|
piperophos
Herbicide
HRAC K3 WSSA 15
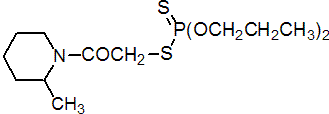
NOMENCLATURE
Common name piperophos (BSI, E-ISO, (m) F-ISO)
IUPAC name S-2-methylpiperidinocarbonylmethyl O,O-dipropyl phosphorodithioate
Chemical Abstracts name S-[2-(2-methyl-1-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethyl] O,O-dipropyl phosphorodithioate
CAS RN [24151-93-7] Development codes C 19 490 (Ciba)
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt. 353.5 M.f. C14H28NO3PS2 Form Pale yellow, slightly viscous clear liquid, with a somewhat sweet odour. B.p. >250 ºC; thermal decomposition begins before c. 190 ºC V.p. 0.032 mPa (20 ºC) KOW logP = 4.3 Henry 4.5 ´ 10-4 Pa m3 mol-1 (calc.) S.g./density 1.13 (20 ºC) Solubility In water 25 mg/l (20 ºC). Miscible with benzene, hexane, acetone, dichloromethane and octanol. Stability Stable under normal storage conditions. Slowly hydrolysed at pH 9; DT50 (20 ºC) (calc.) >200 d (5 £pH £7), 178 d (pH 9).
COMMERCIALISATION
History Herbicide reported by D. H. Green & L. Ebner (Proc. Br. Weed Control Conf., 11th, 1972, 2, 822). Introduced by Ciba-Geigy AG (now Syngenta AG). Patents BE 725992; GB 1255946 Manufacturers Syngenta
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Inhibits cell division. Mode of action Selective, systemic herbicide, absorbed by the roots, coleoptiles, and leaves of young plants. Uses A selective herbicide active against annual grasses and sedges in direct seeded or transplanted rice, at 330-660 g/ha. Used, in combination with dimethametryn, for the control of both grass and broad-leaved weeds. In tropical regions, piperophos is applied in combination with 2,4-D or cinosulfuron to widen the spectrum against broad-leaved weeds. Formulation types EC; WP. Selected products: 'Rilof' (Syngenta); mixtures: 'Avirosan' (+ dimethametryn) (Syngenta)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'PIPSET' (+ cinosulfuron) (Syngenta); 'Stamphos' (+ propanil) (Dow AgroSciences)
ANALYSIS
Product analysis by glc. Residues determined by glc with TID. Details of methods available from Syngenta.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Oral Acute oral LD50 for rats 324 mg/kg. Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats >2150 mg/kg. Non-irritant to skin; slight irritant to eyes (rabbits). Inhalation LC50 (1 h) for rats >1.96 mg/l air. NOEL (90 d) for rats 10 mg/kg diet (0.8 mg/kg daily); for dogs 5 mg/kg diet (0.15 mg/kg daily). Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II EC classification Xn; R22
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds Dietary LC50 (8 d) for Japanese quail 11 629 ppm. Fish LC50 (96 h) for rainbow trout 6, crucian carp 5 mg/l. Daphnia LC50 (48 h) 0.0033 mg/l. Algae EC50 (5 d) for Scenedesmus subspicatus 0.059 mg/l. Bees LD50 (oral) >22 mg/bee; (contact) 30 mg/bee. Worms LC50 (14 d) for earthworms 180 mg/kg soil.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals In urine, no unchanged piperophos was present, indicating extensive degradation of the compound. Degradation proceeds via hydrolysis of the thiolo phosphate followed by methylation of the sulfur or hydroxylation of the piperidine moiety. Hydroxylation at the g-carbon leads via ring opening to carboxylic acids. The derivatives are conjugated with glucuronic acid. Plants Degradation of piperophos takes place rapidly in the plant, forming 2-(2'-methyl-1'-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethane sulfonic acid, 2-(2'-methyl-1'-piperidinyl)-2-oxoethanoic acid and a fraction of unknown polar substances. The proposed pathway involves hydrolysis to the corresponding sulfhydryl and hydroxyl derivatives, followed by further oxidation to the sulfonic acid and oxalic acid derivatives. Injection experiments in plants confirmed the capacity of the rice plant to oxidise piperophos derivatives rapidly. Soil/Environment DT50 (field) <30 d; rapid dissipation by biodegradation from soil and paddy systems. Relatively stable to hydrolysis and photolysis.
|