|
propanil
Herbicide
HRAC C2 WSSA 7; anilide
NOMENCLATURE
Common name propanil (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, WSSA); DCPA (JMAF); no name (Germany)
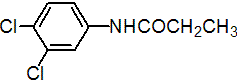
IUPAC name 3',4'-dichloropropionanilide
Chemical Abstracts name N-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)propanamide
Other names 3,4-DCPA CAS RN [709-98-8] EEC no. 211-914-6 Development codes FW-734 (Rohm & Haas); Bayer 30 130; S 10145 (Bayer)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. is 97% nominal. Mol. wt. 218.1 M.f. C9H9Cl2NO Form Colourless, odourless crystals; (tech. is a medium to dark grey, crystalline solid). M.p. 91.5 °C B.p. 351 °C V.p. 0.02 mPa (20 ºC); 0.05 mPa (25 ºC) KOW logP = 3.3 (20 °C) Henry 1.7 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 S.g./density 1.41 g/cm3 (22 ºC) Solubility In water 130 mg/l (20 ºC). In isopropanol, dichloromethane >200, toluene 50-100, hexane <1 (all in g/l, 20 ºC). In benzene 7 ´ 104, acetone 1.7 ´ 106, ethanol 1.1 ´ 106 (all in ppm, 25 ºC). Stability Hydrolysed in strongly acidic and alkaline media to 3,4-dichloroaniline and propionic acid; stable at normal pH range: DT50 (22 ºC) >>1 y (pH 4, 7, 9). Rapidly degraded in water by sunlight; photolysis DT50 12-13 h.
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide (Proc. South. Weed Control Conf., 1960, p. 20). Introduced by Rohm & Haas Co. (now Dow AgroSciences) in 1961, later by Bayer AG (1965) and by Monsanto Chemical Co. Patents DE 1039779; GB 903766 to Bayer Manufacturers Cedar; Chemia; Dow AgroSciences; Griffin; Hegang Heyou; Hesenta; Hodogaya; Inquiport; Milenia; Nufarm Ltd; Proficol; Tifa; Westrade
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Photosynthetic electron transport inhibitor at the photosystem II receptor site. Mode of action Selective contact herbicide with a short duration of activity. Uses Contact herbicide used post-emergence in rice, at 2.5-5.0 kg/ha, to control broad-leaved and grass weeds, including Amaranthus retroflexus,Digitaria spp., Echinochloa spp., Panicum spp., and Setaria spp. Also used, in mixture with MCPA, in wheat. A mixture with carbaryl is used in citrus crops grown in sod culture. Phytotoxicity Phytotoxic to many broad-leaved crops. Normally phytotoxic to crops which have been treated with organophosphate or carbamate insecticides. Formulation types EC; SC; UL. Compatibility Incompatible with a number of pesticides, particularly carbamates and organophosphates. Incompatible with liquid fertilisers. Selected products: 'Stam' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Brioso' (Proficol); 'Khiumo' (Griffin); 'Kome' (Griffin); 'Nox' (Crystal); 'Propasint' (Westrade); 'RiceNil' (Gilmore); 'Riselect' (Isagro); 'Surcopur' (Bayer CropScience); mixtures: 'Advance' (+ butachlor) (Monsanto); 'Lecspro' (+ fentrazamide) (Bayer CropScience)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Diris' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Garil' (Dow AgroSciences); 'Agropur' (AgroSan); 'Herbax' (Westrade); 'Propanac' (Crystal); 'Propanex' (Crystal); 'Propanilo' (Crystal); 'Propax' (Crystal); 'Sorpur' (Bayer CropScience); 'Supernox' (Crystal); 'Wham' (Riceco) mixtures: 'Stamphos' (+ piperophos) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Stampir' (+ triclopyr) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Anilonox' (+ anilofos) (Crystal); 'Arrosolo' (+ molinate) (Syngenta); 'Arroznox' (+ molinate) (Crystal); 'Bandito' (+ butachlor) (Crystal); 'Challenge' (+ butachlor) (Monsanto); 'Duet EDF' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Riceco); 'Herbit-Plus' (+ MCPA-thioethyl) (Hokko); 'Londanil' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Crystal); 'Nox-D' (+ 2,4-D) (Crystal); 'Nox-MCP' (+ MCPA) (Crystal); 'Pendanil' (+ pendimethalin) (Crystal); 'Propacet' (+ quinclorac) (Crystal); 'Pro-Pack 80EDF' (+ bensulfuron-methyl) (Agriliance); 'Propanilate' (+ molinate) (Proficol); 'Pyrasulfonil' (+ pyrazosulfuron-ethyl) (Crystal); 'RiceMax' (+ clomazone) (FMC, Riceco); 'Rizonil' (+ tetradifon) (Papaeconomou); 'Sable' (+ butachlor) (Proficol); 'Satunil' (+ thiobencarb) (Brazil, Thailand) (Iharabras, TJC); 'Sulfonil' (+ metsulfuron-methyl) (Crystal); 'Thionil' (+ thiobencarb) (Crystal); 'Vitanyl' (+ butachlor) (Vipesco) Discontinued products: 'Stampede' * (Dow AgroSciences); 'Strel' * (Dow AgroSciences); 'Rogue' * (Monsanto); 'Synpran' * (Budapest Chemical) mixtures: 'Stampede Cm' * (+ MCPA-2-ethylhexyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Stampro' * (+ sulfometuron-methyl) (Dow AgroSciences); 'Sierra' * (+ MCPA-thioethyl) (Proficol); 'Touche' * (+ molinate) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc (I. L. Adler & W. J. Zogorski, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1984, 13, 281). Residues determined by glc (idem, ibid.; ibid., 1972, 6, 692) or colorimetry of the 3,4-dichloroaniline formed on hydrolysis (C. F. Gordon et al., Anal. Methods Pestic., Plant Growth Regul. Food Addit., 1964, 4, 235). In water, by lc with u.v. detection (AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 992.14). Methods for the determination of residues also available from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats >2500, mice c. 1800 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for rats >5000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin and eyes (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser (guinea pigs). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >1.25 mg/l air (dust). NOEL (2 y) for rats 400, dogs 600 mg/kg diet. ADI (US) 0.005 mg/kg b.w. Water GV 20 mg/l (TDI 5 mg/kg b.w.). Other Not mutagenic, not carcinogenic. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III; EPA (formulation) III (EC) EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for mallard ducks 375, bobwhite quail 196 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for mallard ducks 5627, bobwhite quail 2861 ppm Fish LC50 (48 h) for carp 8-11 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 4.8 mg/l.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals The major metabolic pathway for propanil in microsomal incubations was acylamidase hydrolysis to 3,4-dichloroaniline (D. C. McMillan et al., Tox. Appl. Toxicol., 1990, 103, 90). Plants In rice, propanil is hydrolysed by an aryl acylamidase to 3,4-dichloroaniline and propionic acid as metabolic intermediates. Soil/Environment In soil, rapid microbial degradation to the aniline derivative occurs. Duration of activity in warm, moist conditions is only a few days. Degradation products are propionate which is rapidly metabolised to CO2, and 3,4-dichloroaniline which is bound (80% in 27 h) to the soil. Koc 239-800.
|