|
prochloraz
Fungicide
FRAC 3, G1; DMI: imidazole
NOMENCLATURE
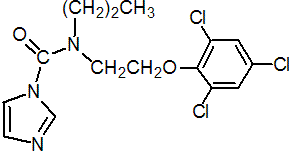
Common name prochloraz (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO, ANSI)
IUPAC name N-propyl-N-[2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl]imidazole-1-carboxamide; 1-{N-propyl-N-[2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl]}carbamoylimidazole
Chemical Abstracts name N-propyl-N-[2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl]-1H-imidazole-1-carboxamide
CAS RN [67747-09-5] EEC no. 266-994-5 Development codes BTS 40 542 (Boots)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. grade is c. 97% pure. Mol. wt. 376.7 M.f. C15H16Cl3N3O2 Form Odourless, colourless crystals; (tech. is a mildly aromatic, golden brown liquid, that tends to solidify on cooling). M.p. 46.5-49.3 ºC (>99% pure) B.p. 208-210 ºC/0.2 mmHg (decomp.) V.p. 1.5 ´ 10-1 mPa (25 ºC); 9.0 ´ 10-2 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.12 (unionised) Henry 1.64 ´ 10-3 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.42 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 34.4 mg/l (25 ºC). Readily soluble in a wide range of organic solvents, e.g. chloroform, diethyl ether, toluene, xylene 2.5, acetone 3.5, hexane c. 7.5 ´ 10-3 (all in kg/l, 25 ºC). Stability No degradation after 30 d (pH 5-7, 22 °C). Decomposes in concentrated acids and alkalis, in the presence of sunlight, and on prolonged heating at high temperatures (200 ºC). pKa 3.8, weak base F.p. 160 °C (closed cup)
COMMERCIALISATION
History Fungicide reported by R. J. Birchmore et al. (Proc. Br. Crop. Prot. Conf. - Pests Dis., 1977, 2, 593). Introduced by The Boots Co., Ltd (now Bayer CropScience). Some rights, primarily in Europe, acquired by BASF AG in 2003. Patents GB 1469772; US 3991071; US 4080462 Manufacturers Griffin; Sundat
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Steroid demethylation (ergosterol biosynthesis) inhibitor. Mode of action Fungicide with protective and eradicant action. Uses A protectant and eradicant fungicide effective against a wide range of diseases affecting field crops, fruit, turf, and vegetables. An EC is recommended for use in cereals (400-600 g a.i./ha) against Pseudocercosporella, Pyrenophora, Rhynchosporium, and Septoria spp., with useful activity against Erysiphe spp.; in oilseed rape (500 g/ha) against Alternaria, Botrytis, Pyrenopeziza and Sclerotinia spp. Useful activity is also shown against Ascochyta and Botrytis spp. in field legumes; and Cercospora and Erysiphe spp. in beet. Good activity against storage or transit diseases of citrus and tropical fruit when applied as a dip treatment (0.5-0.7 g/l). A WP is recommended in mushrooms against Verticillium fungicola and Mycogone perniciosa, and in rice against Pyricularia. A seed treatment (0.2-0.5 g/kg) will control several cereal diseases caused by Cochliobolus, Fusarium, Pyrenophora and Septoria spp., and, in flax, Alternaria. Formulation types EC; EW; FS; LS; WP. Compatibility Forms a complex with some metal ions, e.g. prochloraz-manganese used for WP formulations. Selected products: 'Eyetak 40' (Barclay); 'Master' (Vapco); 'Mirage' (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Sportak' (Bayer CropScience, BASF); mixtures: 'Galmano Plus' (+ cuprous chloride + fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Jockey' (+ fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Sportak Alpha' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience, BASF)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Abavit' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Ascurit' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Octave' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Omega' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Orbit' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Poraz' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Prelude' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Rival' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Sporgon' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Sprint' (BASF, Bayer CropScience); 'Atak' (Barclay); 'Fungi' (Stefes); 'Panache 40' (DAPT) mixtures: 'Agate' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, UK) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Allure' (+ chlorothalonil) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Balaika' (+ tebuconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Bonanza' (+ tetraconazole) (Sipcam Phyteurop); 'Bumper P' (+ propiconazole) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Diams' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, France) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Épopée' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, France) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Flamenco Plus' (+ fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Fongral' (+ bromuconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Jockey Plus' (+ cuprous chloride + fluquinconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Kinto' (+ triticonazole+ anthraquinone) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Mirage Extra' (+ fenbuconazole) (PBI, Makhteshim-Agan); 'Mirage F' (+ folpet) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Mirage Plus' (+ folpet) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Nébraska' (+ tebuconazole) (spray, France) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Nordika' (+ fenbuconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Novak' (+ carbendazim) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Profile' (+ cyproconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Sponsor' (+ fenpropidin) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Sportak Delta' (+ cyproconazole) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Sprint HF' (+ fenpropimorph) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Stanza' (+ fenpropimorph) (Bayer CropScience, BASF); 'Tiptor S' (+ cyproconazole) (Syngenta) Discontinued products: 'Sportak Sierra' * (AgrEvo); 'Alpha Mirage 40' * (Makhteshim-Agan) mixtures: 'Rizolex Nova' * (+ tolclofos-methyl) (AgrEvo); 'Hobby' * (+ carbendazim) (Ciba); 'Mirage Super' * (+ fenpropimorph) (Makhteshim-Agan); 'Sopraphal' * (+ diclobutrazol) (Syngenta)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by hplc and glc. Residue analysis by glc. Details available from Bayer CropScience and BASF AG.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 40, 41, 92, 94 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 1600-2400, mice 2400 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2100, rabbits >3000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin; slight eye irritation (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats >2.16 mg/l air. NOEL (2 y) for dogs 30 mg/kg diet (0.92 mg/kg daily). ADI (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1983, 2001]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) III EC classification Xn; R22| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for bobwhite quail 662, mallard ducks >1954 mg/kg. Dietary LC50 (5 d) for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5200 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 1.5, bluegill sunfish 2.2 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 4.3 mg/l. Algae EbC50 (72 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum 0.1 mg/l; ErC50 1.54 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (96 h) for Eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica)0.95, mysid shrimp (Mysidopsis bahia) 0.77 mg/l. Bees Low toxicity to bees. LD50 (topical) 50 mg/bee; (oral) 60 mg/bee. Worms LC50 for earthworms (Eisenia foetida) 207 mg/kg soil. Other beneficial spp. Low toxicity to a range of beneficial arthropods.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In all species examined, prochloraz is rapidly metabolised initially by cleavage of the imidazole ring and quantitatively eliminated from the body, following oral administration. Whilst absorption following dermal exposure is low, residues in plasma and tissues are again rapidly eliminated from the body. Plants The primary plant metabolite, N-formyl-N'-1-propyl-N-(2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl)urea, is formed from cleavage of the imidazole ring. This is degraded to N-propyl-N-(2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl)urea, which occurs in both free and conjugated forms. Other metabolites include 2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethanol, 2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)acetic acid, traces of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol and conjugates of the above. Little unchanged prochloraz is present. Soil/Environment Degrades in the soil to a range of mainly volatile metabolites (degradation is not pH-dependent). Prochloraz is well adsorbed onto soil particles, and is not readily leached; Kd 152 (sandy loam), 256 (silty clay loam). In a further study, mean Koc 1463. Possesses low toxicity to a wide range of soil microflora and microfauna, but has inhibitory effects on soil fungi. DT50 under field conditions is 5-37 d.
|