|
terbuthylazine
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name terbuthylazine (BSI, E-ISO, (f) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
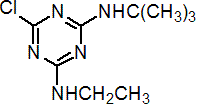
IUPAC name N2-tert-butyl-6-chloro-N4-ethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name 6-chloro-N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N'-ethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [5915-41-3] EEC no. 227-637-9 Development codes GS 13 529 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is ³96 % pure. Mol. wt. 229.7 M.f. C9H16ClN5 Form Colourless powder. M.p. 177-179 ºC V.p. 0.15 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.21 (unionised) Henry 4.05 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.188 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 8.5 mg/l (pH 7, 20 ºC). In acetone 41, ethanol 14, n-octanol 12, n-hexane 0.36 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable in neutral, weakly acidic and weakly alkaline media; hydrolysed in acidic or alkaline media; DT50 (20 ºC) (calc.) 8 d (pH 1), 12 d (pH 13). In natural sunlight, DT50 >40 d. pKa 2.0, v. weak base F.p. >150 ºC
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by A. Gast & E. Fankhauser (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 8th, 1966, 2, 485). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 540590; GB 814947 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences; Makhteshim-Agan; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Maize tolerance of triazines is attributed to conjugation with glutathione. Mode of action Herbicide, absorbed mainly by the roots. Uses Broad-spectrum pre- or post-emergence weed control in maize, sorghum, vines, fruit trees, citrus, coffee, oil palm, cocoa, olives, potatoes, peas, beans, sugar cane, rubber, and in forestry in tree nurseries and new plantings. It remains largely in the topsoil, controlling a wide range of weeds, at rates of 0.6-3 kg/ha; high rates are only recommended as band applications. In Europe, used mainly on maize and sorghum with a maximum application rate of 1.5 kg/ha, mainly in mixture with other herbicides. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many annual plants and to aquatic plants. Formulation types SC; WG. Selected products: 'Folar' (Syngenta); 'Gardoprim' (Syngenta); 'Click' (Sipcam); 'Tyllanex' (Makhteshim-Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Fenican' (Syngenta) mixtures: 'Bolero' (+ diflufenican) (Syngenta); 'Gardo Gold' (+ S-metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Gardobuc' (+ bromoxynil octanoate) (Syngenta, Bayer CropScience); 'Gardoprim Plus Gold' (+ S-metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Lido' (+ pyridate) (Syngenta); 'Alanex TBA' (+ alachlor) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Alpha Bromotril PT' (+ bromoxynil) (name used for all forms of bromoxynil) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Arpix Ter' (+ bromoxynil) (Aragro); 'Artett' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF); 'Athado Invierno' (+ atrazine+ terbumeton) (Probelte); 'Athado Liquido' (+ terbumeton) (Probelte); 'Athado Super' (+ glyphosate) (Probelte); 'Athado Verano' (+ terbutryn+ terbumeton) (Probelte); 'Batallion' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Butazin' (+ glyphosate) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Glifazin' (+ glyphosate) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Olagan' (+ terbutryn) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'RPA 04481H' (+ bromoxynil) (Bayer CropScience); 'Titer' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont); 'Topanex Ter' (+ diuron+ glyphosate) (Aragro); 'Wonder' (+ rimsulfuron) (DuPont) Discontinued products: 'Primatol M' * (Ciba-Geigy); 'Stentan' * (Ciba-Geigy) mixtures: 'Angle' * (+ cyanazine) (Novartis); 'Caragard' * (+ terbumeton) (Novartis); 'Gardoprim Plus' * (+ metolachlor) (Syngenta); 'Opogard' * (+ terbutryn) (Syngenta); 'Primafit' * (+ pendimethalin) (Novartis); 'Skirmish' * (+ isoxaben) (Novartis); 'Topogard' * (+ terbutryn) (Syngenta); 'Zintan' * (+ metolachlor+ pyridate) (Syngenta); 'Primatol 3588' * (+ secbumeton) (Ciba-Geigy); 'Templar' * (+ bromoxynil) (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1899; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 981.04, 971.08; FAO Specification (CP/61); J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 504) or by titration (CIPAC Handbook, 1983, 1B, 1897; see also method for simazine, ibid., 1344); particulars available from Syngenta. Residues determined by glc with MCD or FPD (K. Ramsteiner et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1974, 57, 192; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 13).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1590->2000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. No skin or eye irritation. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.3 mg/l air. NOEL (1 y) for dogs 0.4 mg/kg b.w. daily; (lifetime) for rats 0.22 mg/kg b.w. daily; (2 y) for mice 15.4 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.0022 mg/kg. Water GV 7 mg/l (TDI 2.2 mg/kg b.w.). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification (R22)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for ducks and quail >1000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for ducks and quail >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 3.8-4.6, bluegill sunfish 7.5, carp and catfish 7.0 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 21-50.9 mg/l. Algae EC50 (72 h) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.016-0.024 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (7 d) for earthworms >200 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. No effects on bacterial respiration and nitrification in range 10.9-109 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, 72-84% is eliminated in the urine and faeces within 24 h, and almost all within 48 h. A de-ethyl metabolite forms rapidly, followed by conjugates of products formed by oxidation of one methyl group of the tert-butyl moiety. All are rapidly excreted. Plants Triazine-tolerant plants (e.g. maize) rapidly de-chlorinate terbuthylazine to hydroxy-terbuthylazine. Various amounts of de-ethylated and hydroxy de-ethylated metabolites are produced, depending on the plant species. Soil/Environment Adsorption on soils is strong: Koc 162-278, Kd 2.2-25 are typical values for light agricultural soils. Terbuthylazine is only slightly mobile. Microbial degradation proceeds mainly by de-ethylation and hydroxylation, with eventual ring cleavage. DT50 30-60 d in biologically active soil.
|