|
thifensulfuron-methyl
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
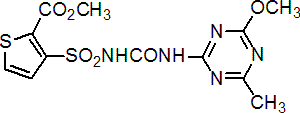
NOMENCLATURE
thifensulfuron-methyl
Common name thifensulfuron-methyl
IUPAC name methyl 3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)thiophen-2-carboxylate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 3-[[[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-2-thiophenecarboxylate
CAS RN [79277-27-3] Development codes DPX- M6316 (DuPont)
thifensulfuron
Common name thifensulfuron (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO); thiameturon* (WSSA former name)
IUPAC name 3-(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)thiophen-2-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 3-[[[[(4-methoxy-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]-2-thiophenecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [79277-67-1]
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Mol. wt. 387.4 M.f. C12H13N5O6S2 Form Off-white solid with no odour. M.p. 176 ºC; (tech. 171.1 ºC) V.p. 1.7 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 ºC, Knudsen method) KOW logP = 1.06 (pH 5), 0.02 (pH 7), 0.0079 (pH 9) Henry 9.7 ´ 10-16 Pa m3 mol-1 (pH 7, 25 ºC) S.g./density 1.580 Solubility In water 223 (pH 5), 2240 (pH 7), 8830 (pH 9) (all in mg/l, 25 ºC). In hexane <0.1, o-xylene 0.212, ethyl acetate 3.3, methanol 2.8, acetonitrile 7.7, acetone 10.3, dichloromethane 23.8 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Aqueous hydrolysis DT50 4-6 (pH 5), 180 (pH 7), 90 (pH 9) (all in days). pKa 4.0 (25 ºC)
thifensulfuron
Mol. wt. 373.4 M.f. C11H11N5O6S2
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicidal activity of thifensulfuron-methyl reported by R. M. Ambach et al. (Proc. North Cent. Weed Control Conf., 1985, 39, 1220). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.; first approval in 1988. Manufacturers DuPont; Fengle
APPLICATIONS
thifensulfuron-methyl
Biochemistry Affects sensitive weeds through inhibition of the enzyme acetolactate synthase (ALS). Inhibition of ALS leads to the rapid cessation of cell division and subsequent growth processes in plants. Mode of action Post-emergence, selective herbicide acting primarily through foliar uptake with little or no soil activity Uses Selective control of a wide range of annual weeds in cereals, maize and pasture. Phytotoxicity Treated cereals may experience a temporary inhibition of growth and colour changes in the leaves, but these have no ultimate effect on the yield. Formulation types TB; WG. Selected products: 'Harmony' (DuPont); 'Pinnacle' (DuPont); mixtures: 'Canvas' (+ tribenuron-methyl+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
thifensulfuron-methyl
'Prospect' (DuPont); 'Refine' (DuPont) mixtures: 'Basis' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Calibre' (+ tribenuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Concert' (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont); 'Grid' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Harmony Express' (+ carfentrazone-ethyl) (DuPont); 'Harmony Extra' (+ tribenuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Harmony M' (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Lexus Millenium' (+ flupyrsulfuron-methyl-sodium) (DuPont); 'Millenium' (+ flupyrsulfuron-methyl-sodium) (DuPont); 'Reliance' (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont); 'Scoop' (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Synchrony STS' (+ chlorimuron-ethyl) (DuPont) Discontinued products: 'Crackshot' * (Cyanamid) mixtures: 'DP 928' * (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'DUK 110' * (+ tribenuron-methyl) (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc/ms/ms (Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods, pp 400-410).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin or eyes. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >7.9 mg/l air. NOEL NOAEL (90 d) for rats 100 mg/kg diet; (2 y) for rats 500 mg/kg diet. NOAEL in reproduction (2 generation) in rats 2500 mg/kg diet; teratogenicity in rats 200 mg/kg daily. ADI 0.26 mg/kg. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames and three other mutagenicity tests. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV (TB, WG)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
thifensulfuron-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and Japanese quail >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 410, bluegill sunfish 520 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 970 mg/l. Algae NOEC (120 h) for green algae 15.7 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees. LD50 (48 h, topical) >12.5 mg/bee. Worms LC50 >2000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration of thifensulfuron-methyl, 70-75% of the unchanged material is excreted in the urine and faeces. The primary degradation mechanism involves hydrolysis of the methoxycarbonyl group, O-demethylation of the heterocyclic ring, and hydrolysis of the sulfonylurea group. Plants In field-grown wheat and corn, residues dissipate rapidly, involving cleavage of the urea bridge and metabolism of the methoxy group on the triazine ring and hydrolysis of the methyl ester group on the thiophene ring. Soil/Environment Thifensulfuron-methyl degrades rapidly in soil by microbial degradation, chemical hydrolysis and photoylsis; DT50 <1 to 7 days, DT90 <1 to 50 days.
|