|
thiazopyr
Herbicide
HRAC K1 WSSA 3; pyridine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name thiazopyr (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
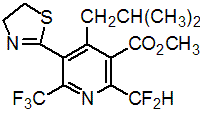
IUPAC name methyl 2-difluoromethyl-5-(4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-4-isobutyl-6-trifluoromethylnicotinate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 2-(difluoromethyl)-5-(4,5-dihydro-2-thiazolyl)-4-(2-methylpropyl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3-pyridinecarboxylate
CAS RN [117718-60-2] Development codes MON 13200 (Monsanto); RH-123652 (Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 93%. Mol. wt. 396.4 M.f. C16H17F5N2O2S Form Light tan, crystalline solid, with a sulfur odour. M.p. 77.3-79.1 ºC V.p. 0.27 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.89 (21 °C) S.g./density 1.373 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 2.5 mg/l (20 ºC). In methanol 28.7, hexane 3.06 (both in g/100 ml, 20 ºC) Stability Aqueous photolysis DT50 15 d.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by Monsanto Co. in 1992 and subsequently sold to Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences) in 1994. Patents US 4988384 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits cell division by disrupting spindle microtubule formation. Mode of action Symptoms include root growth inhibition and swelling in meristematic regions; may also show swollen hypocotyls or internodes. Seed germination is not affected. Uses Pre-emergence control of annual grass and some broad-leaved weeds in tree fruit, vines, citrus, sugar cane, pineapples, alfalfa and forestry. Generally applied at 0.1-0.56 kg/ha. Formulation types EC; GR; WP. Selected products: 'Mandate' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Visor' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Hatchet' * (Rohm & Haas); 'Improvise' * (Rohm & Haas); 'Spindle' * (Rohm & Haas)
ANALYSIS
Details from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Slightly irritating to eyes; practically non-irritating to skin (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.2 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 0.36 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 0.5 mg/kg b.w. daily. Other Non-mutagenic, non-genotoxic, non-teratogenic. Toxicity class EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 1913 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 3.4, rainbow trout 3.2, sheepshead minnow 2.9 mg/l. Lifecycle NOEC for fathead minnow 0.092 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 6.1 mg/l. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum 0.04, Anabaena 2.6, Skeletonema 0.094 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 for Eastern oyster 0.82, mysid shrimp 2.0 mg/l. IC50 (14 d) for Lemna gibba 0.035 mg/l. Bees LD50 >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. In laboratory studies, harmless to spiders, slightly harmful to predatory mites and beetles, moderately harmful to parasitic wasps.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly and extensively metabolised and eliminated. Oxidised by rat liver microsomes via sulfur and carbon oxidations and via oxidative de-esterification. Bioconcentration factor in bluegill sunfish 220; rapidly eliminated, with 98% elimination within 14 d. Plants Studies in several species indicate thiazopyr is initially metabolised in the dihydrothiazole ring by plant oxygenases to the sulfoxide, sulfone, hydroxy derivative and thiazole, and is also de-esterified to the carboxylic acid; see P. C. C. Feng et al., Pestic. Sci., 45(3), 203 (1995). Soil/Environment In soil, degraded by both soil micro-organisms and hydrolysis. Soil dissipation studies across multiple locations in the US indicate average DT50 64 d (8-150 d). Vertical mobility was found to be minimal, with few detections below 18 inches. The monoacid metabolite also has limited vertical mobility under normal use. Not significantly photolysed in soil, but DT50 15 d in aqueous solution, indicating limited potential for surface water contamination.
|