|
terbacil
Herbicide
HRAC C1 WSSA 5; uracil
NOMENCLATURE
Common name terbacil (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA, JMAF)
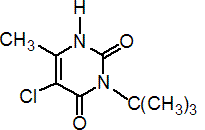
IUPAC name 3-tert-butyl-5-chloro-6-methyluracil
Chemical Abstracts name 5-chloro-3-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-methyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione
CAS RN [5902-51-2] Development codes DPX-D732 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 97%. Mol. wt. 216.7 M.f. C9H13ClN2O2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 175-177 ºC B.p. Sublimation begins below the m.p. V.p. 0.0625 mPa (29.5 ºC) KOW logP = 1.91 Henry 1.3 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.34 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 710 mg/l (25 ºC). In dimethylformamide 337, cyclohexanone 220, methyl isobutyl ketone 121, butyl acetate 88, xylene 65 (all in g/kg, 25 ºC). Sparingly soluble in mineral oils and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Readily soluble in strong aqueous alkalis. Stability Very stable, even at m.p. Stable in aqueous alkaline media at room temperature. Stable 31 d in the dark in aqueous solution (c. pH 6, 25 °C), and in an aqueous solution containing 0.05 M ferric chloride (c. pH 2). Stable 14 d in artificial sunlight (continuous exposure, 25 °C). Stable 14 d in the dark (25 °C, 54 °C). pKa 9.5
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. C. Bucha et al. (Science, 1962, 137, 537). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.; first registered in US in 1966. Patents US 3235357; BE 625897 Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective herbicide, absorbed primarily through the roots, with lesser absorption through the leaves and stems. Uses Selective control of many annual and some perennial weeds in apples, citrus, alfalfa, peaches and sugar cane, at 0.5-4 kg/ha (as area actually treated); also Cynodon dactylon and Sorghum halepense in citrus, at 4-8 kg/ha. Formulation types WP. Selected products: 'Sinbar' (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Discontinued products: 'Geonter' * (Richter Gedeon)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc (H. L. Pease et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1978, 10, 483) or by i.r. spectrometry; details from DuPont. Residues determined by glc (H. L. Pease et al., loc. cit.; R. F. Holt & H. L. Pease, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1977, 25, 373). In drinking water, by glc with NPD (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 991.07).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 934 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant; slight skin irritant. Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.4 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats and dogs 250 mg/kg diet. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Pekin ducklings >56 000, pheasant chicks >31 450 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 46.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 68 ppm. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (48 h) for fiddler crab >1000 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The principal biotransformation pathways are hydroxylation of the 6-methyl group, and replacement of the 5-chloro group with a hydroxy group (B. C. Mayo et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1988, 2, 681). Plants In alfalfa, 12% of terbacil plus its metabolites are still found 6-8 months after application (R. F. Holt & H. L. Pease, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1977, 25, 373). Soil/Environment Undergoes microbial decomposition in moist soil. In top soil, 50% still remains 5-7 months after applying 4.5 kg/ha (P. B. Marriage, Weed Res., 1977, 17, 219-225).
|