|
pyrimethanil
Fungicide
FRAC 9, D1; anilinopyrimidine
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pyrimethanil (BSI, draft ISO)
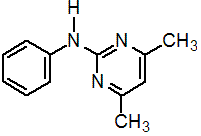
IUPAC name N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-yl)aniline
Chemical Abstracts name 4,6-dimethyl-N-phenyl-2-pyrimidinamine
CAS RN [53112-28-0] Development codes SN 100309 (Schering); ZK 100309
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 199.3 M.f. C12H13N3 Form Colourless crystals. M.p. 96.3 ºC V.p. 2.2 mPa (25 ºC) (OECD 104) KOW logP = 2.84 (pH 6.1, 25 ºC) Henry 3.6 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.15 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.121 g/l (pH 6.1, 25 ºC). In acetone 389, ethyl acetate 617, methanol 176, dichloromethane 1000, n-hexane 23.7, toluene 412 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable in water within the relevant pH range. Stable for 14 d at 54 ºC. pKa 3.52, weak base (20 °C) (OECD 112)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by G. L. Neumann et al. (Proc. Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1992, 1, 395). Introduced by Schering (now Bayer CropScience). Some rights, primarily in Europe, acquired by BASF AG in 2003.
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Proposed inhibitor of methionine biosynthesis, leading to inhibition of the secretion of enzymes necessary for infection. Mode of action Protectant (in Botrytis) and both protective and curative action (in Venturia). Uses Control of grey mould (Botrytis cinerea) on vines, fruit, vegetables and ornamentals. Control of leaf scab (Venturia inaequalis or V. pirina) on pome fruit. Phytotoxicity May be phytotoxic in closed systems at ³80% r.h. on certain species. Formulation types SC. Selected products: 'Mythos' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Scala' (Bayer CropScience, BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Clarinet' (+ fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Vision' (+ fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Walabi' (+ chlorothalonil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF)
ANALYSIS
Product and residue analysis by hplc. Details available from Bayer CropScience and BASF AG.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 4150-5971, mice 4665-5359 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >5000 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits), and not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >>1.98 mg/l. NOEL (2 y) for rats 20 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.17-0.2 mg/kg. Other Negative in mutagenicity tests, and non-teratogenic in rats and rabbits. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV ('Scala' and 'Mythos')
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >2000 mg/kg. LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >5200 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for mirror carp 35.4, rainbow trout 10.6 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 2.9 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (96 h) 1.2 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral and contact) >100 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 625 mg/kg dry soil. Other beneficial spp. Classified as harmless to a range of beneficials.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly absorbed, extensively metabolised and rapidly excreted in all species examined. No evidence of accumulation, even on repeated dosing. Metabolism proceeds by oxidation to phenolic derivatives which are excreted as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. Plants Little metabolism occurs in fruit; residues at maturity consist essentially of unchanged parent compound only. For this reason, a crop residue monitoring method has been developed for the direct determination of pyrimethanil itself. Soil/Environment DT50 in laboratory studies 27-82 d; field studies indicate rapid degradation, DT50 7-54 d. Koc 265-751. Low potential for leaching to groundwater; field studies show minimal movement of pyrimethanil into deeper soil layers. Pyrimethanil disappears rapidly from surface water and moderately adsorbs to the sediment, from which it is further degraded.
|