|
terbumeton
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; 1,3,5-triazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name terbumeton (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
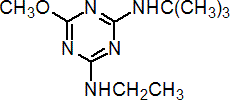
IUPAC name N2-tert-butyl-N4-ethyl-6-methoxy-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
Chemical Abstracts name N-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N'-ethyl-6-methoxy-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine
CAS RN [33693-04-8] Development codes GS 14 259 (Geigy)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 225.3 M.f. C10H19N5O Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 123-124 ºC V.p. 0.27 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 3.04 Henry 4.68 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.08 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 130 mg/l (20 ºC). In acetone 130, toluene 110, methanol 220, dichloromethane 360, n-octanol 90 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). Stability Stable in neutral, weakly acidic and weakly alkaline media. Hydrolysed by strong acids and alkalis, especially at higher temperatures, with the formation of hydroxytriazine; DT50 (20 ºC) (calc.) 29 d (pH 1), 1.6 y (pH 13).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by A. Gast & E. Fankhauser (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 8th, 1966, 2, 485). Introduced by J. R. Geigy S.A. (became Novartis Crop Protection AG, who ceased to manufacture or market it). Patents CH 337019; GB 814948
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed by the leaves and roots. Uses Selective control of annual and perennial grasses and broad-leaved weeds in citrus orchards. Used in combination with terbuthylazine for herbicidal control in vineyards, apple and citrus orchards, and in forestry, at 3-6 kg total a.i./ha. Phytotoxicity Should not be applied to the vine variety Airen. May be phytotoxic to most annual plants, by drift, etc. Formulation types SC; WP.
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Athado Invierno' (+ terbuthylazine+ atrazine) (Probelte); 'Athado Liquido' (+ terbuthylazine) (Probelte); 'Athado Verano' (+ terbuthylazine+ terbutryn) (Probelte) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Caragard' * (+ terbuthylazine) (Novartis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc or by acidimetric titration; details available from Syngenta. Residues determined by glc with MCD (K. Ramsteiner et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1974, 57, 192; E. Knüsli, Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 13).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 651, mice 2343 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >3170 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin (rats); slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >10 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 7.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice 25 mg/kg b.w. daily; (13 w) for dogs 25 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.075 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 14, channel catfish 10, bluegill sunfish 30, crucian carp 30 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 40 mg/l. Algae LC50 0.009 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, following oral administration, terbumeton is rapidly absorbed. More than 95% is eliminated within 96 hours, predominantly in the urine, with c. 25% in the faeces. Plants Demethoxylation, dealkylation (primarily de-ethylation) and conjugation are the main metabolic steps in crop plants. Soil/Environment In soil, terbumeton undergoes microbial demethylation to the hydroxytriazine. There is uncertainty about subsequent degradation. DT50 in soil c. 300 d. Moderately mobile under lab. conditions, but only slightly mobile under typical conditions of use; Koc 37.5-158, Kd 0.6-8.9.
|