|
tetramethrin
Insecticide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
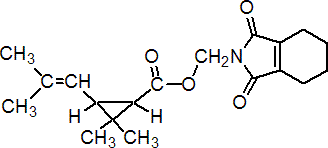
NOMENCLATURE
Common name tetramethrin (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI); tétraméthrine ((f) F-ISO); phthalthrin (JMAF)
IUPAC name cyclohex-1-ene-1,2-dicarboximidomethyl (1RS,3RS;1RS,3SR)-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
Alt: cyclohex-1-ene-1,2-dicarboximidomethyl (?-cis-trans-chrysanthemate
Roth: cyclohex-1-ene-1,2-dicarboximidomethyl (1RS)-cis-trans-2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methylprop-1-enyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
3,4,5,6-tetrahydrophthalimidomethyl (?-cis-trans-chrysanthemate
Chemical Abstracts name (1,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-1,3-dioxo-2H-isoindol-2-yl)methyl 2,2-dimethyl-3-(2-methyl-1-propenyl)cyclopropanecarboxylate
CAS RN [7696-12-0] EEC no. 213-711-6 Development codes FMC 9260; SP 1103 (Sumitomo) Official codes OMS 1011
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is c. 92% pure. Mol. wt. 331.4 M.f. C19H25NO4 Form Colourless crystals, with slight pyrethrum-like odour; (tech. is a colourless to light yellow-brown solid). M.p. 68-70 °C; (tech., 60-80 ºC) V.p. 2.1 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 4.6 (25 ºC) S.g./density 1.1 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 1.83 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone, ethanol, methanol, hexane, n-octanol all >2 g/100 ml. Stability Sensitive to alkalis and strong acids; DT50 16-20 d (pH 5), 1 d (pH 7), <1 h (pH 9). Stable on storage up to c. 50 ºC. Stable in ketones, chloroform, xylene, common aerosol propellants, etc. Variable stability with inorganic carriers. F.p. 200 °C (Cleveland open cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd and later by FMC Corp. (who no longer manufacture or market it). First registered in Japan in 1964. Patents JP 453929; JP 462108; US 3268398 all to Sumitomo Manufacturers Agro-Chemie; Changzhou Kangmei; Endura; Jiangsu Yangnong; Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Non-systemic insecticide with contact action. Gives rapid knockdown. Uses Normally used in combination with synergists (e.g. piperonyl butoxide) and other insecticides for control of flies, cockroaches, mosquitoes, wasps, and other insect pests in public health and home and garden use. Formulation types AE; DP; EC; EW; OE; UL; Oil. Compatibility Incompatible with mineral carriers such as kieselguhr, acidic clays and kaolin. Selected products: 'Neo-Pynamin' (Sumitomo); mixtures: 'Chinethrin' (+ permethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Agro-Chemie); 'Duracide' (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Endura); 'Multi-Fog DTP' (+ deltamethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Trithin)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Py-Kill' (Killgerm) mixtures: 'Pesguard NB' (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Sumitomo); 'Amber' (+ cypermethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Trithin); 'Duracide P' (+ permethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Endura); 'Lexan Forte' (+ chlorpyrifos) (Kwizda); 'Metra-Side CTP' (+ chlorpyrifos+ piperonyl butoxide) (Trithin); 'Multi-Fog ATP' (+ alpha-cypermethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Trithin); 'PB' (+ Permethrin) (Trithin); 'Phinco - T 22' (+ permethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Vapco); 'Tornado-Forte+' (+ lambda-cyhalothrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (public health) (Vapco); 'ULV500' (+ phenothrin [(1R)-trans- isomer]+ piperonyl butoxide) (Trithin) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Duracide Cyp' * (+ cypermethrin+ piperonyl butoxide) (Endura)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By glc (M. Horiba et al., Botyu-Kagaku, 1975, 40, 123), or by u.v. spectrometry (J. Miyamoto, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 345).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews See A. J. Gray & D. M. Soderlund, Chapt. 5 in "Insecticides". Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.73 mg/l air. NOEL In 13 w feeding trials, dogs receiving 5000 mg/kg diet showed no ill-effects. In 6 mo feeding trials, no-effect level for rats was 1500 mg/kg diet. Other No evidence of oncogenicity. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.7, bluegill sunfish 16 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.11 mg/l. Bees Toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 98 (WHO, 1990). EHC 98 notes rapid abiotic degradation in air and water, rapid metabolism and excretion in mammals, and no tendency to accumulate in tissues. Animals In rats, following oral administration, around 95% of tetramethrin (metabolised) is eliminated in the urine and faeces within 5 days. The principal metabolite is 3-hydroxycyclohexan-1,2-dicarboximide (J. Miyamoto et al., J. Agric. Biol. Chem., 1968, 32, 628). Soil/Environment Degradation involves cleavage of the ester bond, leading to chrysanthemic acid derivatives and phenoxybenzoic acid. These are further metabolised by hydroxylation and conjugation.
|