|
quinclorac
Herbicide
HRAC O, also L WSSA 4; quinolinecarboxylic acid
NOMENCLATURE
Common name quinclorac (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
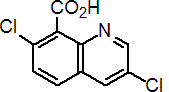
IUPAC name 3,7-dichloroquinoline-8-carboxylic acid
Chemical Abstracts name 3,7-dichloro-8-quinolinecarboxylic acid
CAS RN [84087-01-4] EEC no. 402-780-1 Development codes BAS 514 H (BASF)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 242.1 M.f. C10H5Cl2NO2 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 274 ºC V.p. <0.01 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = -1.15 (pH 7) Henry 4.4 ´ 10-10 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.75 Solubility In water 0.065 mg/kg (pH 7, 20 ºC). In ethanol, acetone 2 g/kg (20 ºC). Practically insoluble in other organic solvents. Stability Stable to heat and light and between pH 3 to 9. pKa 4.34 (20 ºC)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by E. Haden et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1985, 1, 77). Introduced in Spain and Korea (1989) by BASF AG. Patents EP 60429; US 4497651; US 4632696; DE 3108873 Manufacturers BASF; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Synthetic auxin (acting like indolylacetic acid); also inhibitor of cell wall (cellulose) biosynthesis. Mode of action Rapidly absorbed through the foliage. Weak auxin activity as determined in wheat coleoptile elongation test, cucumber root elongation test, cucumber curvature test and ethylene biosynthesis test in soya beans. No influence on Hill reaction. Plant response is similar to IAA or auxin-type herbicides of the class of benzoic acids and pyridine compounds. Uses Pre- and post-emergence control of grass weeds (Echinochloa spp., Aeschynomene spp., Sesbania spp.) and other weeds in direct-seeded and transplanted rice, at 0.25-0.75 kg/ha. Phytotoxicity Non-phytotoxic to transplanted and direct-seeded rice. Under continuous irrigation conditions, injury may occur in adjacent umbelliferous crops if connected to the same waterway. Formulation types GR; SC; WP. Compatibility Good combination partner for all rice herbicides which are insufficiently effective against Echinochloa. Selected products: 'Facet' (BASF); 'Queen' (Sanonda)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Accord' (BASF); 'Drive' (BASF); 'Paramount' (BASF); 'Fas-Nox' (Crystal) mixtures: 'Cao Neng' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Anhui); 'Propacet' (+ propanil) (Crystal)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by rplc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 244). Residues in plant and animal matrices by glc, in soil by hplc.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2680, mice >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to eyes and skin (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.2 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 533 mg/kg b.w. Other Not carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xi; R43
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and quail >2000 mg/kg. Dietary LD50 (8 d) for mallard ducks >5000 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout, bluegill sunfish, carp, and minnows >100 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 113 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 67, blue crab >100 mg/l. LC50 (48 h) for Quahog clam >100 mg/l. Bees Non-toxic by contact or ingestion.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals More than 90% of radiolabelled quinclorac administered orally to rats is excreted in the urine within 5 days. Plants In plants, systemically translocated to the roots and to the leaves. Soil/Environment Only slightly adsorbed by the soil. Depending on soil type and organic matter content, the chemical is relatively mobile, this mobility increasing with higher percolation rates in fields. Quinclorac is degraded by micro-organisms, 3-chloro-8-quinolinecarboxylic acid being a major metabolite. Water regimes causing changes in moisture content in rice soils enhance the microbial degradation. Photolytic decomposition in active paddy water occurs in the presence of sunlight and dissolved humic acids.
|