|
tau-fluvalinate
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 3; pyrethroid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name tau-fluvalinate (BSI, draft E-ISO)
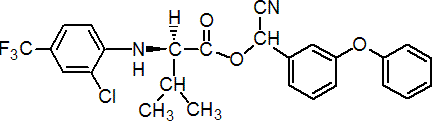
IUPAC name (RS)-a-cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl N-(2-chloro-a,a,a-trifluoro-p-tolyl)-D-valinate
Chemical Abstracts name cyano(3-phenoxyphenyl)methyl N-[2-chloro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-D-valinate
CAS RN [102851-06-9] tau-fluvalinate; [69409-94-5] fluvalinate (DL- isomers) - many references in the literature have been made, erroneously, to the latter rather than the former Development codes SAN 527 I (Sandoz); MK 128
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Material is a 1:1 mixture of (R)-a-cyano-, 2-(R)- and (S)-a-cyano-, 2-(R)- diastereoisomers. Mol. wt. 502.9 M.f. C26H22ClF3N2O3 Form Viscous amber oil, with a moderate or weak sweetish odour (tech.). B.p. 164 ºC/0.07 mmHg (tech.) V.p. 9 ´ 10-8 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = 4.26 (25 ºC) Henry 4.04 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.262 (25 ºC) Solubility In water 1.03 ppb (pH 7, 20 ºC). Soluble in toluene, acetonitrile, isopropanol, dimethylformamide, n-octanol; in iso-octane 108 g/l. Stability Tech. material is stable for 2 years at room temperature (20-28 ºC). Undergoes decomposition on exposure to sunlight; DT50 9.3-10.7 min (aqueous solution buffered pH 5), c. 1 d (thin film on glass), 13 d (on soil surface). On hydrolysis (25 ºC), DT50 for a 9 ppb aqueous solution was 48 d (pH 5), 38.5 d (pH 7), 1.1 d (pH 9). F.p. 90 ºC (tech.; Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticidal and acaricidal activity of the various stereoisomers reported by C. A. Henrick et al. (Pestic. Sci., 1980, 11, 224) and by R. J. Anderson (J. Agric. Food Chem., 1985, 33, 508). Tau-fluvalinate (introduced in 1985) has replaced fluvalinate; both introduced by Zoecon Corp. and purchased by Sandoz Agro AG (became Novartis Crop Protection AG). Sold to Makhteshim-Agan Industries in 2000. Patents US 4243819
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Acts on the nervous system of insects, disturbs the function of neurons by interaction with the sodium channel. Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. Uses Control of a wide range of insects (including Lepidoptera, aphids, thrips, leafhoppers, whitefly, etc.) and spider mites on cereals, oilseed rape and potatoes, at 36-48 g/ha, on vines, vegetables and sunflowers, at up to 72 g/ha, and in orchards at up to 144 g/ha; also on indoor and outdoor ornamentals, cotton, tea, tobacco, and turf. Also used (as 'Apistan') for control of Varroa jacobsoni in beehives. Formulation types EC; EW; UL; Controlled release strips; VP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Klartan' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Mavrik Aquaflow' (Makhteshim-Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Apistan' (Wellmark); 'Mavrik' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Spur' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Talita' (Makhteshim-Agan) mixtures: 'Mavrik B' (+ thiometon) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Mavrik Systo' (+ thiometon) (Makhteshim-Agan) Discontinued products: 'Yardex' * (Sandoz)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis of pyrethroids reviewed by E. Papadopoulou-Mourkidou in Comp. Analyt. Profiles. By hplc (W. L. Fitch et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 79) or by glc with FID. Residues determined by glc with ECD (idem, ibid.; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 998.01).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for female rats 261, male rats 282 mg a.i. (in corn oil)/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg; slight skin irritant, mild eye irritant (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >0.56 mg/l air (as 240 g/l EW formulation). NOEL for rats 1 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.01 mg/kg b.w. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R38| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2510 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish 0.0062, rainbow trout 0.0027, carp 0.0048 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.001 mg/l. Algae LC50 for Scenedesmus subspicatus >2.2 mg/l. Bees Not hazardous to bees at recommended doses; LD50 (24 h, contact topical) 6.7 mg tech./bee; (ingestion) 163 mg tech./bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 ppm. Other beneficial spp. Generally safe to moderately toxic to beneficials, except spiders, predatory mites, some lady beetles and some predatory bugs.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, c. 90% is excreted within 4 d, of which 20-40% is in the urine and 60-80% in the faeces. The principal metabolites are "anilino acid", 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) and 4'-3-PBA as faecal metabolites, and 4'-3-PBA, 3-PBA and 3-phenoxybenzyl alcohol as urinary metabolites. Plants The parent compound itself accounts for >90% of the residue following treatment with tau-fluvalinate. Minor residues include decarboxyfluvalinate, "anilino acid", haloaniline, 3-PBA and 4'-hydroxy-3-PBA. DT50 2-6 w. Soil/Environment In soil under aerobic conditions (lab.), DT50 12-92 d. Primary metabolites include the corresponding anilino acids and the parent aniline. Koc(adsorption) >110 000, (desorption) >39 000.
|