|
quintozene
Fungicide
FRAC 14, F3; aromatic hydrocarbon; chloro/nitrophenyl
NOMENCLATURE
Common name quintozene (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); PKhNB (USSR); PCNB (JMAF)
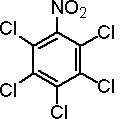
IUPAC name pentachloronitrobenzene
Chemical Abstracts name pentachloronitrobenzene
CAS RN [82-68-8] EEC no. 201-435-0
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is 99% pure. Mol. wt. 295.3 M.f. C6Cl5NO2 Form Colourless needles; (tech., pale yellow crystals). M.p. 143-144 ºC; (tech., 142-145 ºC) B.p. 328 ºC (with slight decomposition) V.p. 12.7 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.1 S.g./density 1907 kg/m3 (21 ºC) Solubility In water 0.1 mg/l (20 ºC). In toluene 1140, methanol 20, heptane 30 (all in g/l). Stability Stable to heat. Stable in acidic media, but hydrolysed by alkalis. Some surface colouring after 10 h exposure to sunlight.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Introduced as a fungicide by I. G. Farbenindustrie AG (now Bayer AG, who no longer manufacture or market it). Patents DE 682048 Manufacturers Amvac; Bayer CropScience; Crompton; Mitsui
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Proposed mode of action is lipid peroxidation. Mode of action Seed and soil, contact fungicide. Uses Control of damping-off diseases in brassicas, lettuce, cotton, flower crops, tomatoes, etc.; Rhizoctonia spp. in brassicas, lettuce, tomatoes, and flower crops; bulb rot and tulip fire in tulips; dollar spot, red thread, and snow mould in turf; Rhizoctonia solani and scab in potatoes; bunt and dwarf bunt of wheat; smut and white rot in onions; white rot in garlic; club root of brassicas; and soil-borne Sclerotium, Sclerotinia, and Botrytis spp. in many glasshouse crops. Also used on peanuts, bananas, beans, peas, rice, maize, safflowers, sorghum, soya beans, etc. Applied at 1-1.5 kg/ha. Formulation types DP; EC; GR; SC; WP; Seed treatment. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials. Selected products: 'Blocker' (Amvac); 'Folosan' (Crompton); 'RTU' (Gustafson); 'Terraclor' (Crompton); mixtures: 'System 3' (+ Bacillus subtilis+ metalaxyl) (Crompton, Helena)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Agromin' (AgroSan); 'Brassicol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Parflo' (Amvac); 'Terrazan' (Crompton); 'Trigran-S' (Gustafson); 'Tritisan' (Bayer CropScience); 'Turfcide' (Crompton); 'Win-Flo' (Amvac) mixtures: 'Dot-Son' (+ disulfoton) (Platte); 'Kodiak A-T' (+ metalaxyl) (Gustafson); 'Mefenoxam PC' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil Gold PC' (+ metalaxyl-M) (Syngenta); 'Ridomil PC' (+ metalaxyl) (Syngenta); 'Terraclor Super X' (+ etridiazole) (Crompton) Discontinued products: 'Avicol' * (Kemira FC); 'Kobu' * (Takeda); 'Kobutol' * (Hokko)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (CIPAC Handbook, 1985, 1C, 2213; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 982.04). Residues determined by glc (Pestic. Anal. Man.,1979, I, 201A, 201G, 201I; Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 4-6, S8, S9, S12, S19; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M1, M12).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 74, 76 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Monograph for the placement of quintozene onto annex 1 of European directive 91/414 (1997). IARC ref. 5 Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits >5000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin; slightly irritating to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.7 mg/l. NOEL (2 y, oncogenic) for rats 1 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y, feeding) for dogs 3.75 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. (for quintozene containing <0.1% hexachlorobenzene) [1995]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xi; R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for mallard ducks 2000 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5000 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.55, bluegill sunfish 0.1 ppm. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.77 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for shrimps 0.012, oyster 0.029 ppm. Bees LD50 (contact) >100 mg/bee.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 41 (WHO, 1984). Animals In mammals, the major routes of elimination are as unchanged material in the faeces or as metabolites in the urine. In rats, sheep and monkeys, the principal metabolite is pentachloroaniline (formed by reduction of the nitro group). Other metabolites include pentachlorophenol, pentachlorothioanisole, pentachlorobenzene, bis-methyl-tetrachlorobenzene, methyl pentachlorophenyl sulfide and N-acetyl-S-pentachlorophenylcysteine (E. J. Kuchar et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 1969, 17, 1237-1240; W. Koegel et al., Chemosphere, 1979, 89-105; P. W. Aschbacher & V. J. Feil, J. Agric. Food Chem., 1983, 31, 1150). Plants In plants, quintozene undergoes conversion to pentachloroaniline, methylthiopentachlorobenzene and a variety of chlorophenyl methyl sulfoxides and sulfones. Soil/Environment Persists in soil, with a half-life of c. 4-10 months. Part is lost from the soil by volatilisation. Biodegradation occurs, mainly to pentachloroaniline and also methylthiopentachlorobenzene. For details of effects on soil organisms, see E. R. Ingham, Crop Prot., 1985, 4, 3-32. Koc for adsorption 6030 (silt loam), 2966 (sand); for desorption 9584 (silt loam), 3285 (sand).
|