|
thidiazuron
Plant growth regulator
phenylurea
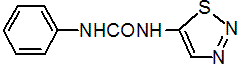
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thidiazuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 1-phenyl-3-(1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-yl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-phenyl-N'-1,2,3-thiadiazol-5-ylurea
CAS RN [51707-55-2] Development codes SN 49 537 (Schering)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 220.2 M.f. C9H8N4OS Form Colourless, odourless crystals. M.p. 210.5-212.5 ºC (decomp.) V.p. 4 ´ 10-6 mPa (25 ºC) (Langmuir method) KOW logP = 1.77 (pH 7.3) Henry 2.84 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) Solubility In water 31 mg/l (pH 7, 25 ºC). In hexane 0.002, methanol 4.20, dichloromethane 0.003, toluene 0.400, acetone 6.67, ethyl acetate 1.1 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Rapidly converted to photoisomer, 1-phenyl-3-(1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)urea, in presence of light (l >290 nm). Hydrolytically stable at room temperature from pH 5-9. No decomposition in accelerated storage stability study (14 d, 54 ºC). pKa 8.86
COMMERCIALISATION
History Plant growth regulator reported by F. Arndt et al. (Plant Physiol., 1976, 57, Supplement, p. 99). Introduced by Schering AG (now Bayer CropScience). Patents DE 2506690; DE 2214632 Manufacturers Bayer CropScience
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cytokinin activity. Mode of action Plant growth regulator, absorbed by the leaves, which stimulates formation of an abscission layer between the plant stem and the leaf petioles, causing the dropping of entire green leaves. Uses Used for defoliation of cotton, in order to facilitate harvesting; applied at 0.21 kg/ha per season. Formulation types EC; WP; SC. Selected products: 'Dropp' (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Separate' (Feinchemie Schwebda) mixtures: 'Ginstar' (+ diuron) (Bayer CropScience); 'Harvade-4198' (+ dimethipin) (Crompton); 'Leafless' (+ dimethipin) (Crompton) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Dropp Ultra' * (+ diuron) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by hplc or by glc with ECD of a derivative. Details available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for mice >5000, rats >4000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >1000, rabbits >4000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; non-irritating to skin (rabbits). No skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.3 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 200 mg/kg diet; (1 y) for dogs 100 mg/kg diet. No significant effects observed in a 2 y carcinogenicity study in mice and a 3-generation reproduction study in rats. Other Acute i.p. LD50 for rats 4200 mg/kg. Non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >3160 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout >19, bluegill sunfish >32 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >10 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to honeybees. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms >1400 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats and goats, metabolism involves hydroxylation of the phenyl group, followed by formation of water-soluble conjugates. Following oral administration, the compound is excreted in the urine and faeces within 96 hours. Plants Only small amounts of residue (normally <0.1 mg/kg) are likely in cottonseed. Soil/Environment Strongly adsorbed by soil. DT50 in soil c. 26-144 d (aerobic), 28 d (anaerobic). Essential soil microbial processes are only temporarily influenced, if at all.
|