|
terbutryn
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name terbutryn (BSI (from 1984), E-ISO, ANSI, WSSA); terbutryne (BSI (before 1984), (m) F-ISO)
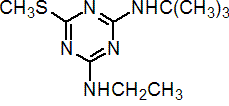
IUPAC name N2-tert-butyl-N4-ethyl-6-methylthio-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N'-ethyl-6-(methylthio)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [886-50-0] EEC no. 212-950-5 Development codes GS 14 260 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 96%. Mol. wt. 241.4 M.f. C10H19N5S Form White powder. M.p. 104-105 ºC B.p. 274 °C/101 kPa V.p. 0.225 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 3.65 (25 ºC, unionised) Henry 1.5 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.12 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 22 mg/l (22 ºC). In acetone 220, hexane 9, n-octanol 130, methanol 220, toluene 45 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Also readily soluble in dioxane, diethyl ether, xylene, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, dimethylformamide. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether. Stability Stable under normal conditions. The methylthio group is hydrolysed in the presence of strong acids or alkalis. At 70 ºC, no significant hydrolysis occurs at pH 5, 7, or 9. pKa 4.3, weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by A. Gast et al. (Proc. Symp. New Herbic., 2nd, 1965, p. 305). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents CH 337019; GB 814948 Manufacturers Makhteshim-Agan; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by the roots and foliage, with translocation acropetally through the xylem, and accumulation in the apical meristems. Uses Used pre-emergence in winter cereals, at 1-2 kg/ha, to control Alopecurus myosuroides (blackgrass) and Poa annua (annual meadow grass). Among the autumn-germinating broad-leaved weeds controlled are Stellaria media (chickweed), Matricaria (mayweed), Papaver (poppies) and Veronica (speedwell), but Galium aparine (cleavers) are rather resistant. Other pre-emergence uses are on sugar cane and sunflowers, and, in mixture with terbuthylazine, on beans, peas and potatoes. In mixture with metolachlor, used in cotton and peanuts. Also used post-emergence (0.2-0.4 kg/ha) in cereals, (1-3 kg/ha) in sugar cane, and as a directed spray in maize. As 'Clarosan', it is used to control algae and submerged vascular plants in waterways, reservoirs and fish ponds. Phytotoxicity Not safe for post-emergence use in cereals which are under stress. Formulation types FW; GR; MG; SC; WP. Selected products: 'Igran' (Syngenta); 'Terbutrex' (Makhteshim-Agan); mixtures: 'Gesaprim' (+ atrazine) (Europe) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Clarosan' (UK) (Syngenta); 'Sorghoprim' (Syngenta); 'Athado' (Probelte); 'Ternit' (Crystal) mixtures: 'Logran extra' (+ triasulfuron) (Syngenta); 'Reflex T' (+ fomesafen-sodium) (Syngenta); 'Tricuran' (+ triasulfuron+ chlorotoluron) (Syngenta); 'Agtryne MA' (+ MCPA-potassium) (Crop Care); 'Amigan' (+ ametryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Aterbutex' (+ atrazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Aterbutox' (+ atrazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Athado Verano' (+ terbumeton+ terbuthylazine) (Probelte); 'Batallion' (+ terbuthylazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Olagan' (+ terbuthylazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Senate' (+ trietazine) (Bayer CropScience); 'Terbalin' (+ trifluralin) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Terbutrex Combi' (+ simazine) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Tomcat' (+ chlorotoluron) (Probelte) Discontinued products: 'Prebane' * (Novartis); 'Plantonit' * (Sagrochem) mixtures: 'Igrater' * (+ metobromuron) (Syngenta); 'Opogard' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Syngenta); 'Topogard' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Syngenta); 'Alpha Terbalin' * (+ trifluralin) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Ashlade Summit' * (+ trifluralin) (Ashlade); 'Lanten' * (+ prometryn) (Aragro); 'Peaweed' * (+ prometryn) (PBI); 'Spudweed' * (+ prometryn) (PBI)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 275; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 971.08; FAO Specification (CP/61); A. H. Hofberg et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1973, 56, 586). Residues determined by glc with MCD or FPD (K. Ramsteiner et al., ibid., 1974, 57, 192; B. G. Tweedy & R. A. Kahrs, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 493; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 13), or by hplc. In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2500, mice 500 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits >20 000 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2200 mg/m3 air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 300 ppm, for mice 3000 ppm; (1 y) for dogs 100 mg/kg diet daily. ADI 0.027 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-mutagenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail 5000, mallard ducks >4640 mg/kg b.w. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.1, bluegill sunfish 1.3, carp 1.4. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 2.66 mg/l. Algae EC50 (7 d) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.013 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (48 h) for Quahog clam 5.6 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees. LD50 (oral) >225 mg/bee; (contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for Eisenia foetida 170 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 73-85% is eliminated as the dealkylated hydroxy metabolite in the faeces within 24 hours (Y. Deng et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1990, 38, 1411). Plants In plants, terbutryn is degraded in a manner similar to other methylthio-s-triazines, viz. by oxidation of the methylthio group to hydroxy metabolites, and by dealkylation of the side-chains. Conjugates are also formed. Soil/Environment Soil micro-organisms play an important role in the degradation of terbutryn. Residual activity in soil is 3-10 weeks, depending upon rate of application, soil type, and weather. DT50 in soil 14-50 d. Koc 2000, indicating a low leaching potential. Degradation in aquatic systems is caused by microbial processes; photolysis also contributes. Considerable amounts of terbutryn are removed from the water by adsorption to the sediment.
|