|
pyridalyl
Insecticide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pyridalyl (BSI, pa ISO)
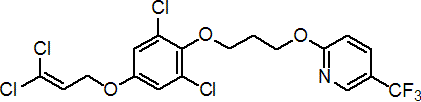
IUPAC name 2,6-dichloro-4-(3,3-dichloroallyloxy)phenyl 3-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridyloxy]propyl ether
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[3-[2,6-dichloro-4-[(3,3-dichloro-2-propenyl)oxy]phenoxy]propoxy]-5-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine
CAS RN [179101-81-6] Development codes S-1812 (Sumitomo)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 491.1 M.f. C18H14Cl4F3NO3 Form Liquid. V.p. 6.24 ´ 10-5 mPa (20 °C) Solubility In water 0.15 ppb (20 °C).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Reported by S. Saito et al., Proc. BCPC Conf. - Pests Dis., 2002, 1, 33. Manufacturers Sumitomo
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Biochemical mode of action has not been identified, but appears to be different from other insecticides. Mode of action Insects lose their vigour and die within 2-3 h. Uses Under development by Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd. Active against larvae of various lepidopterous insects and motile stages of thysanopterous insects, on cotton and vegetables, at 83-300 g/ha. Formulation types EC; WP; SC.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute dermal LD50 for male and female rats >5000 mg/kg. Slight eye irritant; not a skin irritant (rabbits). A skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 for rats >2.01 mg/l.
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail 1133, mallard ducks >5620 mg/l. Fish Acute LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.50 mg/l. Bees No effect on honeybees at 100 mg/l. Other beneficial spp. Low toxicity to various beneficial arthropods; species unaffected at 100 mg/l included Trichogramma japonicum, Chrysoperla carnea, Harmonia axyridis, Orius sauteri, Phytoseiulus persimilis.
|