|
tebufenozide
Insecticide
IRAC 18; diacylhydrazine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name tebufenozide (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
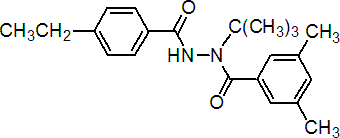
IUPAC name N-tert-butyl-N'-(4-ethylbenzoyl)-3,5-dimethylbenzohydrazide
Chemical Abstracts name 3,5-dimethylbenzoic acid 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-2-(4-ethylbenzoyl)hydrazide
CAS RN [112410-23-8] Development codes RH-5992; RH-75922 (both Rohm & Haas)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 352.5 M.f. C22H28N2O2 Form Off-white powder. M.p. 191 ºC V.p. <1.56 ´ 10-4 mPa (25 ºC, gas saturation method) KOW logP = 4.25 (pH 7) Henry <6.59 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.03 (20 ºC, pycnometer method) Solubility In water 0.83 ppm (25 ºC). Slightly soluble in organic solvents. Stability Stable at 94 ºC for 7 d. Stable to light in pH 7 aqueous solution (25 ºC). Stable in dark, sterile water 30 d (25 ºC). DT50 in natural pond water 67 d, in light, 30 d (25 ºC).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by J. J. Heller et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 59). Developed in USA by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences), under licence in Europe by AgrEvo GmbH (now Bayer CropScience) and in Japan by Hokko Chemical Industry Co., Ltd and Nihon Nohyaku Co., Ltd. Patents US 4985461 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Ecdysone agonist which acts by binding to the receptor site of the insect moulting hormone, ecdysone. Mode of action Lethally accelerates moulting process. Uses Control of lepidopteran larvae on rice, fruit, row crops, nut crops, vegetables, vines, and forestry, generally at 0.06-0.3 lb/a. Formulation types DP; GR; SC; SU; WP. Selected products: 'Confirm' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Mimic' (forestry) (Dow AgroSciences); mixtures: 'Conidan' (+ imidacloprid) (Korea) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Romdan' (Indonesia, Japan) (Dow AgroSciences, Nihon Nohyaku)
ANALYSIS
Details from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 77, 79, 92 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male rats >4.3, female rats >4.5 mg/l. NOEL (24 mo) for rats 5.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (18 mo) for mice 8.1 mg/kg b.w. daily; (12 mo) for dogs 1.9 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1996, 2001]. Other Negative in the Ames test, reverse mutation assay, mammalian point mutation (CHO), in vivo and in vitro cytogenetic assay, and in vitro unscheduled DNA synthesis test. Toxicity class EPA (formulation) III (2 SC) EC classification N; R51, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for quail >2150 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and quail >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 5.7, bluegill sunfish 3.0 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 3.8 mg/l. Algae EC50 (120 h) for Selenastrum >0.64 mg/l; (96 h) for Scenedesmus 0.23 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 1.4, Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 0.64 mg/l. Bees LD50 (96 h, contact) for honeybees >234 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms >1000 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Safe to predatory mites, wasps and other beneficial species.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In the rat, 16 whole-molecule metabolites are formed as a result of oxidation of the alkyl substituents of the aromatic rings, primarily at the benzylic positions. Plants In apples, grapes, rice and sugar beet, the major component is unchanged tebufenozide. Metabolites which are detected in small amounts result from oxidation of the alkyl substituents of the aromatic ring, primarily at the benzylic positions. Soil/Environment Metabolic DT50 in soil 7-66 d (7 soil types); for aerobic, aquatic soil 100 d (25 ºC, 3 soil types); for anaerobic, aquatic metabolism 179 d (25 ºC, silt loam). DT50 for field dissipation 4-53 d (12 sites). Koc 351-894. Field dissipation studies indicate no mobility below 30 cm.
|