|
sulfometuron-methyl
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
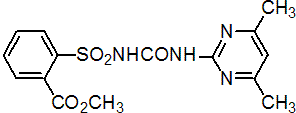
NOMENCLATURE
sulfometuron-methyl
Common name sulfometuron-methyl
IUPAC name methyl 2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid; 2-[3-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)ureidosulfonyl]benzoate
Chemical Abstracts name methyl 2-[[[[(4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]benzoate
CAS RN [74222-97-2] Development codes DPX T5648 (DuPont)
sulfometuron
Common name sulfometuron (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, WSSA)
IUPAC name 2-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid; 2-[3-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)ureidosulfonyl]benzoic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[[[[(4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]benzoic acid
CAS RN [74223-56-6] Development codes DPX T5648 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
sulfometuron-methyl
Composition Tech. is >93%. Mol. wt. 364.4 M.f. C15H16N4O5S Form Colourless solid (tech.). M.p. 203-205 ºC V.p. 7.3 ´ 10-11 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 1.18 (pH 5), -0.51 (pH 7) Henry 1.2 ´ 10-13 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C) S.g./density 1.48 Solubility In water 244 mg/l (pH 7, 25 ºC). In acetone 3300, acetonitrile 1800, ethyl acetate 650, diethyl ether 60, hexane <1, methanol 550, dichloromethane 15 000, dimethyl sulfoxide 32 000, octanol 140, toluene 240 (all in mg/kg, 25 ºC). Stability Aqueous suspensions are stable to hydrolysis at pH 7 to pH 9, DT50 c. 18 d (pH 5). pKa 5.2
sulfometuron
Mol. wt. 350.3 M.f. C14H14N4O5S
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced as a herbicide by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co.; commercially available in 1982. Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
sulfometuron-methyl
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Mode of action Broad-spectrum herbicide, absorbed rapidly by the leaves and roots, with translocation throughout the plant. Uses Control of annual and perennial grasses (especially Sorghum halepense) and broad-leaved weeds in non-crop land. Also used for selective weed control in Bermuda grass and certain other turf grasses; and in forestry to control woody tree species in pine trees. Applied either pre- or post- emergence; range of use rates is 26-420 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Not to be applied near desirable trees and plants. Formulation types WG. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Oust' (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
sulfometuron-methyl
Mixtures: 'Oustar' (+ hexazinone) (DuPont) Discontinued products mixtures: 'Stampro' * (+ propanil) (Dow AgroSciences)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc (E. W. Zahnow & T. J. Waeghe, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1988, 16, 105). Details available from DuPont.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
sulfometuron-methyl
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg; slight skin and eye irritant (rabbits). No skin sensitisation (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >11 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 50 mg/kg diet. In 2-generation reproduction studies, NOEL for rats 500 mg/kg diet. Teratogenicity effects in rats at 1000 mg/kg diet, and in rabbits at 300 mg/kg diet. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
sulfometuron-methyl
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >5000, bobwhite quail >5620 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout and bluegill sunfish >12.5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 >12.5 ppm. Bees Contact LD50 >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Metabolised to hydroxylated sulfometuron-methyl. Soil/Environment Degraded by microbial action and by hydrolysis. DT50 in soil c. 4 w. Koc 85.
|