|
spinosad
See also The BioPesticide Manual, 2nd Ed., entry 2:144
Insecticide
IRAC 5; spinosyn
NOMENCLATURE
Common name spinosad (BSI, pa ISO, ANSI)
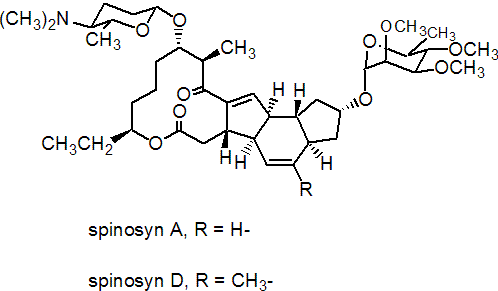
IUPAC name A mixture of (2R,3aR,5aR,5bS,9S,13S,14R,16aS,16bR)-2-(6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-a-L-mannopyranosyloxy)-13-(4-dimethylamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-b-D-erythopyranosyloxy)-9-ethyl-2,3,3a,5a,5b,6,7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16a,16b-hexadecahydro-14-methyl-1H-8-oxacyclododeca[b]as-indacene-7,15-dione and (2R,3aS,5aR,5bS,9S,13S,14R,16aS,16bR)-2-(6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-a-L-mannopyranosyloxy)-13-(4-dimethylamino-2,3,4,6-tetradeoxy-b-D-erythopyranosyloxy)-9-ethyl-2,3,3a,5a,5b,6,7,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16a,16b-hexadecahydro-4,14-dimethyl-1H-8-oxacyclododeca[b]as-indacene-7,15-dione in the proportion 50-95% to 50-5%
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[(6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-a-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-13-[[5-(dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-9-ethyl-2,3,3a,5a,5b,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,16a,16b-tetradecahydro-14-methyl-1H-as-indaceno(3,2-d)oxacyclododecin-7,15-dione (spinosyn A), mixture with 2-[(6-deoxy-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-a-L-mannopyranosyl)oxy]-13-[[5-(dimethylamino)tetrahydro-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy]-9-ethyl-2,3,3a,5a,5b,6,9,10,11,12,13,14,16a,16b-tetradecahydro-4,14-dimethyl-1H-as-indaceno(3,2-d)oxacyclododecin-7,15-dione (spinosyn D)
CAS RN [168316-95-8]; [131929-60-7] spinosyn A; [131929-63-0] spinosyn D Development codes XDE-105; DE-105 (both Dow)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is >90%, composed of 50-95% spinosyn A and 50-5% spinosyn D. Mol. wt. 732.0 (spinosyn A); 746.0 (spinosyn D) M.f. C41H65NO10 (spinosyn A); C42H67NO10 (spinosyn D) Form Light grey to white crystals (tech.). M.p. 84-99.5 °C (spinosyn A); 161.5-170 °C (spinosyn D) V.p. 3.0 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 °C) (spinosyn A); 2.0 ´ 10-5 mPa (25 °C) (spinosyn D) KOW logP = 2.8 (pH 5), 4.0 (pH 7), 5.2 (pH 9) (spinosyn A); logP = 3.2 (pH 5), 4.5 (pH 7), 5.2 (pH 9) (spinosyn D) S.g./density 0.512 (bulk, 20 °C) Solubility Spinosyn A: In water 89 ppm (distilled water), 235 ppm (pH 7) (both 20 °C). In acetone 16.8, acetonitrile 13.4, dichloromethane 52.5, hexane 0.448, methanol 19.0, n-octanol 0.926, toluene 45.7 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Spinosyn D: In water 0.5 ppm (distilled water), 0.33 ppm (pH 7) (both 20 °C). In acetone 1.01, acetonitrile 0.255, dichloromethane 44.8, hexane 0.743, methanol 0.252, n-octanol 0.127, toluene 15.2 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis at pH 5 and 7; DT50 (pH 9) 200 d (spinosyn A), 259 d (spinosyn D). Aquatic photodegradation DT50 (pH 7) 0.93 d (spinosyn A), 0.82 d (spinosyn D). pKa 8.1 (spinosyn A); 7.87 (spinosyn D)
COMMERCIALISATION
Production Derived from the actinomycete Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Following fermentation, spinosad is obtained from a whole broth extraction. History The spinosyns first identified, in a soil sample, by Eli Lilly & Co. (agrochemical interests now Dow AgroSciences) in 1982. Commercially introduced during 1997. Patents US 5202242; EP 375316 Manufacturers Dow AgroSciences
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Activation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, but at a different site from nicotine or imidacloprid. Mode of action Active by contact and ingestion; causes paralysis. Uses For control of pest Lepidoptera (e.g. Ostrinia nubilalis, Helicoverpa zea, Trichoplusia ni, Plutella xylostella, Spodoptera spp., Heliothis spp., Pieris rapae, Keiferia lycopersicella, Lobesia botrana), thrips (e.g. Frankliniella occidentalis, Thrips palmi), flies (e.g. Liriomyza spp., Ceratitis capitata), beetles (e.g. Leptinotarsa decemlineata) and grasshoppers in cotton, row crops, vegetables, and fruits, at 4.8-36 g/hl. Also used for urban pest control (e.g. Agrotis ipsilon, Spodoptera spp., Parapediasia teterella) in turf and ornamentals, for structural control of drywood termites (e.g. Cryptotermes brevis, Incisitermes snyderi), and for fire ant (Solenopsis spp.) control. Effective as a bait for fruit flies (Ceratitis spp., Bactrocera spp., etc) and some ants (Solenopsis spp.).Under development for use on livestock animals for control of chewing and sucking lice (e.g. Linognathus vituli, Bovicola ovis, Solenopotes capillatus) and flies (e.g. Haematobia irritans, Lucilia cuprina), and in livestock premises for control of nuisance flies (e.g. Stomoxys calcitrans, Musca domestica, H. irritans). Formulation types SC; WG. Selected products: 'Conserve' (Dow AgroSciences); 'SpinTor' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Success' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Tracer' (Dow AgroSciences)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Entrust' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Extinosad' (veterinary use) (Elanco); 'GF-120' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Justice' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Laser' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Naturalyte' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Spinoace' (Dow AgroSciences) Discontinued products: 'Spintech' * (Dow AgroSciences)
ANALYSIS
Residues by hplc or immunoassay. Details available from Dow AgroSciences.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3783, female rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; slight irritation to eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.18 mg/l. NOEL (13 w) for dogs 5, mice 6-8, rats 9-10 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [2001]; (US) 0.027 mg/kg b.w.; (Japan, Australia) 0.024 mg/kg b.w. Other Non-neurotoxic, non-mutagenic; no reproductive effects. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV (tech.), IV ('Tracer')
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Acute dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5156 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 30, bluegill sunfish 5.9, common carp 5, Japanese carp 3.5, sheepshead minnow 7.9 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 14 ppm. Algae EC50 for Selenastrum capricornutum >105.5, Skeletonema costatum 0.2, Navicula pelliculosa 0.09, Anabaena flos-aquae 8.9 ppm. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster 0.3, grass shrimp >9.76 ppm. EC50 for Lemna gibba 10.6 ppm. Bees Highly toxic to honeybees when sprayed directly; topical LD50 (48 h) 0.0029 mg/bee; residues have little effect once dry. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Non-toxic to sucking insects, predacious insects (e.g. ladybirds), lacewings, big-eyed bugs or minute pirate bugs. See also M. Miles & R. Dutton Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 2000, 1, 339.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Spinosad is rapidly absorbed, extensively metabolised, and eliminated mainly via urine and faeces. Metabolites include glutathione conjugates and N- and O- demethylated macrolides. No residues of spinosad were found in meat, milk or eggs. Plants On plant surfaces, DT50 1.6-16 d; degradation is mainly by photolysis. No residues of spinosad or metabolites were found in cotton seed. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded by u.v. light and soil microbes to naturally-occurring substances. Soil DT50 for aerobic metabolism 9.4-17.3 d (spinosyn A), 14.5 d (spinosyn D); the major metabolite from spinosyn A is spinosyn B (N-demethylation product); spinosyn D is metabolised similarly. DT50 for photodegradation on soil 8.7 d (spinosyn A), 9.4 d (spinosyn D). DT50 for anaerobic aquatic metabolism 161 d (spinosyn A), 250 d (spinosyn D). Adsorption Freundlich K for spinosyn A 5.4-323; not determined for spinosyn D (expected to be less mobile); for A metabolite (spinosyn B) 4.3-179. DT50 for field dissipation is £0.5 d, with no detectable radiolabel below 24 inches.
|