|
rimsulfuron
Herbicide
HRAC B WSSA 2; sulfonylurea
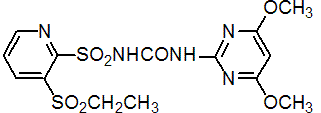
NOMENCLATURE
Common name rimsulfuron (BSI, pa E-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name 1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-(3-ethylsulfonyl-2-pyridylsulfonyl)urea
Chemical Abstracts name N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(ethylsulfonyl)-2-pyridinesulfonamide
CAS RN [122931-48-0] Development codes DPX-E9636 (DuPont)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 99%. Mol. wt. 431.4 M.f. C14H17N5O7S2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 172-173 °C (purity >98%) V.p. 1.5 ´ 10-3 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 0.288 (pH 5), -1.47 (pH 7) (25 ºC) S.g./density 0.784 (25 ºC) Solubility In water (25 ºC) <10 mg/l (unbuffered); 7.3 g/l (buffered, pH 7). Stability On hydrolysis (25 ºC), DT50 4.6 d (pH 5), 7.2 d (pH 7), 0.3 d (pH 9). pKa 4.0
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by H. L. Palm et al. (Proc. 1989 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 23). Introduced by E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Co. and first marketed in Europe in 1991. Manufacturers DuPont
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Branched chain amino acid synthesis (ALS or AHAS) inhibitor. Acts by inhibiting biosynthesis of the essential amino acids valine and isoleucine, hence stopping cell division and plant growth. Crop selectivity derives from rapid, selective metabolism by contraction of the sulfonylurea group and ring migration (L. Martinetti et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 1, 405) and by hydroxylation on the pyrimidine ring, followed by glucose conjugation (M. K. Koeppe, IUPAC 5E-003 (1998)); see Environmental Fate. Mode of action Selective systemic herbicide, absorbed by the foliage and roots, with rapid translocation to the meristematic tissues. Uses Rimsulfuron is a post-emergence sulfonylurea herbicide that effectively controls most annual and perennial grasses and several broad-leaved weeds in maize. Also used in tomatoes and potatoes. The target rate for most situations is 15 g/ha. Rimsulfuron has a wide crop-safety margin under most conditions. Formulation types WG. Selected products: 'Matrix' (USA) (DuPont); 'Titus' (Europe, Africa, Mediterranean) (DuPont)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Rush' (DuPont); 'Aducksbackside' (Me2) mixtures: 'Accent Gold' (+ clopyralid+ flumetsulam+ nicosulfuron) (DuPont); 'Basis Gold' (+ atrazine+ nicosulfuron) (DuPont); 'Basis' (+ thifensulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Grid' (+ thifensulfuron-methyl) (DuPont); 'Pilar' (+ metribuzin) (DuPont); 'Steadfast' (+ nicosulfuron) (DuPont); 'Titer' (+ terbuthylazine) (DuPont); 'Ultim' (+ nicosulfuron) (DuPont); 'Wonder' (+ terbuthylazine) (DuPont) Discontinued products: 'Shadeout' * (DuPont)
ANALYSIS
Product by glc. Residues by hplc. Details from DuPont. Methods for sulfonylurea residues in crops, soil and water reviewed (A. C. Barefoot et al., Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1995, 2, 707).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; moderately irritating to eyes (rabbits). Non-sensitising to skin (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.4 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for male rats 300, female rats 3000 ppm; (18 mo) for mice 2500 ppm; (1 y) for dogs 50 ppm. NOEL in 2-generation rat reproduction study 3000 ppm. Not teratogenic or oncogenic. Other Non-mutagenic in the Ames test. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail >2250, mallard ducks >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5620 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish and rainbow trout >390, carp >900, sheepshead minnow 110 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) >360 mg/l. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 mg/bee; (dietary) >1000 ppm. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms (Eisenia foetida) >1000 mg/kg.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly metabolised and excreted in the urine and faeces. Plants Half-life in maize 6 h, blackgrass 46 h, Johnsongrass 25 d and Sorghum bicolor 52 d. See also Biochemistry. Soil/Environment Degraded rapidly in soil, predominantly via chemical pathways (microbial degradation plays a minor role). Major metabolite is [1-(3-ethylsulfonyl)-2-pyridinyl]-4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidineamine. Rates of degradation are influenced by pH, and the compound is most stable in neutral pH soil and degrades more rapidly in alkaline and acidic soils. DT50 in soil 10-20 d (25 °C, lab. study).
|