daily, for female rats 1.0 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 1.0 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.009 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic, non-teratogenic and non-oncogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for hens 2629, bobwhite quail >7800, mallard ducks >10 000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 3.6, bluegill sunfish 2.4 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.1 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Anabaena flos-aquae >3.1, Navicula pelliculosa 0.38, Selenastrum capricornutum 0.017, Skeletonema costatum 0.073 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.99 mg/l. Bees LC50 (oral) >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 76 (WHO, 1988; general review of thiocarbamates). Animals Thiobencarb was metabolised principally by S-oxygenation to the corresponding sulfoxide by liver microsomes from the striped bass (J. R. Cashman et al., Chem. Res. Toxicol., 1990, 3, 433). Soil/Environment Rapidly adsorbed by soil, and not readily leached. Degradation is primarily by microbial breakdown, with little loss from volatilisation and photodegradation. Half-life in soil varies from 2-3 w under aerobic conditions to 6-8 mo under anaerobic conditions. Koc 3170.
|