|
资料收集库(DocBook) 小笨象工作室 /www.9ele.com/
Tebuconazole
Fungicide
NOMENCLATURE
Common Name: Tebuconazole
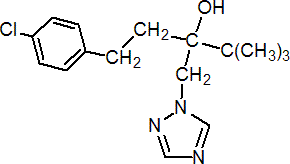
IUPAC name (RS)-1-p-chlorophenyl-4,4-dimethyl-3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)pentan-3-ol
CAS RN: 107534-96-3
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY OF ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Form: Colourless crystals; (tech., colourless to light brown powder).
M.p. :105 ºC
V.p.: 1.7 x10-3 mPa (20 ºC) (OECD 104)
KOW: logP = 3.7 (20 °C)
S.g./density: 1.25 (26 °C)
Solubility: In water 36 mg/l (pH 5-9, 20 ºC). In dichloromethane >200, isopropanol, toluene 50-100, hexane <0.1 (all in g/l, 20 ºC).
Stability: Stable to elevated temperatures, and to photolysis and hydrolysis in pure water, under sterile conditions; hydrolysis DT50 >1 y (pH 4-9, 22 °C). See also Environmental Fate.
SPECIFICATION
95%Tech, 25%EC
APPLICATION:
Biochemistry: Steroid demethylation (ergosterol biosynthesis) inhibitor.
Mode of action: Systemic fungicide with protective, curative, and eradicant action. Rapidly absorbed into the vegetative parts of the plant, with translocation principally acropetally.
Uses: As a seed dressing, tebuconazole is effective against various smut and bunt diseases of cereals such as Tilletia spp., Ustilago spp., and Urocystis spp., also against Septoria nodorum (seed-borne), at 1-3 g/dt seed; and Sphacelotheca reiliana in maize, at 7.5 g/dt seed. As a spray, tebuconazole controls numerous pathogens in various crops including: rust species (Puccinia spp.) at 125-250 g/ha, powdery mildew (Erysiphe graminis) at 200-250 g/ha, scald (Rhynchosporium secalis) at 200-312 g/ha, Septoria spp. at 200-250 g/ha, Pyrenophora spp. at 200-312 g/ha, Cochliobolus sativus at 150-200 g/ha, and head scab (Fusarium spp.) at 188-250 g/ha, in cereals; leaf spots (Mycosphaerella spp.) at 125-250 g/ha, leaf rust (Puccinia arachidis) at 125 g/ha, and Sclerotium rolfsii at 200-250 g/ha, in peanuts; black leaf streak (Mycosphaerella fijiensis) at 100 g/ha, in bananas; stem rot (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) at 250-375 g/ha, Alternaria spp. at 150-250 g/ha, stem canker (Leptosphaeria maculans) at 250 g/ha, and Pyrenopeziza brassicae at 125-250 g/ha, in oilseed rape; blister blight (Exobasidium vexans) at 25 g/ha, in tea; Phakopsora pachyrhizi at 100-150 g/ha, in soya beans; Monilinia spp. at 12.5-18.8 g/100 l, powdery mildew (Podosphaera leucotricha) at 10.0-12.5 g/100 l, Sphaerotheca pannosa at 12.5-18.8 g/100 l, scab (Venturia spp.) at 7.5-10.0 g/100 l, white rot in apples (Botryosphaeria dothidea) at 25 g/100 l, in pome and stone fruit; powdery mildew (Uncinula necator) at 100 g/ha, in grapevines; rust (Hemileia vastatrix) at 125-250 g/ha, berry spot disease (Cercospora coffeicola) at 188-250 g/ha, and American leaf disease (Mycena citricolor) at 125-188 g/ha, in coffee; white rot (Sclerotium cepivorum) at 250-375 g/ha, and purple blotch (Alternaria porri) at 125-250 g/ha, in bulb vegetables; leaf spot (Phaeoisariopsis griseola) at 250 g/ha, in beans; early blight (Alternaria solani) at 150-200 g/ha, in tomatoes and potatoes.
Phytotoxicity: Good plant compatibility in most crops with any formulation, and achieved in more sensitive crops by appropriate formulations, e.g. WP, WG or SC.
|