|
请下载《资料收集库-农药电子书》获得更多农药资料。想获得更多更系统的农药资料?想创建自己的农资电子书?请访问 http://www.9ele.com/pesticide.html |
||||||||||||
|
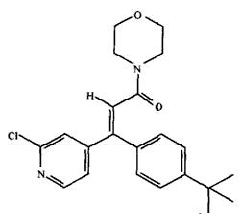
丁吡吗啉 化学名:(E)-3-(2-氯吡啶-4-基)-3-(4-叔丁基苯基)-丙烯酰吗啉
理化性质:丁吡吗啉纯品为白色粉末,密度为1.249×103 kg/m3(20℃);pH7.5(溶液浓度为50 g/L)、pH7.3(溶液浓度为10 g/L);熔点:128-130℃,沸点:≥420℃,溶解度(20℃,g/L):苯55.95、甲苯20.40、二甲苯8.20、丙酮16.55、二氯甲烷315.45、三氯甲烷257.95、乙酸乙酯17.90、甲醇1.60、乙醇5.35。稳定性:水中易光解,土壤表面为中等光解,难水解,在土壤中较易降解。 【生产厂家】江苏耕耘化学有限公司
环境生物安全评价: 相关简介: 丁吡吗啉(pyrimorph)是一种结构新颖的杀菌剂,室内生物测定结果表明,其对致病疫霉Phytophthora infestans的菌丝生长、孢子囊产生、休止孢萌发具有较强的抑制作用,其EC50值分别为0.066、0.059和0.550 μg/mL,但对游动孢子释放的抑制作用较弱,其EC50值为 9.78 μg/mL。显微镜下观察结果表明,经丁吡吗啉处理后的菌丝分枝相对较少,分枝间距拉长,但对 菌丝直径无影响;从致病疫霉对番茄叶片的侵染过程来看,丁吡吗啉浓度为100 μg/mL时,处理24 h后在叶片表面只能看到少量休止孢萌发,96 h后未产生孢子囊。丁吡吗啉在1 μg/mL和10 μg/mL 时对菌丝体细胞膜的电导率无影响,但当浓度为50 μg/mL时其电导率值明显上升;初步测定结果表明,在100 μg/mL浓度下,其对致病疫霉菌丝体的蛋白质合成有一定的抑制作用,但对其菌丝体内的DNA合成没有明显的抑制作用。 |
||||||||||||
Refer to <docbook-pesticides> for more data. Want more and better data of pesticides? Create your own ebook? Please visit: http://www.9ele.com/pesticide_en.html |
||||||||||||
|
Pyrimorph Chemical Name: (E)-3-[(2-chloropyridine-4-y1)-3-(4-tert-butylpheny1)acryloyl]morpholin The antifungal activity of the novel fungicide pyrimorph, , against Phytophthora capsici was investigated in vitro. Pyrimorph inhibited different stages in the life cycle of P. capsici including mycelial growth, sporangium production, zoospore release, and cystospore germination with EC(50) values of 1.84, 0.17, 4.92, and 0.09 microg mL(-1), respectively. The effect of pyrimorph on mycelial growth was reduced by the addition of different concentrations of ATP, which suggested that the action mechanism of pyrimorph was connected with impairment of the energy generation system. Meanwhile, pyrimorph exhibited certain inhibition on metabolic approaches of Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas (EMP), tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), and hexosemonophosphate (HMP) by measuring the oxygen consumption of pyrimorph combining with three representative inhibitors to the metabolic approaches. The results indicated that pyrimorph could inhibit the approach of HMP significantly. Morphological and ultrastructural studies showed that pyrimorph caused excessive septation and swelling of hyphae, distortion and disruption of most vacuoles, thickening and development a multilayer cell wall, and accumulation of dense bodies. These results suggested pyrimorph exhibited multiple modes of action including impairment of the energy generation system and effect on cell wall biosynthesis directly or indirectly. Pyrimorph is a novel fungicide developed by China Agricultural University and Institute of Plant Protection.Bioassay of pyrimorph to Phytophthora infestans was conducted.The results showed that the toxicity of pyrimorph was high in controlling P.infestans.It could intensively inhibit the mycelium growth,sporangium production and cystospore germination of P.infestans and the EC50 value was 0.066, 0.059 and 0.550 μg/mL, respectively.It was insufficient in inhibiting the release of zoospores from sporangia and the EC50 value was 9.78 μg/mL.Microscopic observation of pyrimorph treatment showed that the mycelium branch was fewer and the space was longer than that of CK.The difference of hypha diameter was not distinct between pyrimorph treatment and CK.When P.infestans invaded inside tomato leaves,it showed that only a few cystospores germinated 24 hours after inoculation and there was no sporangium 96 hours after inoculation of pyrimorph treatment at 100 μg/mL.Pyrimorph was found to influence on the permeability of the cell membrane of P.infestans at 50 μg/mL,and the difference was not distinct at 1 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL.It showed that pyrimorph had some effect on the protein biosynthesis of P.infestans at 100μg/mL,but had little effect on the DNA biosynthesis. A modified QuEChERS method for analysis of pyrimorph residue in tomatoes, cucumbers and soil was developed and validated. Residue dynamics and final residues in greenhouse vegetables and soil were studied. At fortification levels of 0.05, 0.1 and 1 mg kg(-1) in tomatoes, cucumbers and soil, the method got recoveries ranged from 86.1% to 99.3% with relative standard deviations of 1.0%-7.7%, in agreement with directives for method validation in residue analysis. The limit of determination in tomatoes, cucumbers and soil was 0.05 mg kg(-1). The proposed method was successfully employed for the determination of pyrimorph residue levels and dissipation rates in vegetables and soil. At six experimental sites, pyrimorph residues in tomatoes and cucumbers showed relatively fast dissipation rates, with half-lives of 5.8-7.7 days and 5.7-7.1 days respectively. Half-lives of pyrimorph in soil were 8.5-11.0 days. The final residues of pyrimorph in tomatoes ranged from 0.19 to 3.66 mg kg(-1), 0.18 to 4.35 mg kg(-1) in cucumbers and 0.22 to 16.5 mg kg(-1) in soil with pre-harvest interval of 3-7 days. 5 mg kg(-1) was proposed as the MRL of pyrimorph in tomatoes and cucumbers. |