|
propamocarb hydrochloride
Fungicide
FRAC 28, F4; carbamate fungicide
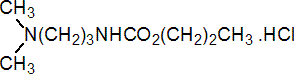
NOMENCLATURE
propamocarb hydrochloride
IUPAC name propyl 3-(dimethylamino)propylcarbamate hydrochloride
Chemical Abstracts name propyl [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbamate hydrochloride
CAS RN [25606-41-1] EEC no. 247-125-9 Development codes AE B066752 (AgrEvo); EXP 10382A; HOE 102791 (Hoechst)
propamocarb
Common name propamocarb (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI); propamocarbe ((m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name propyl 3-(dimethylamino)propylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name propyl [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbamate
CAS RN [24579-73-5] Development codes SN 39744 (Schering)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
propamocarb hydrochloride
Composition The aqueous concentrate contains 780 g/l propamocarb hydrochloride. Mol. wt. 224.7 M.f. C9H21ClN2O2 Form Colourless, faintly aromatic, hygroscopic crystals. M.p. 64.2 °C V.p. 3.85 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 °C) KOW logP = -1.21 (pH 7) Henry <1.7 ´ 10-8 Pa m3 mol-1 (20 °C, calc.) S.g./density 1.085 g/ml (20 °C, aqueous concentrate) Solubility In water >500 g/l (20 °C). In methanol 656, dichloromethane >626, acetone 560, ethyl acetate 4.34, toluene 0.14, hexane <0.01 (all in g/l, 20 °C). Stability Stable to hydrolysis, to temperatures up to 400 ºC, and to photolysis. pKa 9.3 (20 °C) Other properties Surface tension 40.9 mN m-1 (40 °C).
propamocarb
Mol. wt. 188.3 M.f. C9H20N2O2 V.p. 730 mPa (25 °C) KOW logP = 0.84 (20 °C) Henry 1.5 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (25 °C) Solubility In water >900 g/l (pH 7.0, 20 °C). In hexane >883, methanol >933, dichloromethane >937, toluene >852, acetone >921, ethyl acetate >856 (all in g/l, 20 °C). pKa 9.5, strong base (K. Chamberlain et al., Pestic. Sci., 47,265 (1996))
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by E. A. Pieroh et al. (Meded. Fac. Landbouwwet. Rijksuniv. Gent, 1978, 43, 933). Discovered and developed by Schering AG; now owned and distributed by Bayer CropScience. Patents DE 1567169; DE 1643040 Manufacturers Agriphar; Bayer CropScience; Synthesia
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Reduces mycelial growth and development of sporangia and (zoo)spores; influences the biochemical synthesis of membranes. Mode of action Systemic fungicide with protective action. Absorbed by the roots and leaves, and transported acropetally.
propamocarb hydrochloride
Uses Specific control of phycomycetous diseases (Pythium, Phytophthora, Aphanomyces, Bremia, Peronospora, and Pseudoperonospora spp.). In particular, control of Pythium and Phytophthora spp. in vegetables, ornamentals, glasshouse tomatoes, glasshouse cucumbers, tulips, tobacco, and in forestry seedbeds; Pythium blight on turf; downy mildew on lettuce, cucurbits and cabbages; Phytophthora infestans in potatoes and tomatoes; Phytophthora cactorum on strawberries; etc. Applied to the soil, or used as a dip treatment (for bulbs and tubers) or seed treatment, and as a foliar spray in late-season applications. Formulation types SC; SL. Selected products: 'Banol' (Bayer CropScience); 'Previcur N' (Bayer CropScience); 'Proplant' (Agriphar); 'Salvador' (Rocca)
propamocarb
Selected products: 'Promo' (Agrimix)
OTHER PRODUCTS
propamocarb hydrochloride
Mixtures: 'Tattoo C' (+ chlorothalonil) (Bayer CropScience); 'Tattoo' (+ mancozeb) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Prevex' * (AgrEvo); 'Previcur' * (Aventis) mixtures: 'Merlin' * (+ chlorothalonil) (Aventis)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by lc with u.v. detection (CIPAC Handbook, 1992, E, 184-6). Residues determined by glc with FID (I. A. Gentile & E. Passera, J. Chromatogr., 1982, 236,254). Methods for the determination of residues are available upon request from Bayer CropScience.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 47, 49 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
propamocarb hydrochloride
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 2000-2900, mice 2650-2800, dogs c. 1450 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and mice >3000 mg/kg. Not a skin or eye irritant (rabbits). Not a skin sensitiser. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >5.54 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for rats 26-32 mg/kg b.w. ADI (JMPR) 0.1 mg/kg b.w. (for base) [1986].; 0.4 mg/kg b.w. (company proposed) Other Negative in Ames and micronucleus tests. Not teratogenic in rats and rabbits, no reproductive, developmental or carcinogenic effects. EC classification (Xi; R43)
propamocarb
Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >3.96 mg/l air. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
propamocarb hydrochloride
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard duck >1842 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard duck >4789 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for bluegill sunfish >92, for rainbow trout >99 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 106 mg/l. Algae ErC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >85 mg/l; EbC50 >120 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica) 43.9 mg/l; LC50 (96 h) for mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 105 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >84 µg/bee; (contact) >100 µg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) >660 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals Rapidly absorbed and almost totally excreted (>90% in 24 h), mainly via urine. Mineralisation occurs via oxidation and hydrolytic decomposition. Plants Mainly unchanged in plants. Soil/Environment Rapidly degraded in soil by microbial processes, following a brief lag phase, DT50 <30 d, DT90 <70 d. Propamocarb hydrochloride is retained in the upper soil layer (4-20 cm) and little is found in leachate. Stable in aqueous medium, but rapidly degraded by aquatic micro-organisms (up to 97% in 35 d). It is adsorbed onto sediment, but with limited desorption.
|