|
propaquizafop
Herbicide
HRAC A WSSA 1; aryloxyphenoxypropionate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name propaquizafop (BSI, draft E-ISO, (m) draft F-ISO)
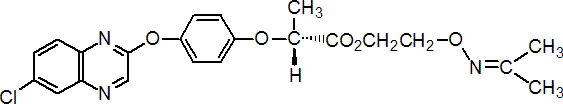
IUPAC name 2-isopropylideneamino-oxyethyl (R)-2-[4-(6-chloroquinoxalin-2-yloxy)phenoxy]propionate
Chemical Abstracts name (R)-2-[[(1-methylethylidene)amino]oxy]ethyl 2-[4-[(6-chloro-2-quinoxalinyl)oxy]phenoxy]propanoate
CAS RN [111479-05-1] Development codes Ro 17-3664/000 (Dr Maag); CGA 233 380 (Ciba)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition (R)- isomer. Mol. wt. 443.9 M.f. C22H22ClN3O5 Form Off-white powder; tech. is an orange to brown mixture of fine powder and granular material. M.p. 66.3 °C B.p. decomp. 260 °C V.p. 4.4 ´ 10-7 mPa (25 ºC, OECD 104; EEC A.4) KOW logP = 4.78 (25 ºC) Henry 9.2 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.30 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 0.63 g/m3 (20 ºC, pH 6.8).In acetone, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate and toluene >500, n-hexane 11, methanol 76, n-octanol 30 (all in g/l, 25 ºC). Stability Stable ³2 y in closed container at room temperature. Hydrolytic DT50 10.5 d (pH 5), 32.0 d (pH 7), 12.9 h (pH 9) (all at 25 °C). Stable to u.v. light. pKa -2.3 (est.)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by P. F. Bocion et al. (Proc. 1987 Br. Crop Prot. Conf. - Weeds, 1, 55). Introduced by Dr R. Maag Ltd. (became Novartis Crop Protection AG). Sold to Makhteshim-Agan Industries in 2000. Patents EP 52798, US 4545807 Manufacturers Makhteshim-Agan
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Fatty acid synthesis inhibitor, by inhibition of acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACCase). Mode of action Systemic post-emergence herbicide. Absorbed by foliage and roots and translocated throughout the plant. Treated grasses cease growth within 3-4 days, show chlorosis of younger plant tissues, followed by a progressive collapse of the entire plant 10-20 days later. Uses Control of a wide range of annual and perennial grasses (including Sorghum halepense, Agropyron repens and Cynodon dactylon) in soya beans, cotton, sugar beet, potatoes, peanuts, peas, oilseed rape and vegetables, at 60-200 g/ha. Phytotoxicity Occasionally soya beans and peas may show some chlorotic and necrotic spots on treated leaves at higher dosage rates; this does not affect further vegetative growth or yield. Formulation types EC. Selected products: 'Agil' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Claxon' (Makhteshim-Agan)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Correct' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Falcon' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'PQF 100' (Landgold); 'Satchmo' (GreenCrop); 'Shogun' (Makhteshim-Agan)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc. Residues determined by hplc or by gc with ECD.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >5000, mice 3009 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin and eyes (rabbits). No allergic sensitisation in open epicutaneous test (guinea pigs); sensitising in maximisation test. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.5 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats and mice 1.5 mg/kg b.w. daily; (1 y) for dogs 20 mg/kg b.w. daily. ADI 0.015 mg/kg b.w. Other Not mutagenic, not teratogenic, no reproduction effects. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U EC classification (R43)
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds LD50 for bobwhite quail >2000, mallard ducks >2198 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks and bobwhite quail >6593 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.2, carp 0.19, bluegill sunfish 0.34 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) >2.1 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >2.1 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. NOEC (7 d) for Lemna gibba 1.5 mg/l. Bees LD50 (48 h) (oral) >20 mg/bee; (contact) >200 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >1000 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. No risk to beneficial arthropods (e.g. Typhlodromus pyri and Aphidius rhopalosiphi) or to soil micro-organisms, at normal application rates.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals After oral administration, propaquizafop was rapidly absorbed and excreted mainly in faeces and urine. Elimination half lives 15.6-27.2 hours. Extensively metabolised in rats; the major metabolite in faeces and urine was the propionic acid of the parent compound, which was further oxidised and degraded by cleavage. Propaquizafop and its metabolites do not accumulate in the body tissues. Plants Plants (soya bean, sugar beet and cotton) readily take up propaquizafop through roots and leaves. The parent compound is degraded by hydrolysis to the major metabolite, the propionic acid. Soil/Environment Laboratory and field studies in aerobic soils indicate that propaquizafop was rapidly degraded by soil microorganisms; DT50 (lab, 20 °C) in various soil types <3 days; DT50 for the major metabolite 7-39 days. DT50 (field) for parent and metabolites 15-26 days after spring application. Laboratory and field studies indicated that propaquizafop and its metabolites are unlikely to accumulate in the soil or leach to ground water. In aquatic systems (water/sediment) DT50 <1 day; DT50 for the major metabolite 27-39 days.
|