|
pirimicarb
Insecticide
IRAC 1A; carbamate
NOMENCLATURE
Common name pirimicarb (BSI, E-ISO, ANSI, JMAF); pirimicarbe ((m) F-ISO); pyrimicarbe (France)
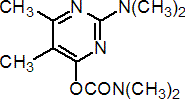
IUPAC name 2-dimethylamino-5,6-dimethylpyrimidin-4-yl dimethylcarbamate
Chemical Abstracts name 2-(dimethylamino)-5,6-dimethyl-4-pyrimidinyl dimethylcarbamate
CAS RN [23103-98-2] EEC no. 245-430-1 Development codes PP062 (ICI) Official codes ENT 27 766; OMS 1330
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Composition Tech. material is 95% pure. Mol. wt. 238.3 M.f. C11H18N4O2 Form White solid. M.p. 91.6 °C V.p. 4 ´ 10-1 mPa (20 °C, by interpolation) KOW logP = 1.7 (unionised) Henry 3.6 ´ 10-5 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.18 (25 °C); tech. 1.21 (25 ºC) Solubility In purified water 3.0 g/l (20 ºC). In acetone, methanol, xylene >200 g/l (20 ºC). Stability Stable under normal storage conditions for more than 2 years. Hydrolytically stable at pH 4-9 (25 °C). Aqueous solutions are unstable to u.v. light; DT50 <1 d (pH 5, 7 or 9). pKa 4.44 (20 °C), weak base
COMMERCIALISATION
History Aphicide reported by F. L. C. Baranyovits & R. Ghosh (Chem. Ind. (London), 1969, p. 1018). Introduced by ICI Plant Protection Division (now Syngenta AG) and first marketed in 1970. Patents GB 1181657 Manufacturers Jiangsu Eternal; Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Cholinesterase inhibitor. Mode of action Selective systemic insecticide with contact, stomach, and respiratory action. Absorbed by the roots, and translocated through the xylem. Penetrates the leaves, but is not translocated extensively. Uses A selective aphicide used in a wide range of crops, including cereals and oilseeds (at 125-250 g/ha), potatoes and other vegetables (at 125-375 g/ha), fruit (at 250-750 g/ha), ornamentals and other non-food uses (at 50-500 g/ha). Effective against organophosphorus-resistant Myzus persicae. Formulation types AE; DP; EC; FU; WG; WP. Selected products: 'Aphox' (Syngenta); 'Pirimor' (Syngenta); 'Honolulu' (Rocca); 'Pilly' (Sanonda); 'Pirimisect' (Barclay); 'Tomba' (Cequisa); mixtures: 'Okapi' (+ lambda-cyhalothrin) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
'Abol' (Syngenta); 'Glenroe' (GreenCrop); 'Phantom' (Bayer CropScience); 'Piriflor' (Azot) mixtures: 'Dovetail' (+ lambda-cyhalothrin) (Syngenta); 'Karate K' (+ lambda-cyhalothrin) (Syngenta); 'Adage' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Best' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Evidence' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience); 'Kabuto' (+ esfenvalerate) (Philagro); 'Patriot' (+ deltamethrin) (Bayer CropScience) Discontinued products: 'Pronto' * (Atlas Interlates)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc with FID (J. E. Bagness & W. G. Sharples, Analyst (London), 1974, 99, 225; AOAC Methods, 17th Ed., 982.08; CIPAC Handbook, 1998, H, 217). Identity also by glc, tlc, i.r. or nmr (CIPAC Handbook, 1994, F, 406). Residues determined by glc with FID or by colorimetry (Man. Pestic. Residue Anal., 1987, I; D. J. W. Bullock, Anal. Methods Pestic. Plant Growth Regul., 1973, 7, 399). Details available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews FAO/WHO 38, 39 (see part 2 of the Bibliography). Oral Acute oral LD50 for female rats 142, mice 107, dogs 100-200 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2000, rabbits >500 mg/kg. Non-irritating to skin; mild irritant to eyes (rabbits). Moderate skin sensitiser (guinea pigs, M&K test). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for female rats 0.86 mg/l. NOEL Chronic NOEL for dogs 3.5 mg/kg daily; for rats 75 mg/kg diet (3.7-4.7 mg/kg daily). Not carcinogenic; no adverse reproductive effects. ADI (JMPR) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [1982]. Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification T; R25| N; R50, R53
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Acute oral LD50 for poultry 25-50, mallard ducks 28.5, bobwhite quail 20.9 mg/kg. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 79, bluegill sunfish 55, fathead minnow >100 mg/l. Daphnia EC50 (48 h) 0.017 mg/l. Algae EC50 (96 h) 140 mg/l. Other aquatic spp. EC50 (48 h) for Lymnaea stagnalis 19, Gammarus pulex 48, Chironomus riparius 60 mg/l. Bees Not toxic to bees. LD50 (24 h) (oral) 4 mg/bee (tech.); (contact) 53 mg/bee (tech.). Worms LC50 (14 d) >60 mg/kg. Other beneficial spp. Not toxic to Collembola (J. A. Wiles & G. K. Frampton, Pestic. Sci., 47, 273 (1996)).
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
EHC 64 (WHO, 1986; a review of carbamate insecticides in general). Animals In mammals, the major metabolites are 2-dimethylamino-5,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxypyrimidine, 2-methylamino-5,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxypyrimidine, 2-amino-5,6-dimethyl-4-hydroxypyrimidine and 2-dimethylamino-6-hydroxymethyl-5-methyl-4-hydroxypyrimidine. Soil/Environment For details of degradation in soil, see I. R. Hill, ACS Symp. Series, 1976, 29, 358. DT50 in soil 7-234 d, according to soil type (range o.m. 1.7-51.9%, pH 5.5-8.1).
|