|
propargite
Acaricide
IRAC 14
NOMENCLATURE
Common name propargite (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI, ESA); BPPS (JMAF)
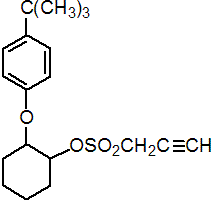
IUPAC name 2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy)cyclohexyl prop-2-ynyl sulfite
Chemical Abstracts name 2-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenoxy]cyclohexyl 2-propynyl sulfite
CAS RN [2312-35-8] EEC no. 219-006-1 Development codes DO 14 (Uniroyal) Official codes ENT 27 226
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is ³87% w/wpure. Mol. wt. 350.5 M.f. C19H26O4S Form Brownish-yellow, oily viscous liquid (tech.). B.p. decomp. 210 °C (atmospheric pressure) without boiling V.p. 0.04 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 5.70 Henry 6.4 ´ 10-2 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.12 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.215 mg/l (25 ºC). Fully miscible with hexane, toluene, dichloromethane, methanol and acetone. Stability Hydrolysis DT50 66.3 (25 ºC), 9.0 (40 ºC) (both days, pH 7); DT50 1.1 (25 ºC) 0.2 (40 ºC) (both days, pH 9); stable at pH 4. Photolysis DT50 c. 6 d (pH 5). Half-life in atmosphere 2.155 h (Atkinson calculation). pKa >12 F.p. 71.4 ºC (Pensky-Martens closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Acaricide introduced by Uniroyal Inc. (now Crompton Corp.) in 1969. Patents US 3272854; US 3463859 Manufacturers Crompton; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Jin Hung; Sundat; Zhejiang
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits mitochondrial ATPase, which results in interruption of normal mite metabolism and respiration. Mode of action Non-systemic acaricide with predominantly contact action; some additional action by inhalation. Uses Control of phytophagous mites (particularly motile stages) on a variety of crops, including vines, fruit trees (e.g. top fruit, stone fruit, citrus fruit), hops, nuts, tomatoes, vegetables, ornamentals, cotton, maize, peanuts, and sorghum. Used at rates from 0.75-1.8 kg/ha on row crops and foliar sprays of 0.85-3.0 kg/ha on perennial fruit and nut crops. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to pears, strawberries, roses, and cotton under 10 inches in height. Citrus fruit and beans may also show some injury. Formulation types EC; EW; WP. Compatibility Incompatible with alkaline materials, oil sprays, and pesticides containing a large amount of petroleum solvents. Selected products: 'Omite' (Crompton); 'Dictator' (Vapco)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Comite' (Crompton); 'Ornamite' (Crompton); 'Acarit' (Milenia); 'Chemit' (Chemia); 'Mantelin' (Zhejiang) mixtures: 'Akaridecis' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Dictator-Plus' (+ tetradifon) (Vapco); 'Miejingthrin' (+ fenvalerate) (Zhong-Xi); 'Superman' (+ fenpyroximate) (China) (Nihon Nohyaku) Discontinued products: 'Retador' * (Productos OSA)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by i.r. spectroscopy; details available from Crompton. Residues determined by glc (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I, 6; Anal. Methods Residues Pestic., 1988, Part I, M1; A. Ambrus et al., J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., 1981, 64, 733; G. M. Stone, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 355).
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 86, 88 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2800 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rabbits 4000 mg/kg. Severe eye and skin irritant to rabbits. Not a skin sensitiser to guinea pigs. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats 0.05 mg/l. NOEL NOEL (1 y) for dogs 4 mg/kg b.w. daily; LOAEL (2 y) for SD rats 3 mg/kg b.w. daily, based on occurrence of jejunal tumours. Tumours not seen in Wistar rats or mice. NOAEL for SD rats (28 d) is 2 mg/kg b.w., indicating that cell proliferation is the cause of carcinogenicity and that there is a threshold dose; therefore, carcinogenicity is species and strain specific. ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1999]. Other Not genotoxic. Acute i.p. LC50 for male rats 260, female rats 172 mg/kg. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III (tech.); EPA (formulation) III EC classification Xn; R22| Xi; R36| N; R50, R53: (draft 29th ATP proposes R40| T; R23| Xi; R38, R41| N; R50, R53, concentration dependent)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks >4640 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks >4640, bobwhite quail 3401 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 0.043, bluegill sunfish 0.081 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.014 mg/l. Algae LC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >1.08 mg/l (no effects at highest test concentration). Other aquatic spp. LC50 (96 h) for grass shrimp 0.101, Quahog clam embryo larvae 0.110 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h, contact) 47.92 µg/bee; (oral) >100 µg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for Eisenia foetida 378 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. No adverse effects on Amblyseius andersoni, Orius laevigatus or Trichogramma cacoeciae, following exposure to field aged-residues after 1 week, 1 day and 1 day, respectively (hence no long-term impact expected on natural populations). No adverse effects on Chrysoperla carnea, following exposure to fresh residues on leaf material.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In mammals, propargite is hydrolysed at the sulfite ester linkage to 1-[4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenoxy]-2-cyclohexanol and subsequent hydroxylation of the tert-butyl side-chain. Additional metabolites are formed by further oxidation or sulfation of the tert-butyl group and oxidation of the cyclohexyl moiety. Plants Although propargite is considered a non-systemic pesticide, a small portion of the applied dose penetrates the outside layer of the foliage and undergoes the same metabolism as is observed in animals. In most fruits (apples, citrus), propargite stays mainly on the surface and, to a lesser extent, in the peel; only trace residues are detected in the pulp. Soil/Environment DT50 40-67 d (aerobic soil, pH 6.0-6.9, o.c. 1.0-2.55%, 22-25 ºC). Log Koc 3.6-3.9; no leaching in aged column study or in field dissipation studies. DT50 in water-sediment studies 1.7-2.5 d (water phase), 18.3-22.5 d (whole system). Half-life in atmosphere 2.155 h (Atkinson calculation).
|