|
sethoxydim
Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; cyclohexanedione oxime
NOMENCLATURE
Common name sethoxydim (BSI, draft E-ISO); séthoxydime ((f) draft F-ISO)
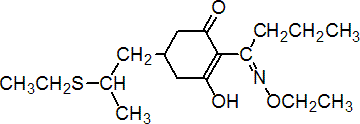
IUPAC name (?-(EZ)-2-(1-ethoxyiminobutyl)-5-[2-(ethylthio)propyl]-3-hydroxycyclohex-2-enone
Chemical Abstracts name (?-2-[1-(ethoxyimino)butyl]-5-[2-(ethylthio)propyl]-3-hydroxy-2-cyclohexen-1-one (i); first publication on the compound presented the structure as a tautomer, 2-[1-(ethoxyamino)butylidene]-5-[2-(ethylthio)propyl]-1,3-cyclohexanedione (ii)
CAS RN [74051-80-2] (i); [71441-80-0] (ii) EEC no. 277-682-3 (for i) Development codes NP-55 (Nippon Soda); BAS 90 520H (BASF); SN 81 742 (AgrEvo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 327.5 M.f. C17H29NO3S Form Oily, odourless liquid. B.p. >90 ºC/3 ´ 10-5 mmHg V.p. <0.013 mPa KOW logP = 4.51 (pH 5), 1.65 (pH 7) S.g./density 1.043 at 25 ºC Solubility In water 25 (pH 4), 4700 (pH 7) (both in mg/l, 20 ºC). Soluble in most common organic solvents e.g. acetone, benzene, ethyl acetate, hexane, methanol all >1 kg/kg (25 ºC). Stability The commercial product is stable for at least 2 y under normal storage conditions. At 10 mg/l, 12 h/d illumination with xenon lamp, DT50 is 5.5 d (pH 8.7, 25 ºC).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced in USA (1983) by Nippon Soda Co., Ltd. Patents JP 52112945; US 4249937; UK 1589003; DE 2822304. Manufacturers Nisso BASF Agro; Shenyang
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Inhibits mitosis. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed predominantly by the foliage, and, to a lesser extent, by the roots. Translocated rapidly both acropetally and basipetally. Uses Control of annual (at 0.20-0.25 kg/ha) and perennial (0.2-0.5 kg/ha) grasses (except Poa spp.) in broad-leaved crops, including cotton, oilseed rape, soya beans, sugar beet, fodder beet, sunflowers, spinach, potatoes, tobacco, peanuts, strawberries, alfalfa, flax, and vegetables. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to broad-leaved crops, but phytotoxic to most monocotyledonous crops (except onions, garlic, and asparagus). Formulation types EC. Compatibility Incompatible with organic and inorganic copper compounds. Selected products: 'Nabu' (Nippon Soda); 'Poast' (BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Checkmate' (Certis UK); 'Conclude G' (BASF); 'Fervinal' (Certis); 'Grasidim' (Sipcam); 'Manifest G' (BASF); 'Prestige' (BASF); 'Torpedo' (BASF); 'Ultima 160' (BASF); 'Vantage' (BASF) mixtures: 'Conclude Ultra' (+ acifluorfen-sodium+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF); 'Rezult' (+ bentazone-sodium) (BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 193-6). Residues determined by hplc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 3200, female rats 2676, male mice 5600, female mice 6300 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and mice >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits); no skin sensitisation. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >6.28 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 17.2, mice 13.7 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (Japan) 0.14 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for Japanese quail >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 153, trout 38 mg tech./l. Daphnia LC50 (3 h) 1.5 mg/l. Bees No significant hazard to bees.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rats, following oral administration, 78.5% is eliminated in the urine and 20.1% in the faeces within 48 h. Plants In soya beans, the parent molecule is oxidised, structurally rearranged, and conjugated. Transformation to metabolites is very rapid. Soil/Environment DT50 in soil <1 d at 15 ºC. Metabolism involves molecular rearrangement, oxidation and conjugation processes.
|