|
quinalphos
Insecticide, acaricide
IRAC 1B; organophosphate
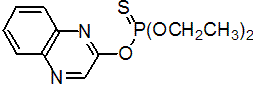
NOMENCLATURE
Common name quinalphos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO); chinalphos ((m) France)
IUPAC name O,O-diethyl O-quinoxalin-2-yl phosphorothioate
Chemical Abstracts name O,O-diethyl O-2-quinoxalinyl phosphorothioate
CAS RN [13593-03-8] EEC no. 237-031-6 Development codes Bay 77 049 (Bayer); SAN 6538; SAN 6626 (both Sandoz) Official codes ENT 27 394
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 298.3 M.f. C12H15N2O3PS Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 31-32 ºC B.p. 142 ºC/0.0003 mmHg (decomp.) V.p. 0.346 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.44 (23 ºC, 10-100 ppm level) S.g./density 1.235 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 17.8 mg/l (22-23 ºC). In hexane 250 g/l (23 ºC). Readily soluble in toluene, xylene, diethyl ether, ethyl acetate, acetone, acetonitrile, methanol, ethanol. Slightly soluble in petroleum ether (23 °C). Stability A.i. stable 14 d at room temperature; liquid tech. grade less stable but stable under ambient storage conditions, when diluted in non-polar organic solvents and in the presence of stabilising agents. Formulations are stable (shelf life at ave. ann. temp. £25 ºCc. 2 y). Susceptible to hydrolysis; DT50 (25 ºC, 17 ppm and 2.5 ppm) 23 d (pH 3), 39 d (pH 6), 26 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Insecticide reported by K-J. Schmidt & L. Hammann (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1969, 22, 314). Introduced by Bayer AG and by Sandoz AG (became Novartis Crop Protection AG); both companies have ceased manufacturing and marketing it. Patents BE 681443; DE 1545817 to Bayer Manufacturers Aimco; Cheminova; Ficom; Gujarat; Sharda; United Phosphorus
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. By penetrating the plant tissues through translaminar action, exhibits a systemic effect. Uses Control of many insect pests of the orders Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Hemiptera, etc. For example, used against caterpillars on fruit trees, cotton, vegetables, and peanuts; scales on fruit trees; and the pest complex on rice. Also controls aphids, bollworms, borers, leafhoppers, mealybugs, mites, planthoppers, thrips, etc. on beet, vines, ornamentals, potatoes, soya beans, tea, coffee, cocoa, and other crops. Dose rates 250-500 g/ha of EC and 0.75-1.0 kg/ha of GR. Phytotoxicity Slightly phytotoxic to certain fruit trees. Formulation types DP; EC; GR; UL; EW. Compatibility Not compatible with alkaline substances. Selected products: 'Danulux' (Dhanuka); 'Deviquin' (Devidayal); 'Hilquin' (Hindustan); 'Hubelux' (Sanonda); 'Iguasu' (Rocca); 'Max' (Crop Health); 'Quinaal' (Ramcides); 'Quinatox' (Aimco); 'Quinguard' (Gharda); 'Smash' (RPG); 'Starlux' (Shaw Wallace); mixtures: 'Chintop' (+ beta-cypermethrin) (Agro-Chemie); 'Quick' (+ cypermethrin) (Nagarjuna Agrichem)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Bayrusil' (Bayer CropScience); 'Ekaquin' (BEC); 'Flash' (Indofil); 'Kinalux' (United Phosphorus); 'Krush' (Biostadt); 'Quinalon' (Papaeconomou); 'Shakthi' (Parry); 'Unifos' (Tecomag) Discontinued products: 'Ekalux' * (Novartis); 'Savall' * (Farm Protection, Novartis); 'Set' * (Cequisa) mixtures: 'Knave' * (+ disulfoton) (Novartis); 'Tombel' * (+ thiometon) (Sandoz)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc or by tlc and subsequent u.v. spectrometric determination of the eluted compound. Residues determined by glc (M. Wisson et al., Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1980, 6,147).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male rats 71 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for male rats 1750 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.45 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) (based on cholinesterase inhibition) for rats 3 mg/kg diet. Other No teratogenic effects (rats and rabbits); no mutagenic potential. Cholinesterase inhibitor in rats, mice, and dogs. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification T; R25| Xn; R21
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute LD50 (14 d) for Japanese quail 4.3, mallard ducks 37 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (8 d) for quail 66, mallard ducks 220 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for carp 3.63, rainbow trout 0.005 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.66 mg/l. Bees Very toxic to bees. LD50 (oral) 0.07 mg/bee; (topical) 0.17 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (7 d) 188 mg/kg soil; (14 d) 118.4 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 63 (WHO, 1986; a general review of organophosphorus insecticides). Animals In rats, following oral administration, rapidly absorbed and metabolised to 2-hydroxyquinoxaline (free and as its conjugates), which are excreted in the urine (c. 87%) and bile (c. 13%) within a short time. Plants In plants, one-third is absorbed by the leaf surface and penetrates into the plant, whilst two-thirds disappears by evaporation within 14 days. The principal metabolite is 2-hydroxyquinoxaline (free and as its conjugates). Soil/Environment In soil, rapidly degraded under aerobic conditions, DT50 c. 3 w. The hydrolysis product 2-hydroxyquinoxaline does not accumulate in the soil, but is further broken down to polar metabolites and CO2. Freundlich K 25-320 mg/kg (o.m. 1.1-35.5%); DT50 21 d (o.m. 2.6%, pH 6.8, 18-22 ºC).
|