|
thifluzamide
Fungicide
FRAC 7, C2; carboxamide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thifluzamide (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
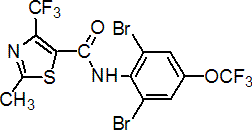
IUPAC name 2',6'-dibromo-2-methyl-4'-trifluoromethoxy-4-trifluoromethyl-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxanilide
Chemical Abstracts name N-[2,6-dibromo-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-2-methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)-5-thiazolecarboxamide
CAS RN [130000-40-7] Development codes MON 24000 (Monsanto); RH-130 753 (Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 96.4% nominal purity. Mol. wt. 528.1 M.f. C13H6Br2F6N2O2S Form White to light brown powder. M.p. 177.9-178.6 ºC V.p. 1.008 ´ 10-6 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.16 (pH 7) S.g./density 2.0 (26 °C) Solubility In water 1.6 mg/l (pH 5.7), 7.6 mg/l (pH 9) (20 ºC). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5.0-9.0 Aqueous photolysis DT50 3.6-3.8 d. pKa 11.0-11.5 (20 °C) F.p. >177 °C
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by P. O'Reilly et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 427). Initially developed by Monsanto Co. and sold to Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences) in 1994. First marketed in Korea in 1997. Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Mode of action Rapidly absorbed by roots and leaves and translocated throughout the plant, when applied as a foliar spray or a soil drench. Uses Control of a wide range of Basidiomycete fungi on rice, cereals, field crops and turf, by foliar application and as a seed treatment. It is particularly effective for foliar treatment of Rhizoctonia, Puccinia and Corticium, and for seed treatment of Ustilago, Tilletia and Pyrenophora. Applied as a foliar treatment in rice at 50-150 g/ha; higher rates (200-300 g/ha) are required when used in rice as a seedling box treatment. Registered for use in rice (Japan, China, Korea), turf (Japan) and potatoes (Latin America). Formulation types FS; SC; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Greatam' (Dow AgroSciences, Nissan); 'Pulsor' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Beaton' * (Dow AgroSciences); 'Thicarbanil' * (Dow AgroSciences)
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >6500 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5 g/l. NOEL For rats 1.4 mg/kg daily, mice 9.2 mg/kg daily, for dogs 10 mg/kg daily. ADI RfD 0.014 mg/kg daily Other Negative in the Ames test; negative for oncogenicity.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 1.2, rainbow trout 1.3, carp 2.9 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 1.4 ppm. Algae EC50 for green algae 1.3 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) for honeybees >1000 ppm; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >1250 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Extensively metabolised by five primary pathways. Plants Thifluzamide resides in the leaf mainly as the parent molecule. Soil/Environment Does not degrade readily by hydrolysis. Microbial degradation in soil is slow. Mobility potential in soil is low.
|