|
rotenone
See also The BioPesticide Manual, 2nd Ed., entry 2:140
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 21
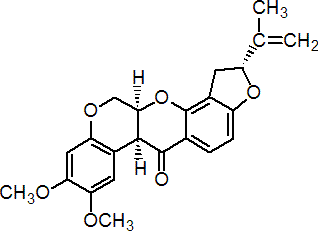
NOMENCLATURE
Common name rotenone (BSI, E-ISO, F-ISO, ESA, accepted in lieu of a common name); derris (JMAF)
IUPAC name (2R,6aS,12aS)-1,2,6,6a,12,12a-hexahydro-2-isopropenyl-8,9-dimethoxychromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6-one
Chemical Abstracts name [2R-(2a,6aa,12aa)]-1,2,12,12a-tetrahydro-8,9-dimethoxy-2-(1-methylethenyl)[1]benzopyrano[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h][1]benzopyran-6(6aH)-one
Other names (for the plant extract) derris root; tuba-root; aker-tuba; (for the plants) barbasco; cub? haiari; nekoe; timbo CAS RN [83-79-4] EEC no. 201-501-9 Official codes ENT 133
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 394.4 M.f. C23H22O6 Form Orthorhombic crystals. M.p. 163 ºC; 181 ºC (dimorphic) V.p. <1 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.16 S.g./density 0.67 (fluffed), 0.78 (packed) Solubility In water 0.142 mg/ml (20 °C). Readily soluble in acetone, carbon disulfide, ethyl acetate and chloroform. Less readily soluble in diethyl ether, alcohols, petroleum ether and carbon tetrachloride. Crystallises from some solvents with the formation of solvates (H. A. Jones, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1931, 33,2738). Stability Decomposes on exposure to light and air. Racemised by alkalis to less insecticidal compounds, more rapidly in certain solvents. Extracts from derris roots can be stabilised with phosphoric acid. Specific rotation [a]D20 -231?(benzene)
COMMERCIALISATION
Production Rotenone and related rotenoids were obtained from Derris, Lonchocarpus and Tephrosia spp. for use as fish poisons. Today, produced by extraction from Derris roots. History Derris root has long been used as a fish poison and its insecticidal properties were known to the Chinese well before it was isolated by E. Geoffrey (Ann. Inst. Colon. (Marseilles), 1895, 2, 1); its structure was established in 1932 (reviewed by L. Crombie, Fortschr. Chem. Org. Naturst. 21, 275; E. B. LaForge et al., Chem. Rev., 1933, 12, 181). Hoechst Schering AgrEvo GmbH sold its business interest in rotenone to Prentiss Inc. in 1999. Manufacturers Prentiss; Tifa
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Respiratory inhibitor acting by inhibiting electron transport at NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I). Selectivity appears to originate from different rates of detoxification. Mode of action Selective non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action. Secondary acaricidal activity. Uses Now used mainly to control fish populations in fish management; applied at 0.005-0.250 ppm. Formulation types DP; EC; WP. Compatibility Not compatible with alkaline substances. Selected products: 'Chem Sect' (Tifa); 'Cube root' (Tifa); 'Prenfish' (Prentiss); 'Vironone' (Vipesco); mixtures: 'Synpren fish' (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Prentiss)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Chem-Fish' (Tifa); 'Noxfish' (Prentiss) mixtures: 'Nusyn-Noxfish' (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Prentiss); 'PB-Nox' (+ piperonyl butoxide) (Penick); 'Pyrellin' (+ pyrethrins (pyrethrum)) (Wright Webb) Discontinued products: 'Derris' * (Devcol, Norcem, Unichem, Whelehan); 'Noxfire' * (Prentiss); 'ToxR' * (Uniroyal)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectrometry (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 961.03*), by rplc with u.v. detection (ibid., 983.06; CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2217). Residues determined by hplc (M. C. Bowman et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1978, 61, 1445).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for white rats 132-1500, white mice 350 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5.0 g/kg. Inhalation LC50 for male rats 0.0235, female rats 0.0194 mg/l. Other Estimated lethal dose for humans 300-500 mg/kg; more toxic when inhaled than when ingested. Very toxic to pigs. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) III, I (EC) EC classification T; R25| Xi; R36/37/38| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.9, bluegill sunfish 4.9 mg/l. Bees Not toxic alone to bees, but toxic in combination with pyrethrum.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In rat liver and in insects, the furan ring is enzymically opened and cleaved, leaving behind a methoxy group. The principal metabolite is rotenonone. An alcohol has been found as a further metabolite, this being formed via oxidation of a methyl group of the isopropenyl residue (I. Yamamoto, Residue Rev., 1969, 25, 161, J-I. Fukami et al., Sci., 1967, 155, 713).
|