|
phthalide
Fungicide
FRAC 16.1, I1; MBI: reductase
NOMENCLATURE
Common name: phthalide (JMAF); fthalide (JMAF, alternative spelling)
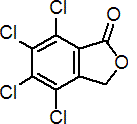
IUPAC name: 4,5,6,7-tetrachlorophthalide
Chemical Abstracts name: 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-1(3H)-isobenzofuranone
Other names: TCP
CAS RN: [27355-22-2]
Development codes: KF-32 (Kureha); Bayer 96 610
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Mol. wt.: 271.9
M.f.: C8H2Cl4O2
Form: Colourless crystals.
M.p.: 209-210 ºC
V.p.: 3 ´ 10-3 mPa (23 ºC)
KOW: logP = 3.01
Solubility: In water 2.5 mg/l (25 ºC). In acetone 8.3, benzene 16.8, dioxane 14.1, ethyl alcohol 1.1, tetrahydrofuran 19.3 (all in g/l, 25 ºC).
Stability: Stable for 12 h at pH 2 (2.5 ppm aq. solution); in weak alkali, DT50 c. 10 d (pH 6.8, 5-10 ºC, 2.0 ppm aq. solution); 15% ring opening in 12 h (pH 10, 25 ºC, 2.5 ppm aq. solution). Stable to heat and light.
COMMERCIALISATION
History: Fungicide reported by K. Nambu (Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1972, No. 10, p. 73) and by K. Wagner & H. Scheinflug (Pflanzenschutz-Nachr. (Engl. Ed.), 1975, 28, 210). Introduced by Kureha Chemical Co., Ltd in 1971 and manufactured by a process licensed from Bayer AG.
Patents: JP 575584 to Kureha; DE 1643347 to Bayer
Manufacturers: Kureha
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry: Anti-penetrant action with melanin biosynthesis inhibition (reduction of 1,3,8-trihydroxynaphthalene).
Mode of action: Foliar fungicide with protective action.
Uses: Control of rice blast (Pyricularia oryzae), at 200-450 g/ha.
Formulation types: DP; SC; WP.
Compatibility: Incompatible with pesticides which are strongly alkaline.
Selected products: 'Rabcide' (Kureha);
mixtures: 'Blasin' (+ ferimzone) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Hinorabcide' (+ edifenphos) (Nihon Bayer)
OTHER PRODUCTS
Mixtures: 'Hustler' (+ validamycin+ cartap hydrochloride+ clothianidin+ ferimzone) (Sumitomo Chemical Takeda); 'Kasai' (+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rabcide' (+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rab-sumibassa' (+ fenitrothion+ fenobucarb+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rab-valida-sumi' (+ validamycin+ fenitrothion+ kasugamycin) (Hokko); 'Kasu-rab-validatrebon' (+ validamycin+ etofenprox+ kasugamycin hydrochloride hydrate) (Hokko); 'Mon-Rab Trebon F' (+ etofenprox+ flutolanil) (Nihon Nohyaku)
ANALYSIS
Product: analysis is by glc with TCD.
Residues: may be determined by glc with ECD (H. Nagayoshi et al., Bull. Agric. Chem. Inspect. Stn., 1973, 13, 27). Details available from Kureha Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
MAMMALIAN TOXICOLOGY
Reviews: J. Pestic. Sci., 15(2), 311-314 (1990).
Oral: Acute oral LD50 for rats and mice >10 000 mg/kg.
Skin and eye: Acute percutaneous LD50 for rats and mice >10 000 mg/kg; non-irritating to eyes and shaved skin of rabbits.
Inhalation: LC50 (4 h) for rats >4.1 g/m3.
NOEL: (2 y) for rats 2000, mice 100 mg/kg diet (M. Ishida & K. Nambu, J. Pestic. Sci., 3, 10-26).
Other: Acute i.p. LD50 for male rats 9780, female rats 15 000, mice 10 000 mg/kg.
Toxicity class: WHO (a.i.) U; EPA (formulation) IV
ECOTOXICOLOGY
Birds: No effect on hens fed 1.5 mg/kg for 7 days, and for another 3 days at 15 mg/kg.
Fish: LC50 (48 h) for young carp >320 mg a.i. (as tech. or DP)/l, 135 mg a.i. (as 50% WP)/l.
Daphnia: LC50 (3 h) >40 ppm.
Algae: EC50 (96 h) for Selenastrum capricornutum >1000 mg/l.
Bees: Non-toxic to bees; LD50 (contact) >0.4 mg/bee.
Worms: LC50 (14 d) >2000 mg/kg substrate.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE
Animals: In rats, principal metabolites are 2-hydroxymethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorobenzoic acid and its oxidation products.
Plants: 4,7-Dichlorophthalide and 4,6,7-trichlorophthalide are formed in rice.
Soil/Environment: Principal metabolites in soil are 2-hydroxymethyl-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorobenzoic acid and its oxidation products (K. Aoki et al., Jpn. Pestic. Inf., 1979, 36, 32).
|