|
sulfluramid
Insecticide
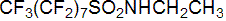
NOMENCLATURE
Common name sulfluramid (BSI, ANSI, draft E-ISO)
IUPAC name N-ethylperfluoro-octane-1-sulfonamide
Chemical Abstracts name N-ethyl-1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptadecafluoro-1-octanesulfonamide
CAS RN [4151-50-2] Development codes GX 071
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 98.0%. Mol. wt. 527.2 M.f. C10H6F17NO2S Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 96 ºC; (tech., 87-93 °C) B.p. 196 ºC V.p. 0.057 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP >6.8 (unionised) Solubility Insoluble in water (25 ºC). In dichloromethane 18.6, hexane 1.4, methanol 833 (all in g/l). Stability Stable >90 d at 50 ºC; to light >90 d in closed jar. pKa 9.5, v. weak acid F.p. >93 °C (Seta flash)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide introduced in USA (1989) by Griffin Corp. Patents US 4921696 Manufacturers Griffin
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Uncouples oxidative phosphorylation. Uses For household control of Formicidae and Blattellidae. Formulation types RB.
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Fluramim' (Milenia); 'Mirex-S' (Chemiplant); 'Raid-Max' (Johnson) Discontinued products: 'Finitron' * (Griffin); 'Volcano' * (Griffin)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Mild skin irritant; practically non-irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.4 mg/l. NOEL (90 d) for male dogs 33, female dogs 100, rats 10 ppm. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 45 mg/kg. LC50 (8 d) for bobwhite quail 300, mallard ducks 165 ppm diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for fathead minnow >9.9, rainbow trout >7.99 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.39 mg/l.
|